Embed presentation
Download to read offline







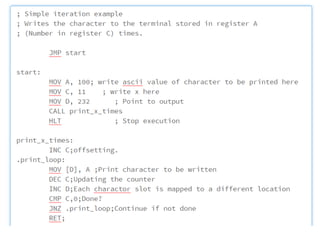
![Plain Text
; Ikuru K
; Simple iteration example
; Writes the character to the terminal stored in register A
; (Number in register C) times.
;intended for use on http://schweigi.github.io/assembler-simulator/
JMP start
start:
MOV A, 100; write ascii value of character to be printed here
MOV C, 11 ; write x here
MOV D, 232 ; Point to output
CALL print_x_times
HLT ; Stop execution
print_x_times:
INC C;offsetting.
.print_loop:
MOV [D], A ;Print character to be written
DEC C;Updating the counter
INC D;Each charactor slot is mapped to a different location
CMP C,0;Done?
JNZ .print_loop;Continue if not done
RET;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/processors-150523132806-lva1-app6891/85/Processors-in-a-nutshell-13-320.jpg)

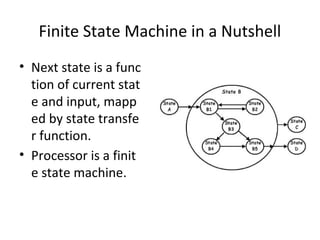
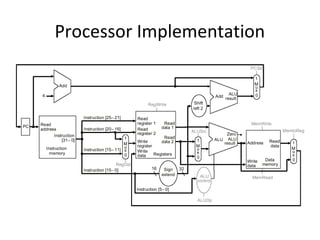
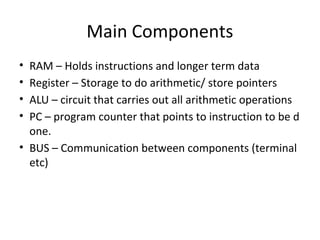
The document summarizes the key components and basic instructions of a processor. It discusses the physical components like RAM, registers, ALU, and bus. It explains that a processor works as a finite state machine where the next state is a function of the current state and input. The basic instructions covered are load, write, arithmetic operations, compare, and jump. An example assembly program is provided to illustrate printing a character a given number of times using these instructions on an online assembler simulator.












![Plain Text
; Ikuru K
; Simple iteration example
; Writes the character to the terminal stored in register A
; (Number in register C) times.
;intended for use on http://schweigi.github.io/assembler-simulator/
JMP start
start:
MOV A, 100; write ascii value of character to be printed here
MOV C, 11 ; write x here
MOV D, 232 ; Point to output
CALL print_x_times
HLT ; Stop execution
print_x_times:
INC C;offsetting.
.print_loop:
MOV [D], A ;Print character to be written
DEC C;Updating the counter
INC D;Each charactor slot is mapped to a different location
CMP C,0;Done?
JNZ .print_loop;Continue if not done
RET;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/processors-150523132806-lva1-app6891/85/Processors-in-a-nutshell-13-320.jpg)