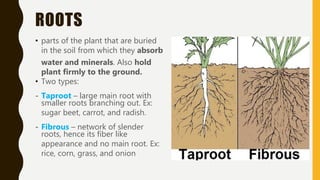
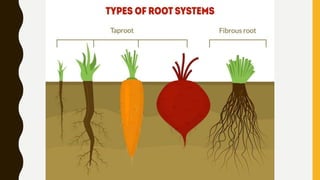
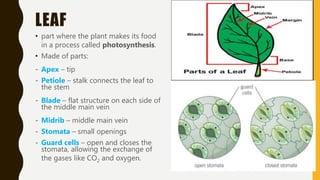
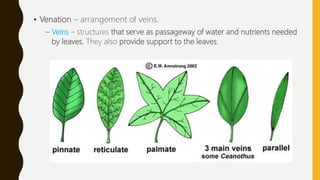
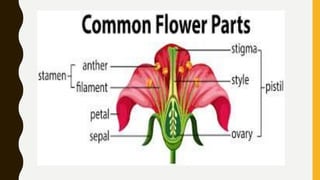
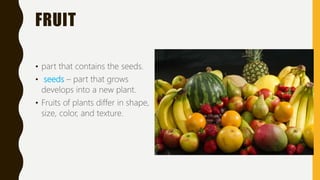
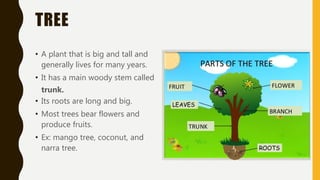
This document summarizes the key parts of plants including roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits. It describes the functions of each part and provides examples. It also outlines the main kinds of plants - trees, shrubs, herbs, and vines - and highlights some distinguishing characteristics such as size, lifespan, and whether they bear flowers or fruit.