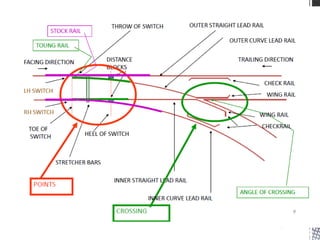
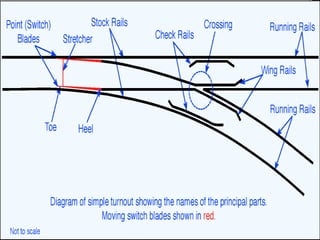
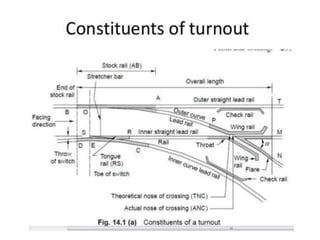
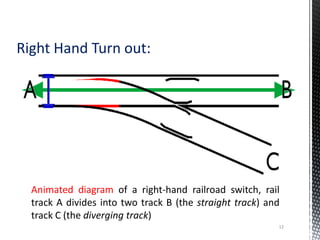
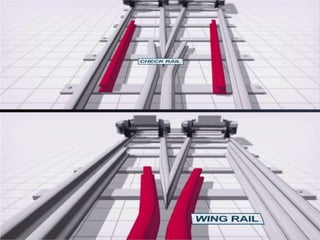
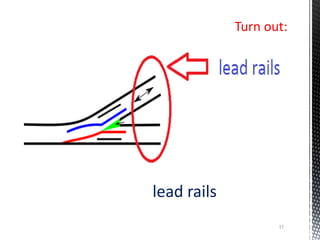
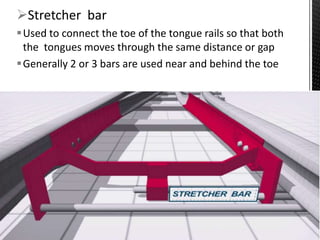
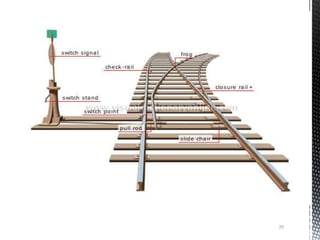
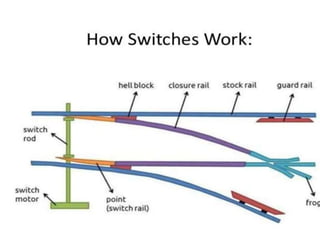
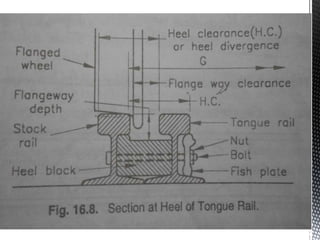
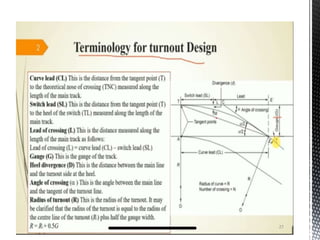
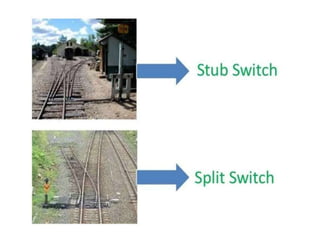
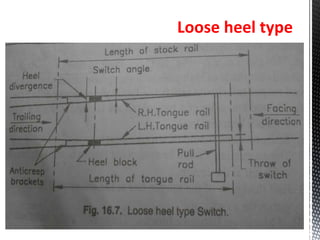
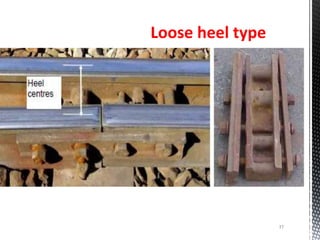
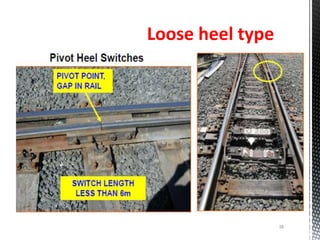
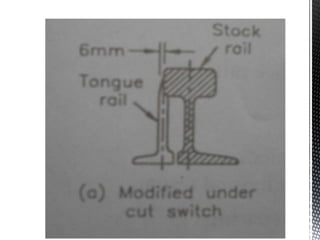
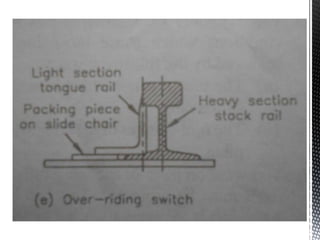
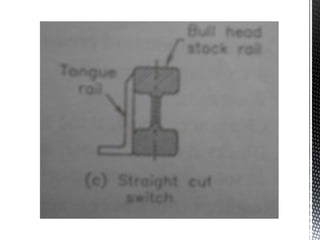
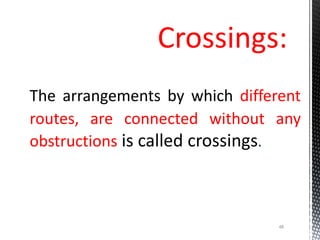
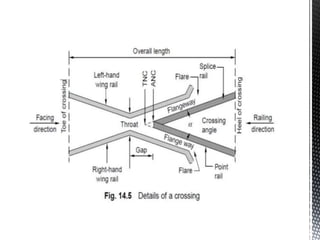
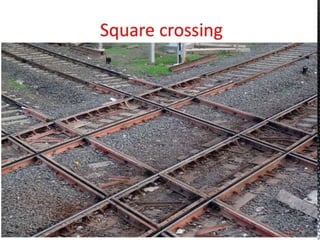
Points and crossings facilitate the diversion of trains from one track to another without obstruction. A turnout provides for diverting trains from a main track to a branch track using a set of points and crossings. There are different types of turnouts including right-hand and left-hand turnouts. Important components of turnouts include tongue rails, stock rails, lead rails, and stretcher bars. Crossings connect different routes without obstructions and can be classified based on shape (square, acute angle, obtuse angle) or assembly (ramped, spring/movable).