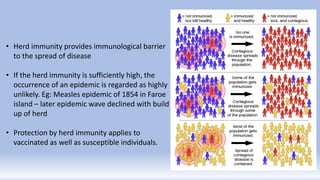
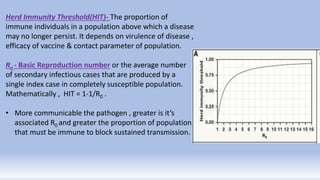
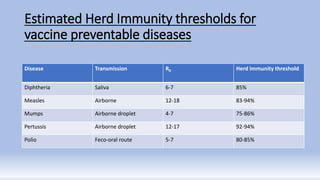
Herd immunity refers to the protection provided to unvaccinated individuals when a sufficient portion of the population is immunized, which can lead to disease elimination. It is crucial for controlling contagious diseases, with specific herd immunity thresholds varying based on disease characteristics. The concept faces limitations, particularly for diseases like rabies and tetanus, and achieving herd immunity through natural infection, such as in the case of COVID-19, is neither scientifically sound nor ethical, as current seroprevalence in India suggests that the herd immunity threshold has not been reached.