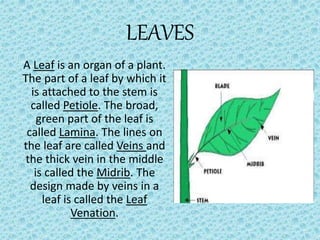
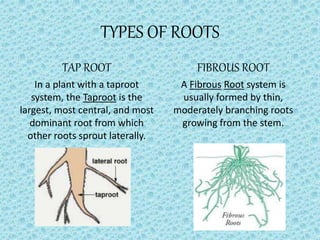
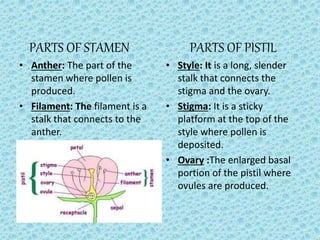
This document provides an overview of different types of plants and their parts. It describes herbs as plants with green, tender stems that are usually short. Shrubs have branching stems near the base. Trees are tall with thick, brown stems and branches above ground. Climbers and creepers take support from other structures. The stem transports water and minerals through tubes. Leaves have a petiole, lamina, veins including a midrib. They undergo transpiration and photosynthesis. Roots anchor the plant and come in tap or fibrous forms. Flowers have sepals, petals, stamens with anthers and filaments, and pistils with styles, stigmas and ovaries.