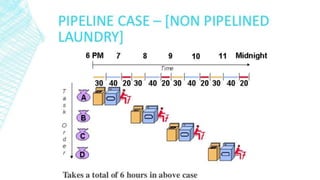
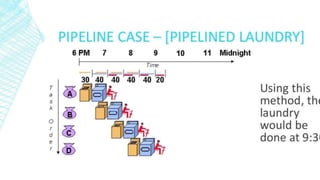
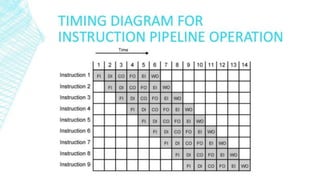
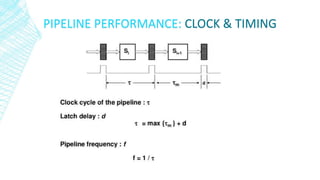
This document discusses instruction pipelining in processors. It explains that pipelining allows multiple instructions to be overlapped in execution by dividing processing into stages like fetch, decode, execute, and writeback. Pipelining improves processor throughput and performance by keeping the pipeline stages continuously busy. While pipelining can significantly increase processor speed, it also introduces complexity and potential issues like pipeline stalls if instructions are dependent on each other.