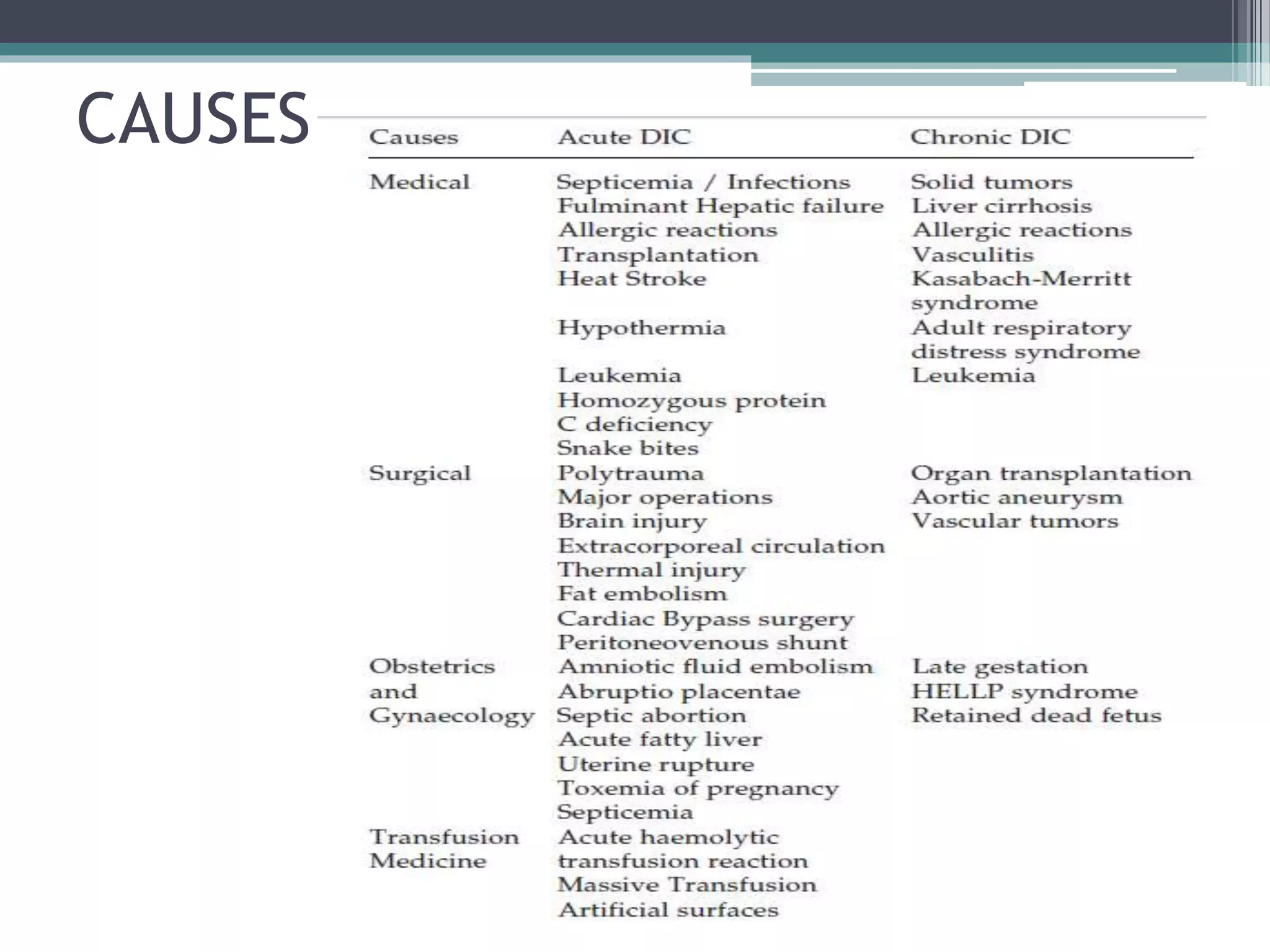
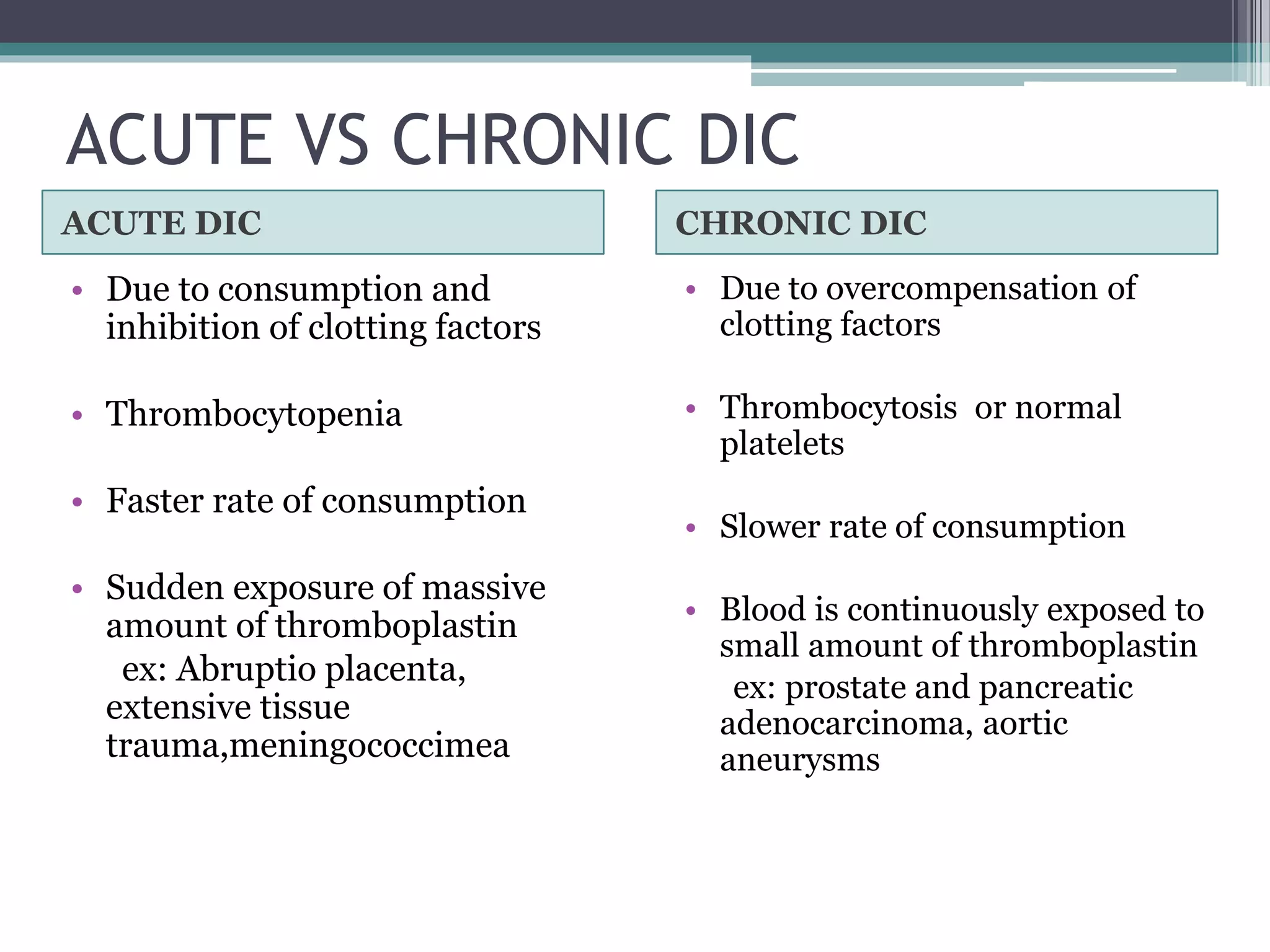
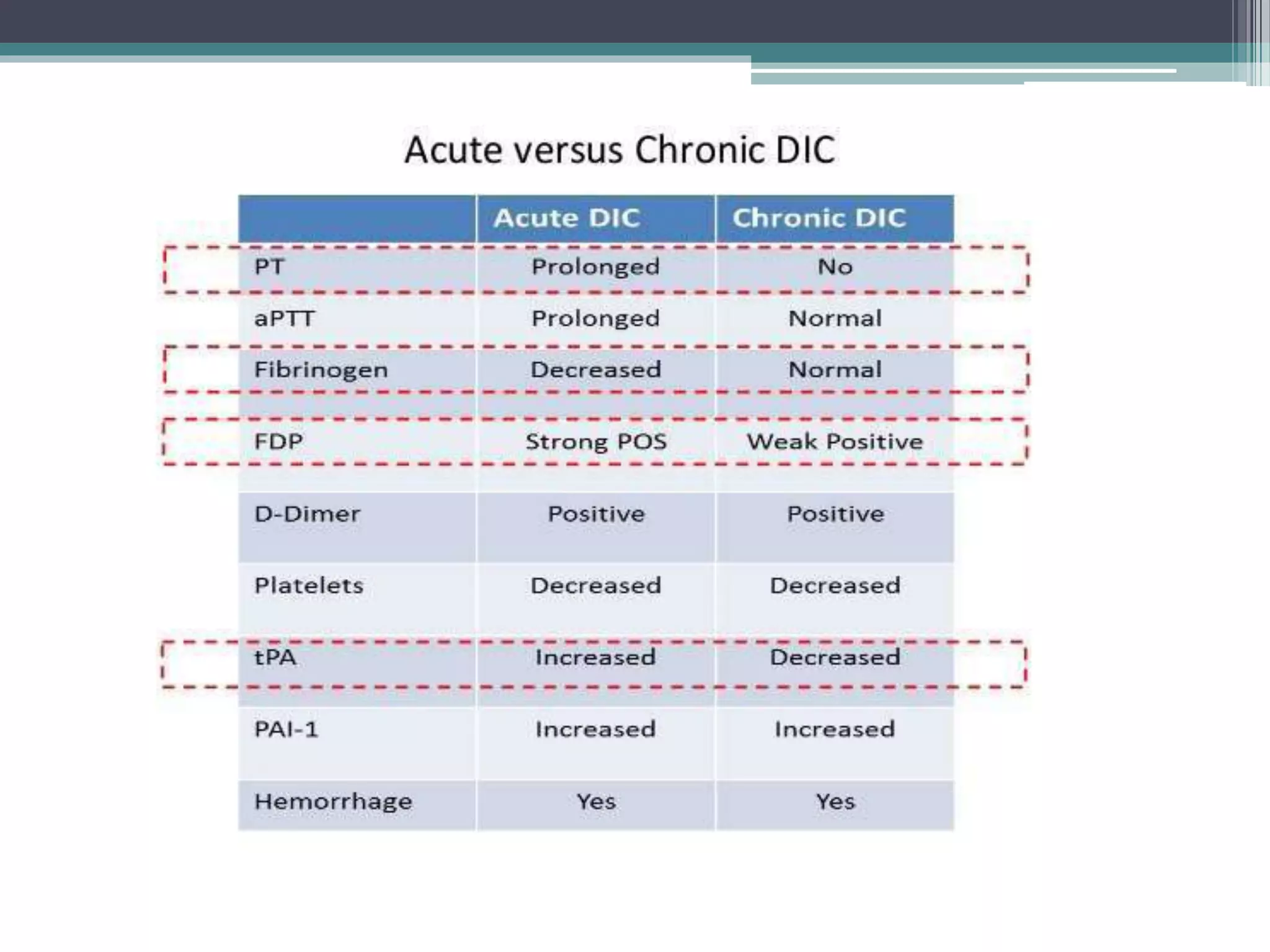
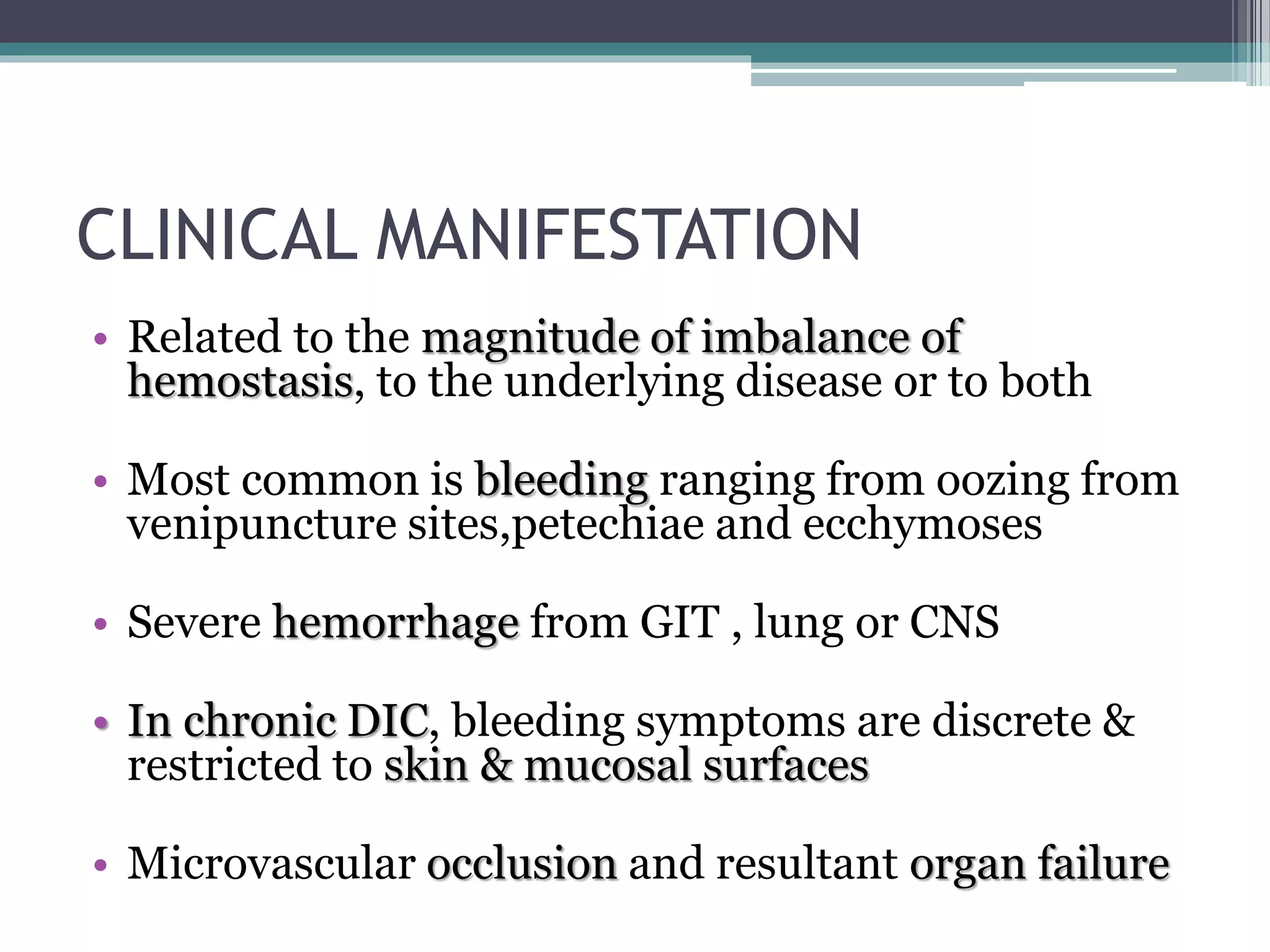
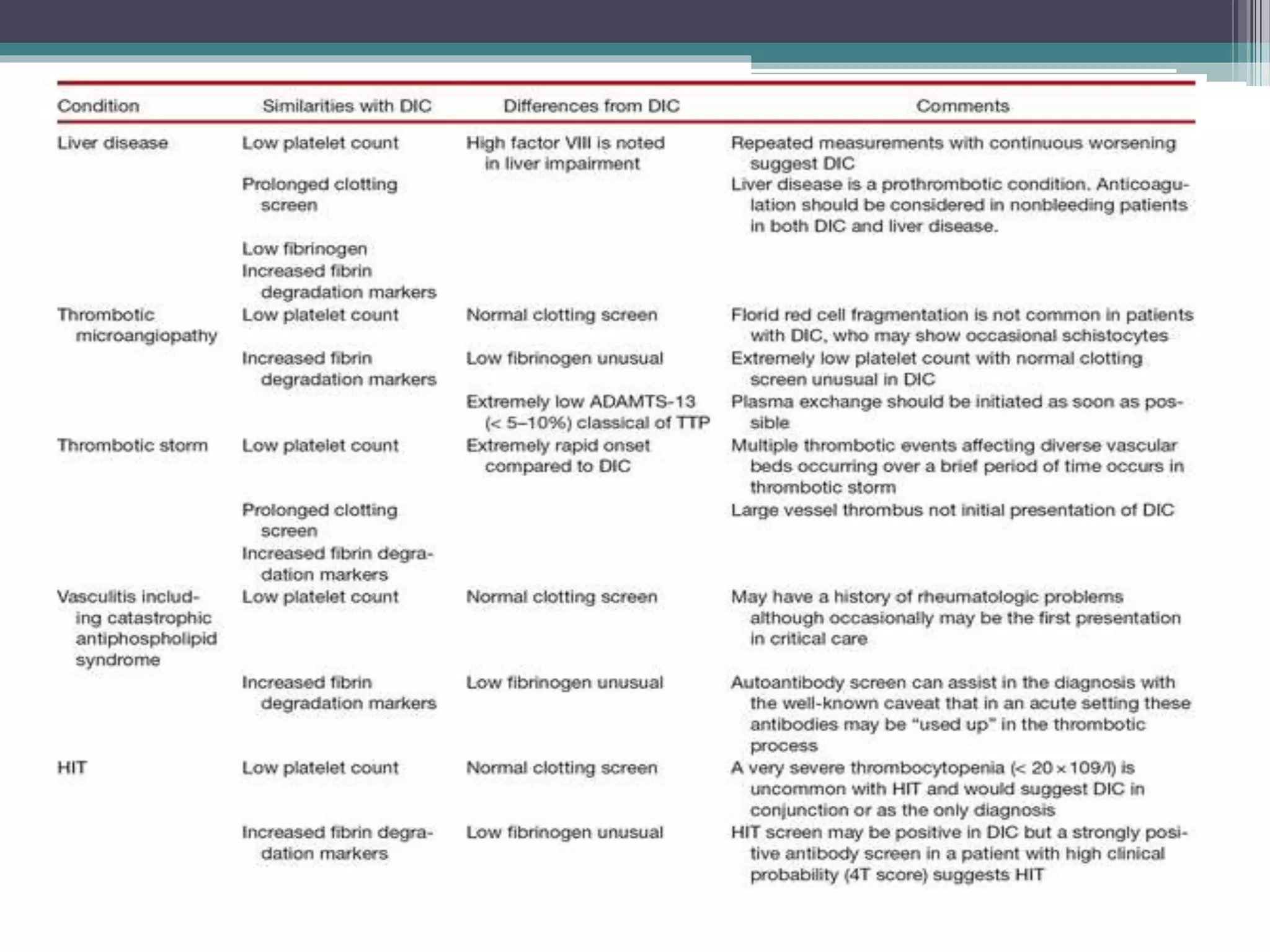
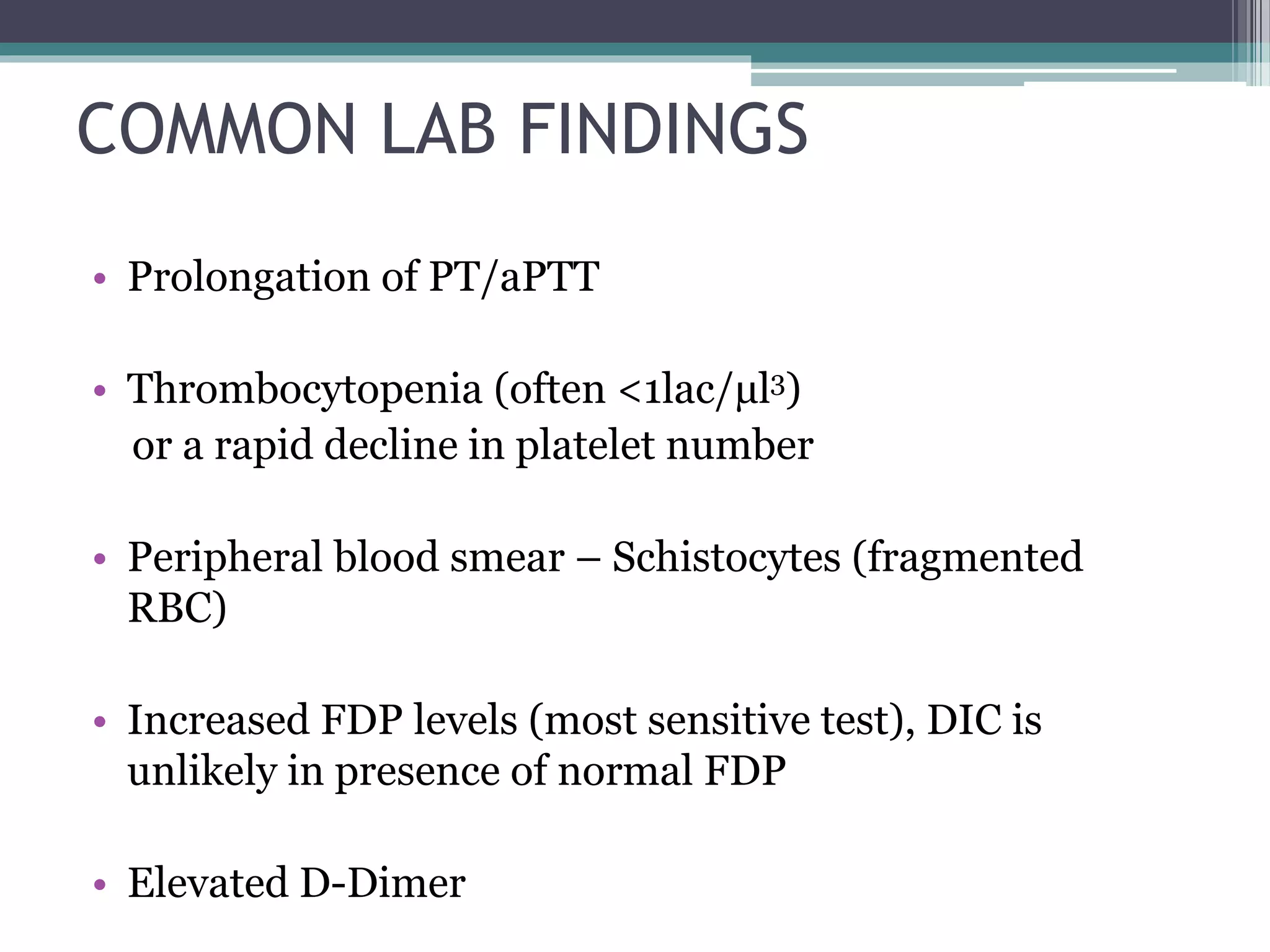
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is an acquired syndrome characterized by the excessive activation of coagulation leading to bleeding and organ dysfunction, often triggered by conditions such as sepsis, trauma, or obstetric complications. Diagnosis relies on clinical presentation and laboratory findings, with a scoring system developed by the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis to identify overt DIC. Management emphasizes addressing the underlying causes while providing supportive therapies like platelet replacement and antifibrinolytics as necessary.



































![Activated Protein C
• In a phase III clinical trial of recombinant APC (rAPC) in patients
with severe sepsis in a dose of 24 μg/Kg/h over 96 h, significant
reduction in 28 day mortality was seen.
• Most significant complication was bleeding
• It is recommended in patients with severe sepsis
Clinical efficacy of APC in severe sepsis was demonstrated in a
Large randomized controlled trial (the protein C worldwide evaluation
In severe sepsis [PROWESS] trial), in which its use was
Associated with a reduced mortality (24.7%) compared with that of
The placebo (30.8%) with highest benefit for those who had DIC.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dic-200720181046/75/DISSEMINATED-INTRAVASCULAR-COAGULATION-46-2048.jpg)






