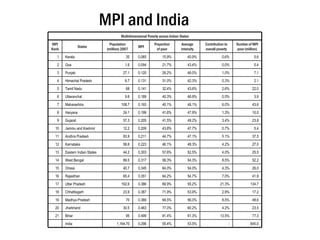
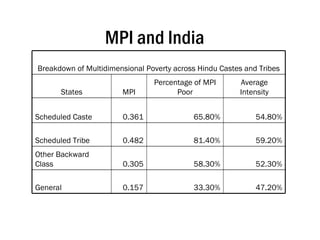
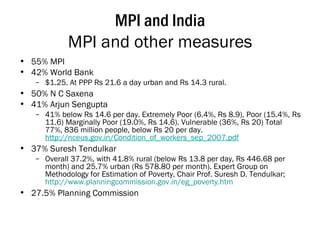
The Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) provides a comprehensive measure of poverty by considering multiple deprivations across three dimensions: education, health, and standard of living. The MPI identifies anyone as multidimensionally poor if they are deprived in at least 30% of weighted indicators. Half of the world's poor according to the MPI live in South Asia, with India home to the largest number at over 400 million. Within India, states such as Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Jharkhand have very high levels of multidimensional poverty.