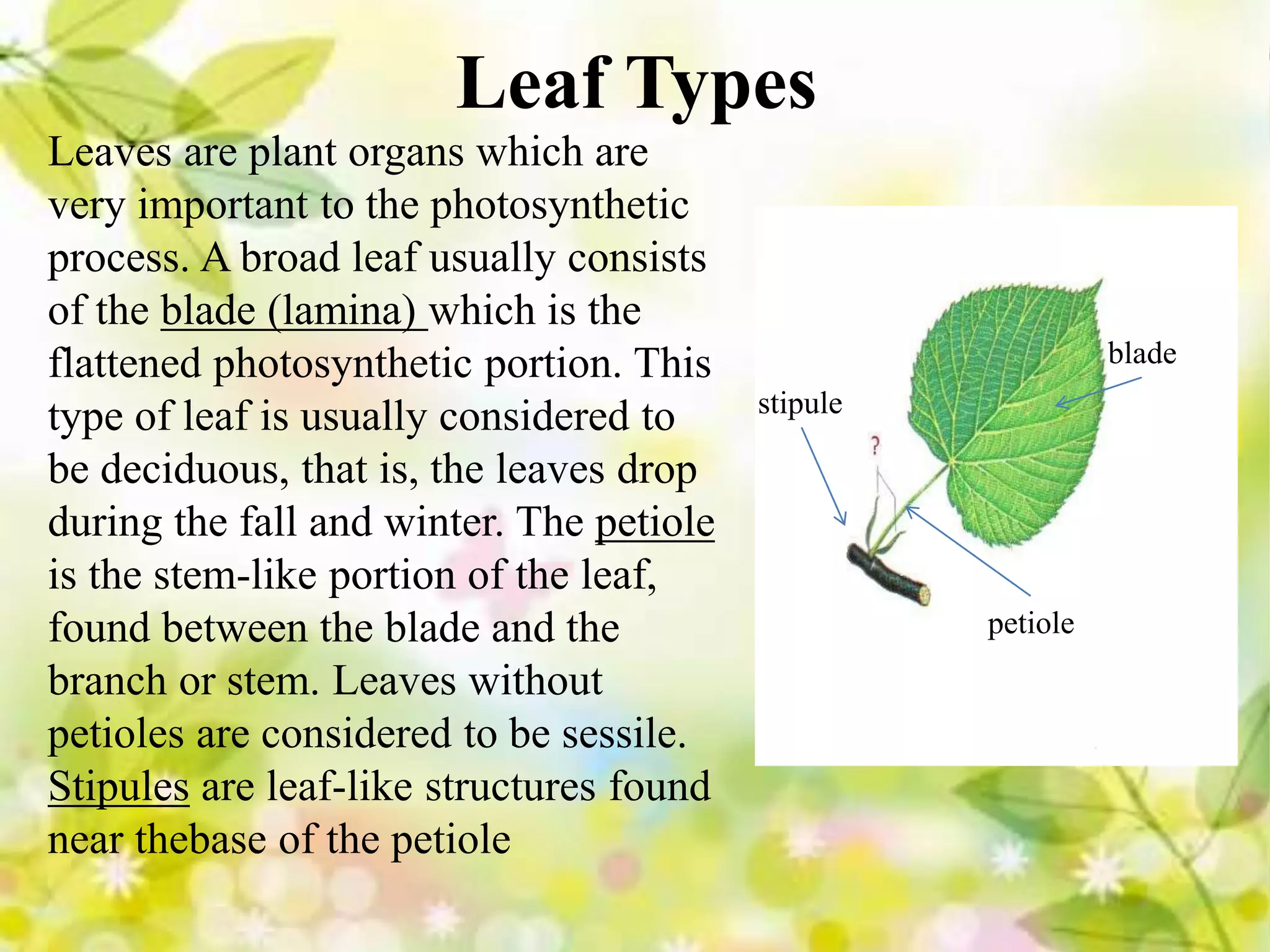
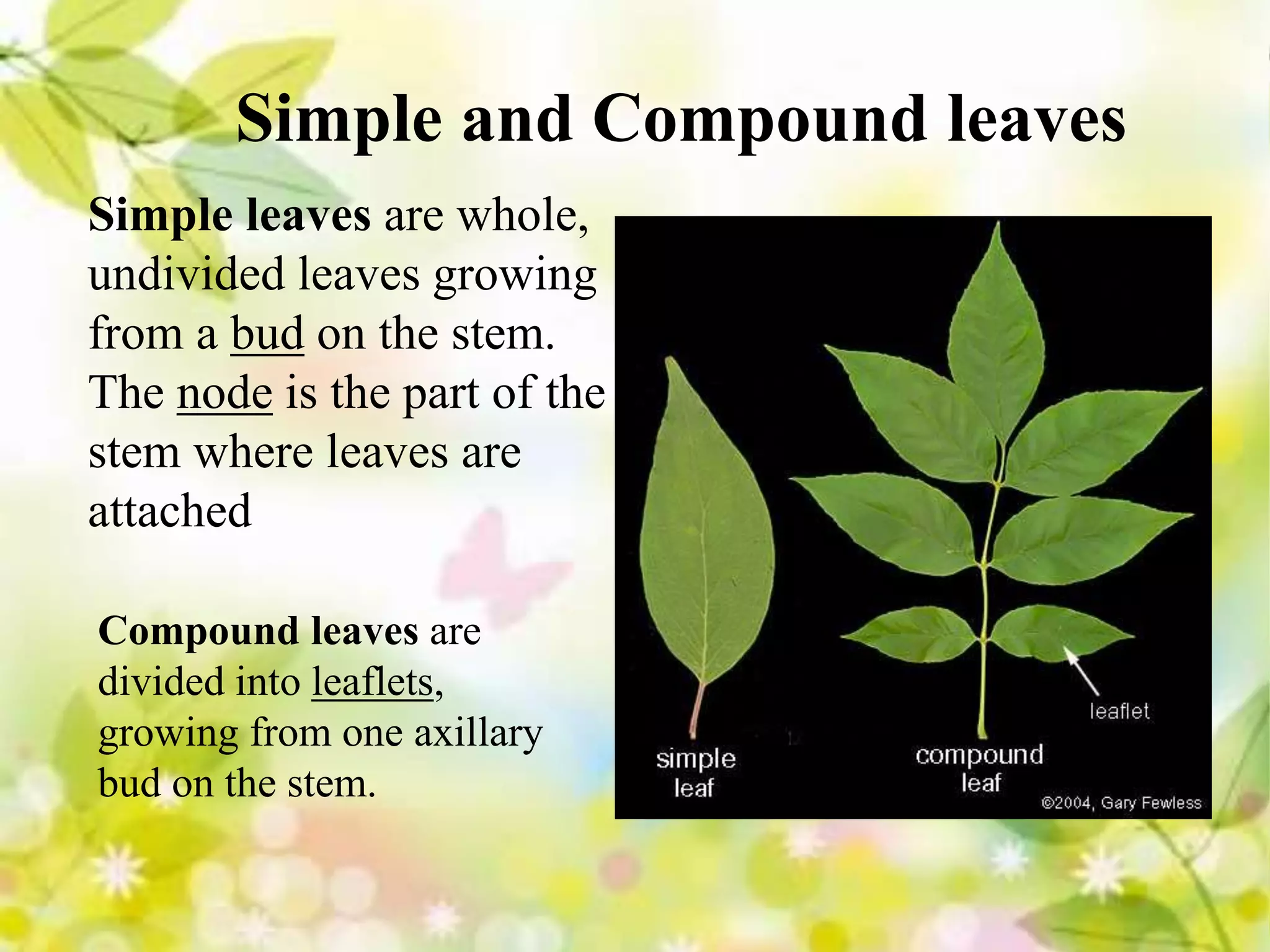
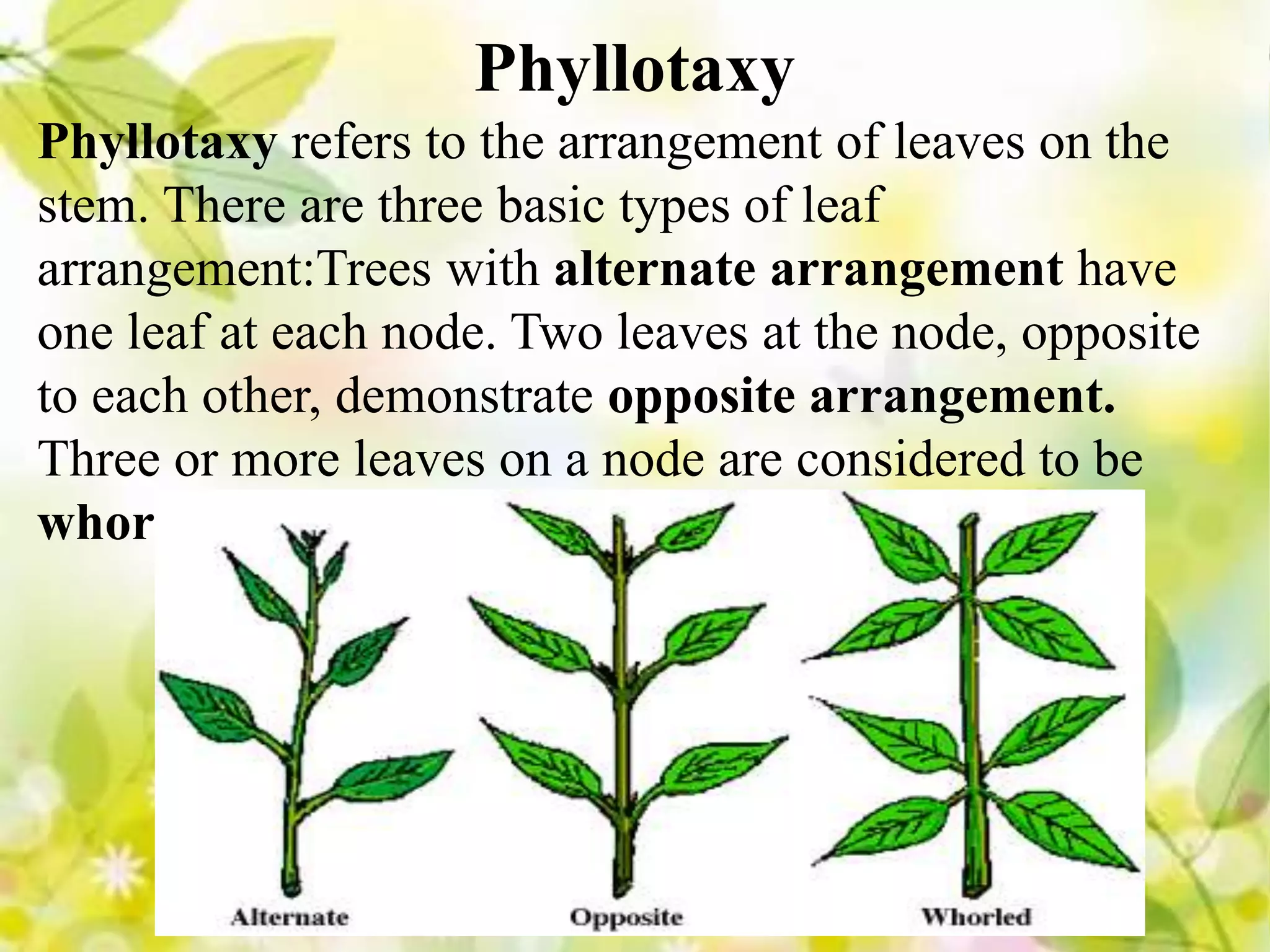
