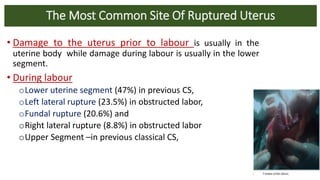
Uterine rupture is a life-threatening condition where the wall of the uterus tears, potentially exposing the fetus and placenta to the mother's abdominal cavity. It most commonly occurs in women with a previous cesarean section scar. Signs include acute abdominal pain, fetal distress, and hemorrhage. Diagnosis is often made using ultrasound or MRI to detect tears in the uterine wall. Immediate exploratory laparotomy and cesarean delivery is usually required for treatment. Conservative uterine repair may be attempted for some cases but hysterectomy is often necessary due to severe hemorrhage. Prevention focuses on careful management of trial of labor for women with previous scars.






![Rupture of the Scarred Uterus Due to Previous CS
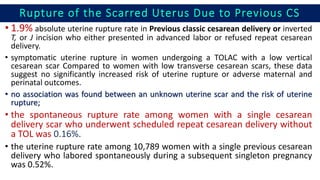
• Previous cesarean delivery with previous successful vaginal delivery in
women with no prior vaginal delivery who underwent a TOLAC, there was an
increased risk of uterine rupture with induction versus spontaneous labor (1.5% vs
0.8%, P =0.02). In contrast, no statistically significant difference was shown for
women with a prior vaginal delivery who underwent spontaneous TOLAC compared
with labor induction (0.6% vs 0.4%, P =0.42).
• Previous cesarean delivery with subsequent successful VBACs an
increased uterine rupture rate of 1.4% (1 per 73) in failed VBAC attempts that
required a repeat cesarean section in labor.
• Inter-delivery interval the combination of a short inter-delivery
interval of ≤24 months and a single-layer hysterotomy closure was associated
with a uterine rupture rate of 5.6%.
• One-layer versus 2-layer hysterotomy closure single-layer closure was
linked to an increased rate of uterine rupture (odds ratio [OR] 2.69; 95%
confidence interval [CI] 1.37–5.28). The authors concluded that single-
layer closure should be avoided in women who contemplate future VBAC
delivery](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ruptureuterus-171129163951/85/Rupture-uterus-8-320.jpg)