The document outlines an extensive staff development program that includes:
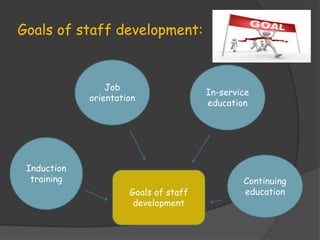
- Defining staff development and its objectives such as improving employee performance and reducing turnover
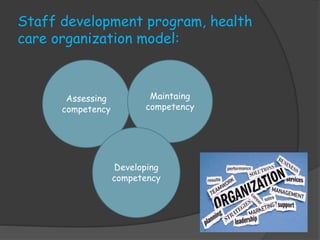
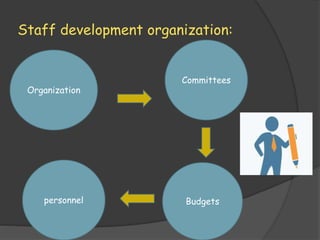
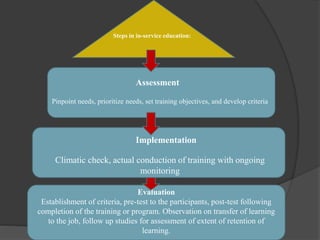
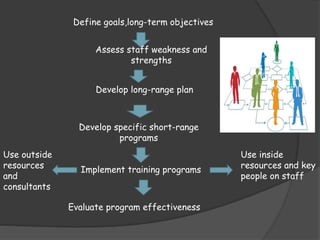
- Describing the staff development process which involves assessing needs, developing plans, implementing programs, and evaluating effectiveness
- Discussing various staff development activities like induction training, orientation, in-service education, and continuing education
- Explaining how to assess staff development needs, set goals, and evaluate programs
The overall purpose is to provide training and education to healthcare employees to enhance their skills and professional growth.














![In-service education(2-8hour):
It refers to an ongoing on the job
instruction that is given to enhance, the
worker’s performance in their present
job. It is planned educational experience
provided in the job setting and closely
identified with service in order to help
person to perform more effectively as a
person and as a worker [national league
for nursing (NLN)].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staffdevelopmentprogramme-210123085743/85/Staff-development-programme-16-320.jpg)