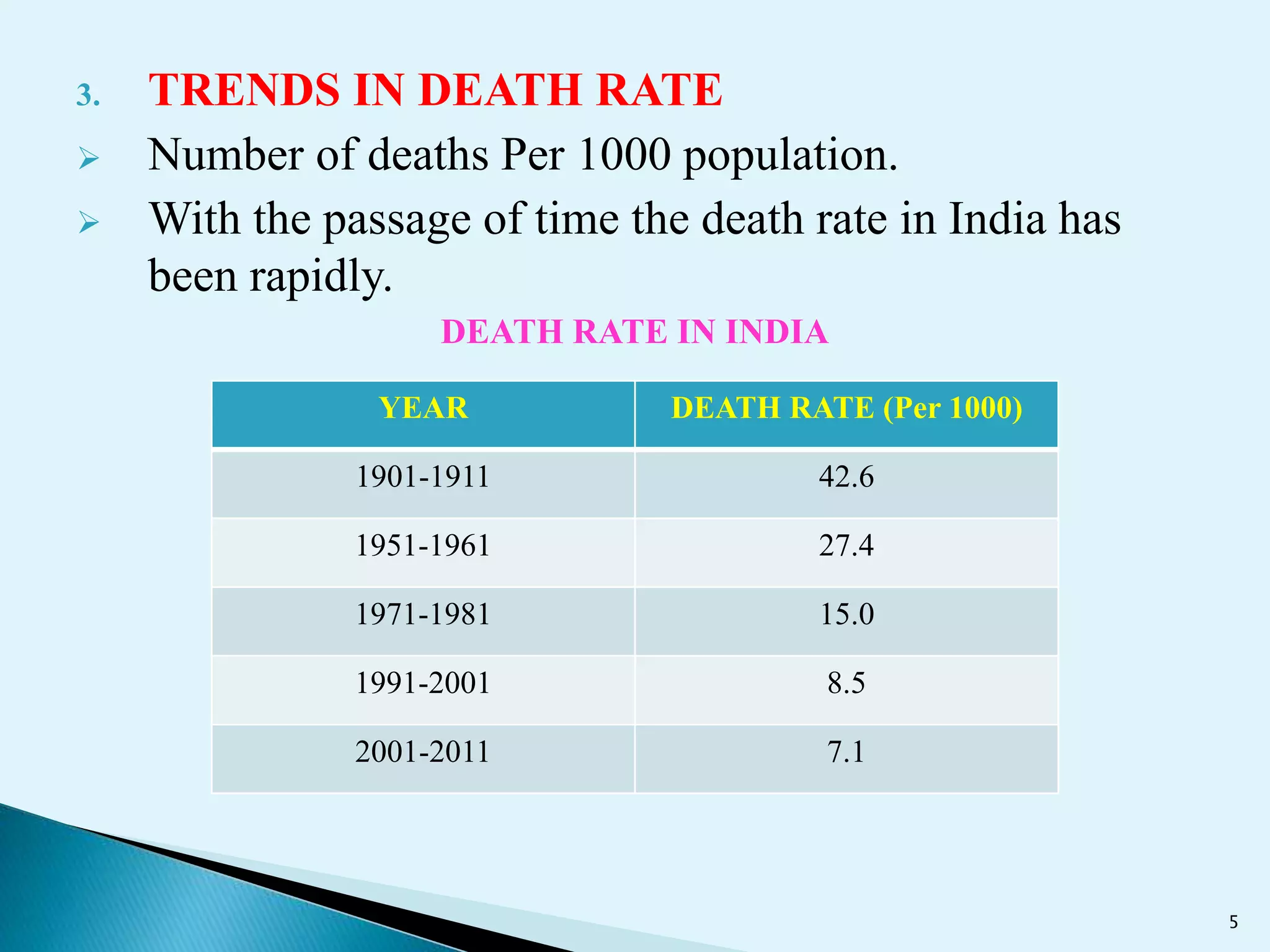
This document discusses key population trends in India based on census data from 1951-2011. It notes that India's population has grown significantly from 361 million in 1951 to over 1.2 billion in 2011, while maintaining a high birth rate and declining death rate. Other trends discussed include population density increasing from 117 to 382 persons per square km from 1951-2011, a declining child population and rising elderly population, improved life expectancy, and increasing literacy rates especially for females.