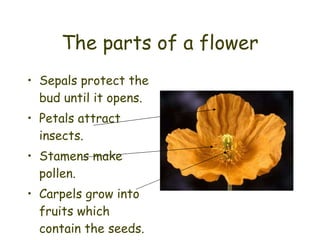
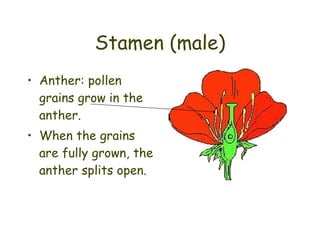
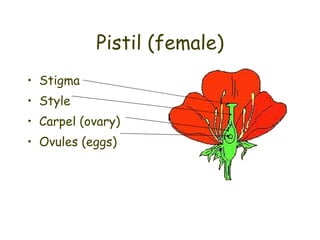
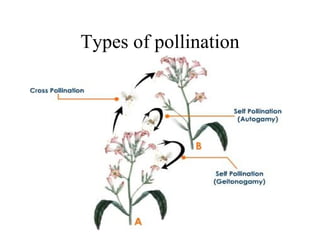
Most flowers have four main parts: sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels. Stamens produce pollen, while carpels become fruits containing seeds. Pollination occurs when pollen is transferred from the stamen to the stigma, fertilizing the ovules within the carpel. Pollination can happen through self-pollination within a flower or plant or cross-pollination between different plants and is aided by wind, insects, birds, and other animals. Successful pollination and fertilization results in the production of seeds contained in fruits.