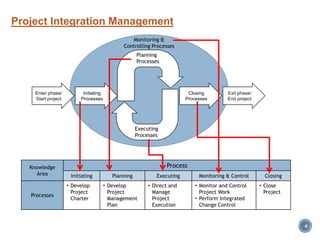
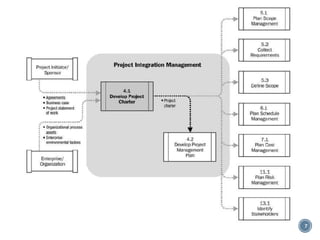
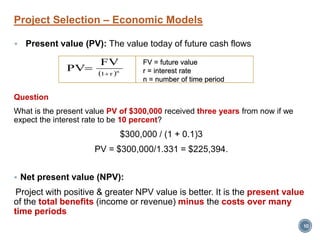
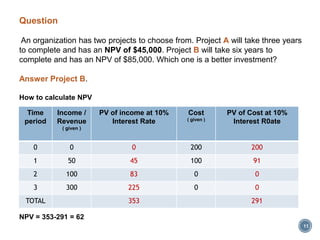
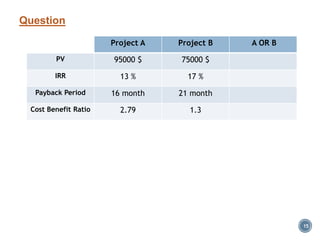
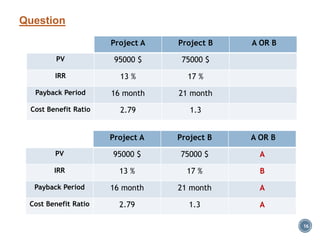
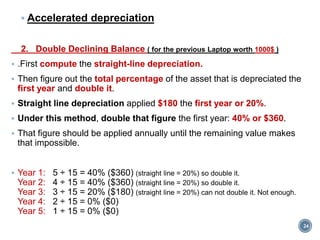
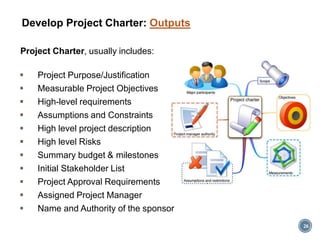
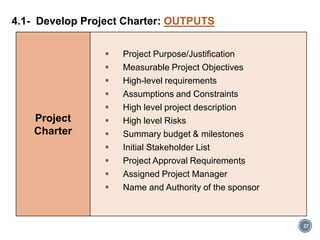
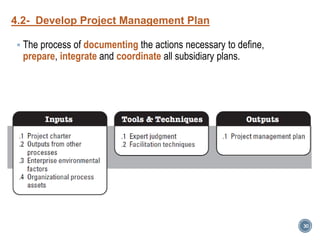
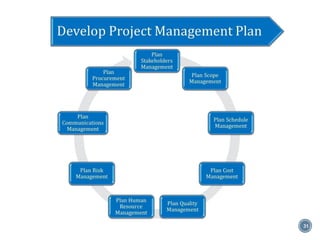
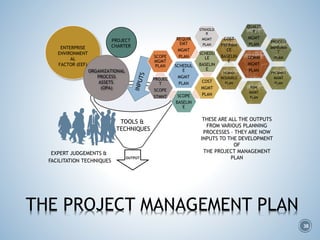
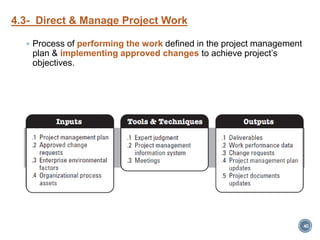
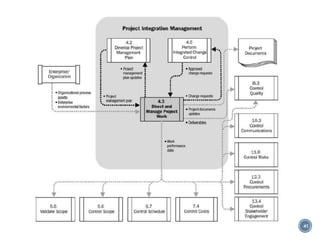
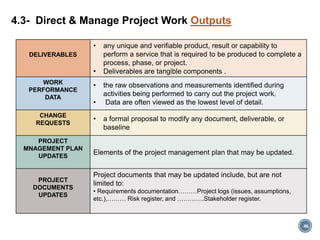
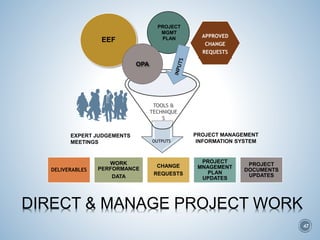
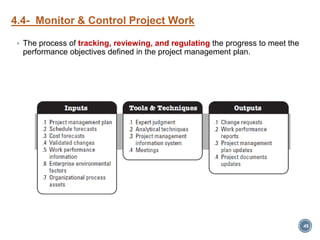
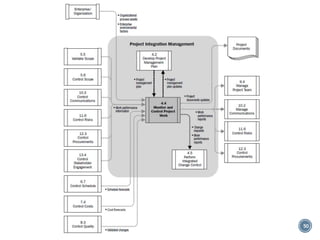
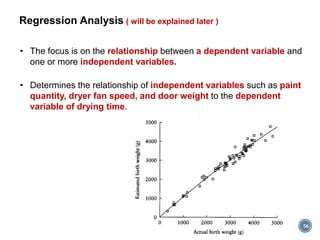
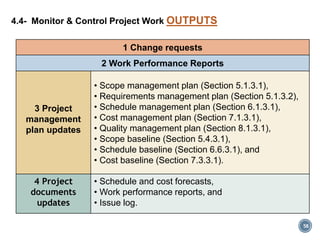
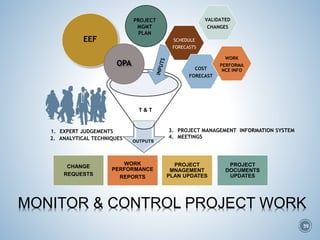
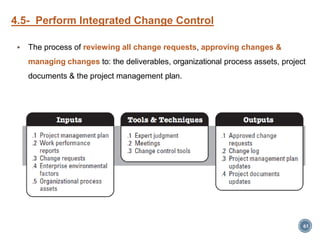
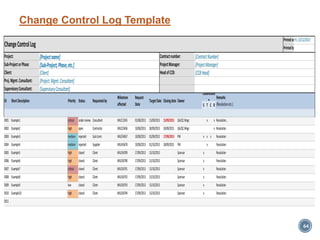
