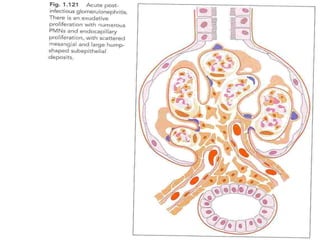
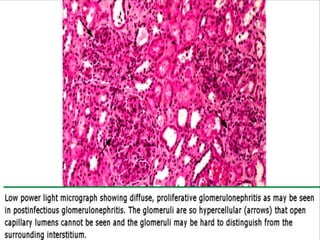
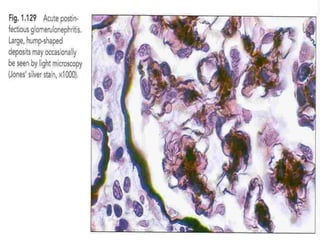
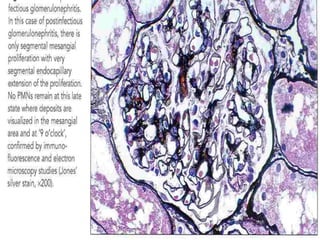
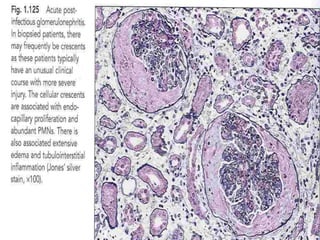
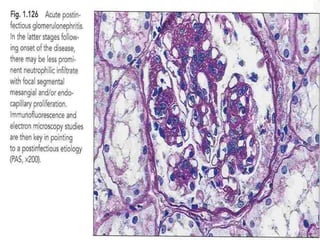
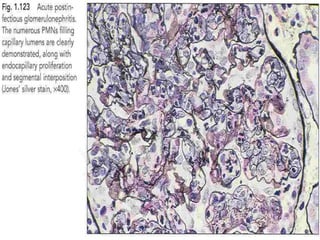
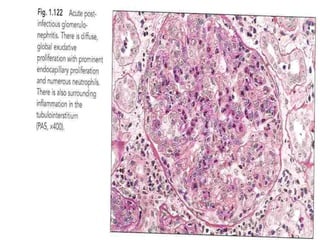
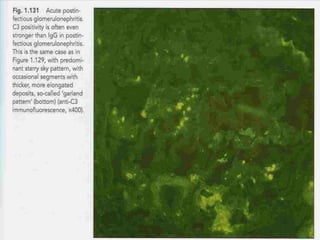
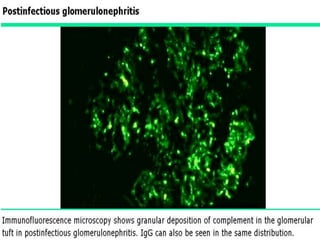
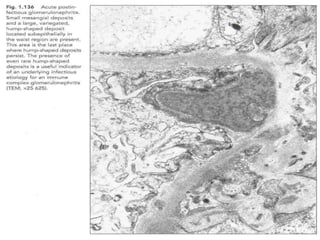
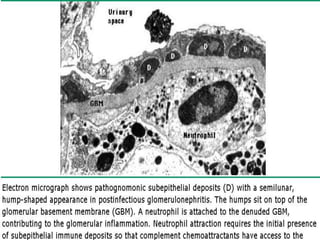
The document discusses poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN), an acute glomerulonephritis that occurs after a streptococcal infection. PSGN is characterized by hematuria, proteinuria, edema, hypertension, and renal impairment. On biopsy, it shows a proliferative glomerulonephritis with immune complex deposition along the glomerular capillary walls and mesangium. While PSGN most commonly affects children in developing countries after streptococcal pharyngitis, it can occur in adults after skin infections in any country. The diagnosis is based on acute nephritis symptoms along with evidence of a recent streptococcal infection by culture, serology or antibody testing