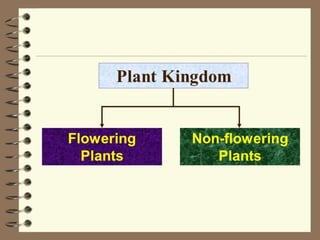
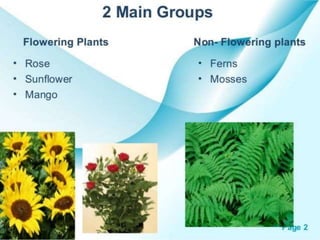
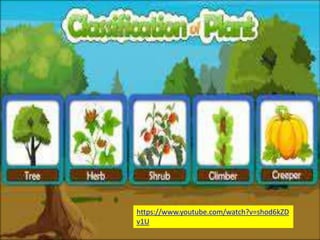
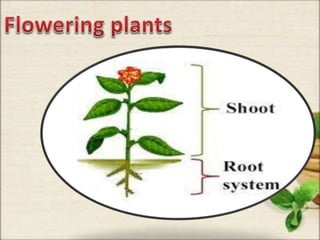
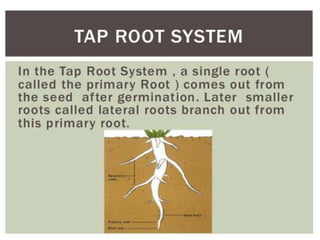
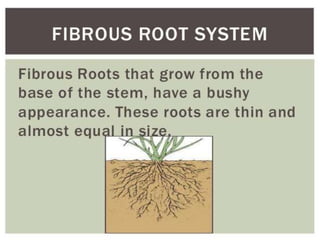
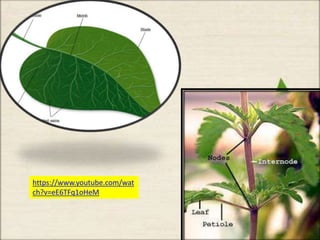
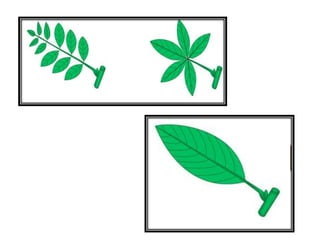
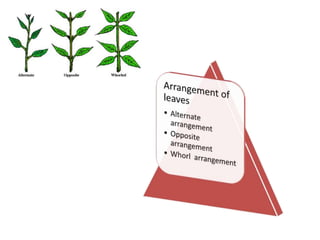
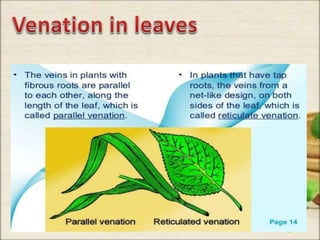
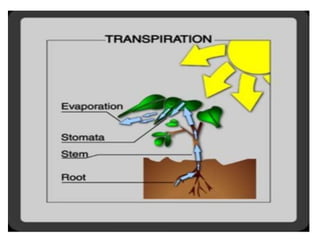
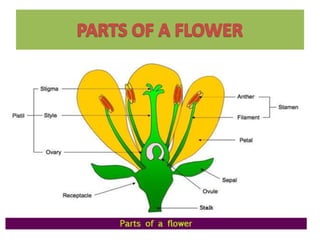
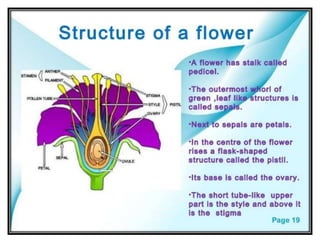
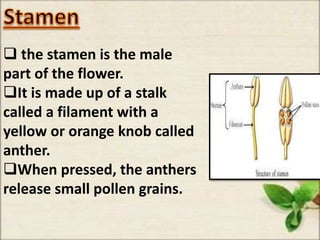
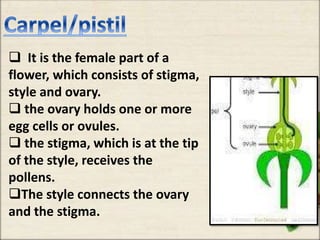
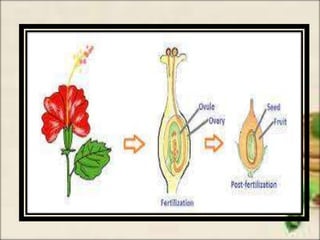
This document discusses the classification and structures of plants. It describes four main categories of plants - herbs, shrubs, trees, climbers and creepers - based on their height and stem properties. It then explains the main internal structures of plants including roots, stems, leaves, flowers and fruits. It provides examples and details on the form and function of each structure.