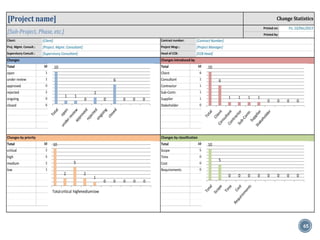
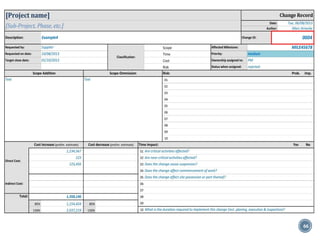
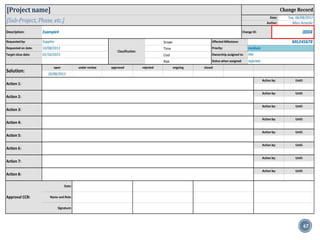
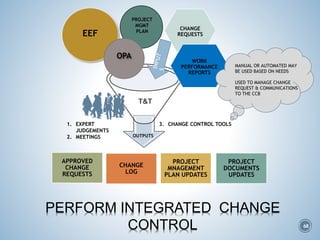
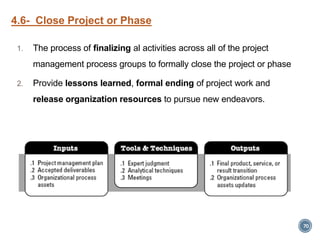
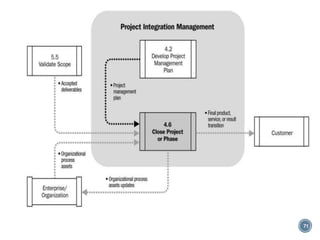
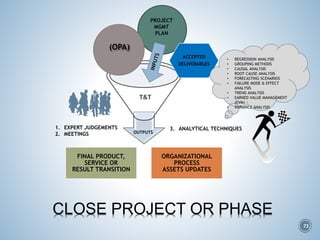
The document summarizes Project Integration Management processes from chapter 4 of an unknown book. It discusses developing the project charter and project management plan. For developing the project charter, it describes inputs like the project statement of work and business case. Tools and techniques include using expert judgement and facilitation. The key output is the project charter. For developing the project management plan, it describes integrating subsidiary plans like scope, schedule, cost, quality and risk management plans. The project management plan consolidates these to describe how the project will be executed.