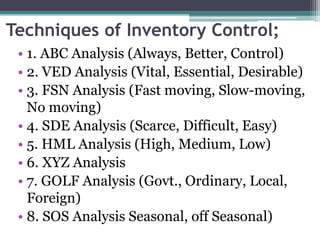
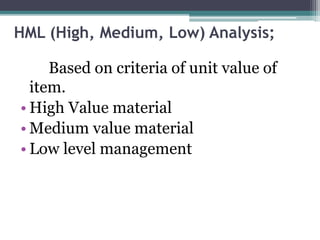
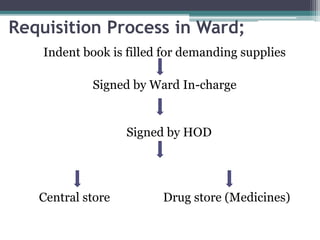
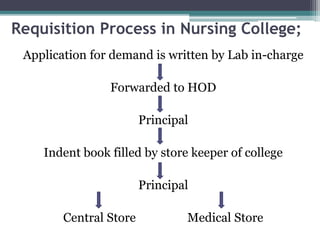
This document discusses inventory control in healthcare settings. It defines inventory control and describes various techniques used, including ABC analysis, VED analysis, and FSN analysis. ABC analysis classifies inventory items into categories A, B, and C based on their annual consumption and cost. Category A items require the most control while category C require the least. VED analysis categorizes items based on their criticality as vital, essential, or desirable. FSN analysis looks at consumption patterns to classify items as fast, slow, or non-moving. The document also outlines the objectives, types, and techniques of inventory control as well as the roles and responsibilities of nurses in ensuring proper inventory management.