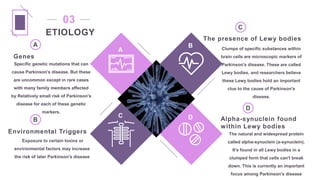
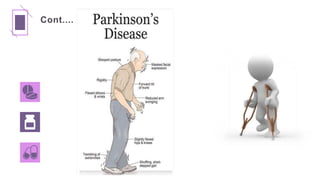
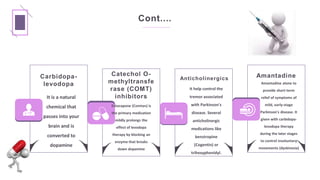
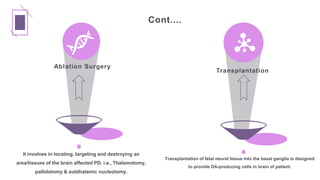
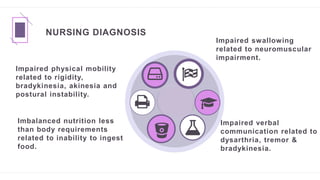
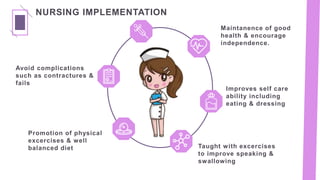
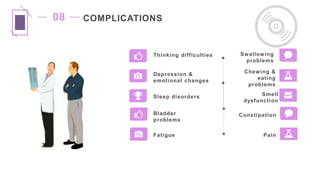
Parkinson's disease is a progressive neurological disorder characterized by tremors, muscle rigidity, bradykinesia, and postural instability. It is more common in older adults, affecting 1% of those over 65 and 5% over 80. The cause is unknown but likely involves genetic and environmental factors. Diagnosis is based on symptoms and examination findings, and management focuses on medications to increase dopamine levels like levodopa as well as exercises, diet, and potential surgical interventions like deep brain stimulation. Nursing care aims to promote mobility, nutrition, communication and prevent complications through exercises and self-care education.