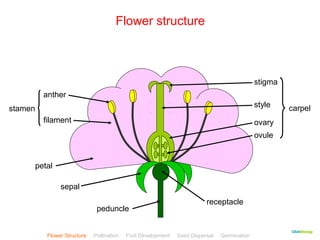
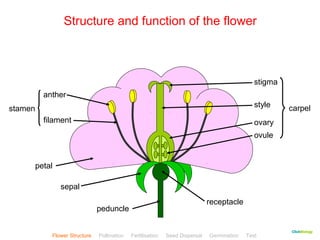
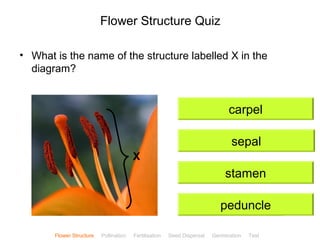
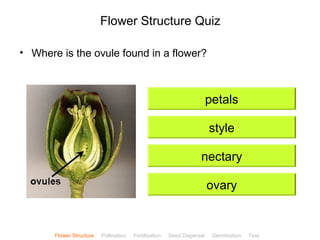
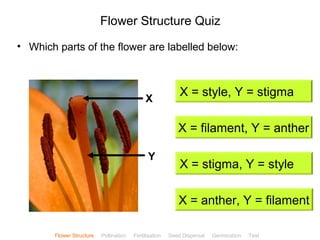
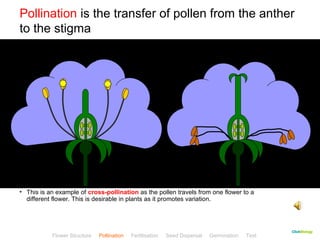
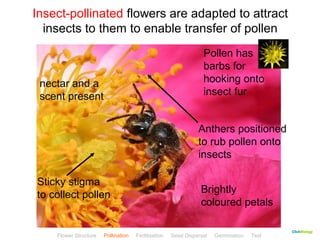
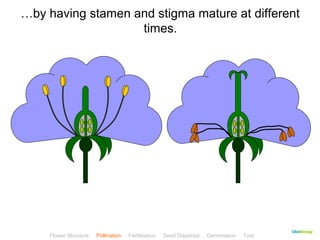
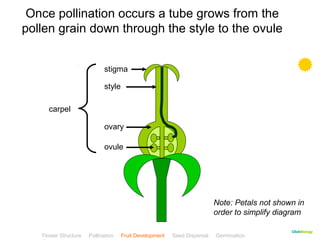
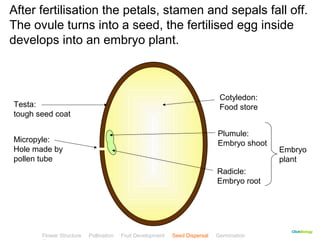
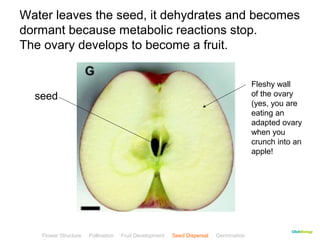
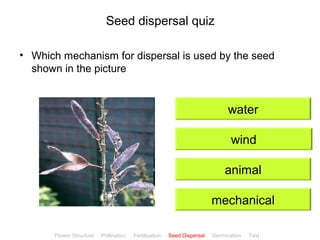
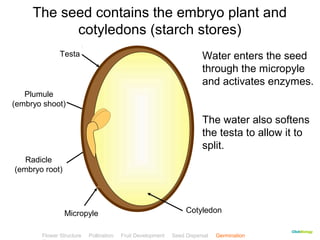
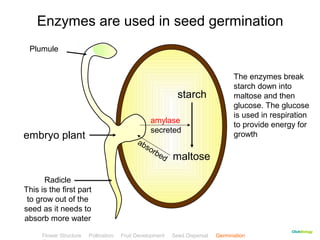
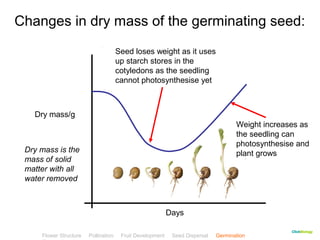
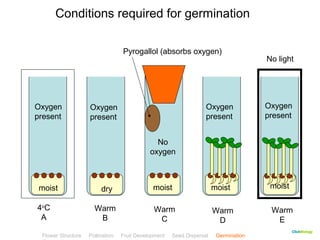
This document provides instructions for navigating an online presentation about plant reproduction. It explains that users should complete all activities and worksheets, navigate through the presentation by clicking, and can view embedded videos by clicking on icons. Some slides have audio explanations. The presentation covers flower structure, pollination, fertilization, fruit development, seed dispersal, germination, and ends with a test.