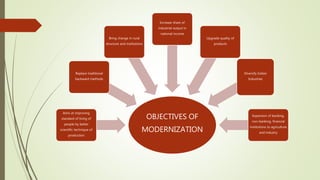
The document outlines several key objectives of economic development:
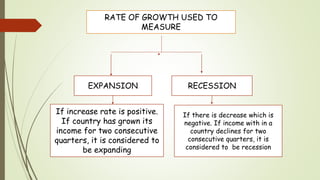
1. High rate of economic growth to steadily increase a country's output of goods and services over time. Countries aim for growth rates of 2-3% annually.
2. Economic self-reliance so a country can rely on its own resources and generate enough surplus to import what it needs, without excessive dependence on foreign aid or imports.
3. Social justice to promote fairness and equitable distribution of wealth across all sections of society, including improving conditions for disadvantaged groups.
4. Modernization to transform traditional economic and social structures through technological and scientific advancements.
5. Economic stability to avoid large fluctuations in the economy and ensure non-inflation




![A healthy rate of growth is 2% to 3%. Economic
growth provides financial stability. It increases
productive capacity. There are huge benefits of
economic growth.
Developing economies or countries were in a view
that high rate of growth can be achieved by giving
importance to primary sector. For instance, after
achieving independence, India’s first five year plan
has focussed on primary sector for growth of real
national income. Initially, rate of economic growth is
not encouraging in economy.
First five year plan [1951-56]
Second five year plan [1956-61]
Third five year plan [1961-66]
THREE FIVE YEAR
PLANNING
Growth was not so encouraging](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objectivesofeconomicdevelopment-220618164510-c2809039/85/OBJECTIVES-OF-ECONOMIC-DEVELOPMENT-pptx-6-320.jpg)
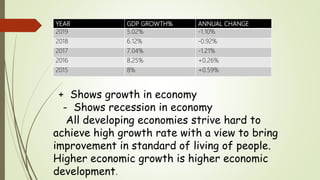
![Till 1980,
Average annual rate of GDP is 3.73%
Average annual rate of population 2.5%
Per capita income is 1%
6th plan -considerable change in economy
7th plan –growth rate is 5.4%
8th plan -growth rate is 6.8%
9th plan –growth rate is 7%[targeted growth]
growth rate is 5.35%[real growth]
Economy achieved high rate of growth of 9%. China
achieved 10% rate in 21st century.
12th plan –Targeted growth[7.9%]
Actual growth[8.2%]
GDP grown at 7.5% during 2014-15 and 2018-19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objectivesofeconomicdevelopment-220618164510-c2809039/85/OBJECTIVES-OF-ECONOMIC-DEVELOPMENT-pptx-7-320.jpg)

![No country is self sufficient, but a country can try become self reliant by paying for
everything that imports. A self reliant country doesn't depend on other counties for
resources of needed to acquire them. It implies that dependence on foreign aid
should be minimum as possible. Excessive dependence on foreign sector may lead to
economic colonialism. Economic colonialism refers to powerful nation extending its
influence on less developed economies to exploit one's nation resources.
3rd plan –Objective of self reliance
4th plan –Importance given on self reliance[production of food grains]
5th plan –Earn sufficient foreign exchange[export promotion and import
substitution]
India’s dependence on foreign aid for
Import food grains
from USA
Process of
industrialisation
Infrastructural
facilities
Meet our domestic
demand
Capital goods in
form of machinery
Roads, Railways,
Power etc](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objectivesofeconomicdevelopment-220618164510-c2809039/85/OBJECTIVES-OF-ECONOMIC-DEVELOPMENT-pptx-10-320.jpg)

![FIVE PILLARS
OF SELF-
RELIANT INDIA
Economy
Demography
Demand
System
Infrastructure
ATMANIRBHAR BHARAT[THE
ROAD AHEAD]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objectivesofeconomicdevelopment-220618164510-c2809039/85/OBJECTIVES-OF-ECONOMIC-DEVELOPMENT-pptx-12-320.jpg)

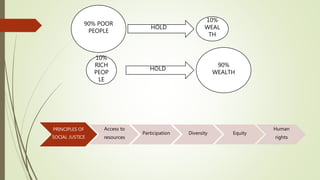
![ASPECTS OF SOCIAL JUSTICE
Adherence to democratic principles in political structure of
country. (adherence-commitment)
Establishment of social and economic equity and removal of
regional disparities. (focus on imbalanced areas)
Putting an end to process of centralization of economic power
and simultaneously attaining decentralized power
[Decentralization is a good sign of development, Centralization
refers to assets in hand of only few people. Rich becomes richer
and poor becomes poorer]
Efforts to raise conditions of backward and depressed classes
9th five year plan focused on social justice and
equity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objectivesofeconomicdevelopment-220618164510-c2809039/85/OBJECTIVES-OF-ECONOMIC-DEVELOPMENT-pptx-15-320.jpg)