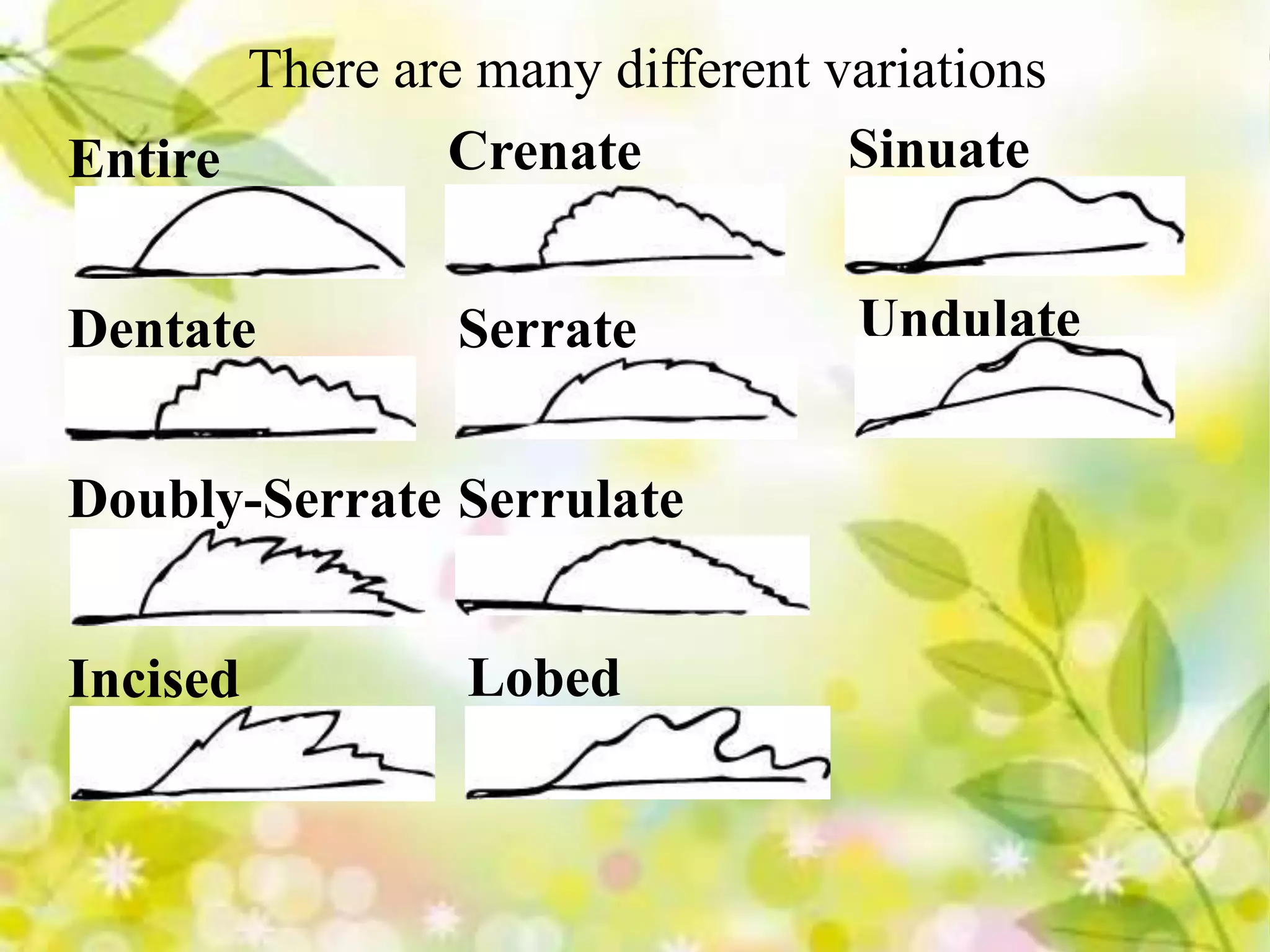
Leaves come in different types including broad, needle-like, scale-like, evergreen, and deciduous. Leaves can be simple or compound. Phyllotaxy refers to the arrangement of leaves on the stem such as alternate, opposite, or whorled. Leaf features include venation which is the arrangement of veins, and margin which is the shape of the leaf edge such as entire, crenate, dentate, or lobed.