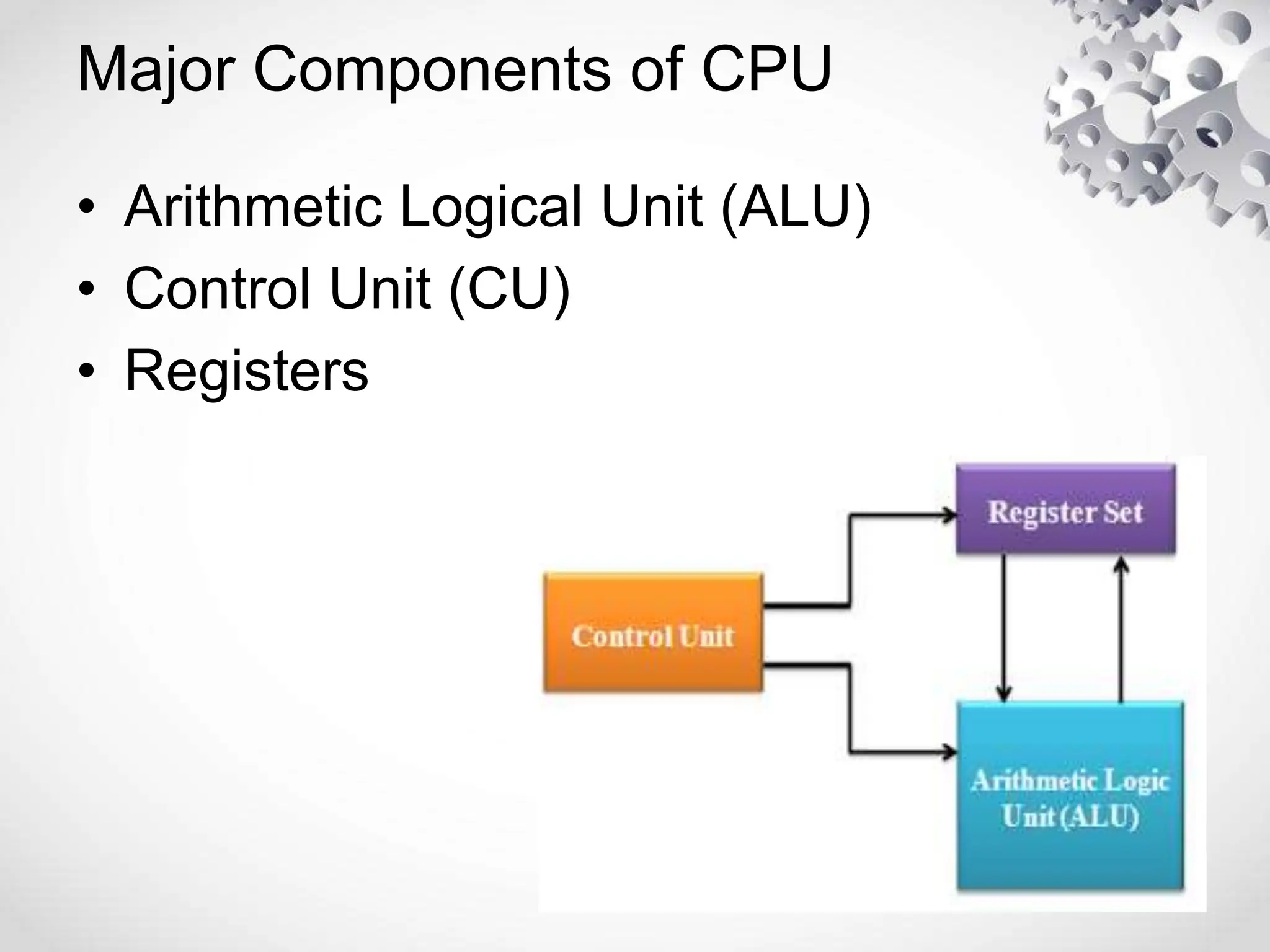
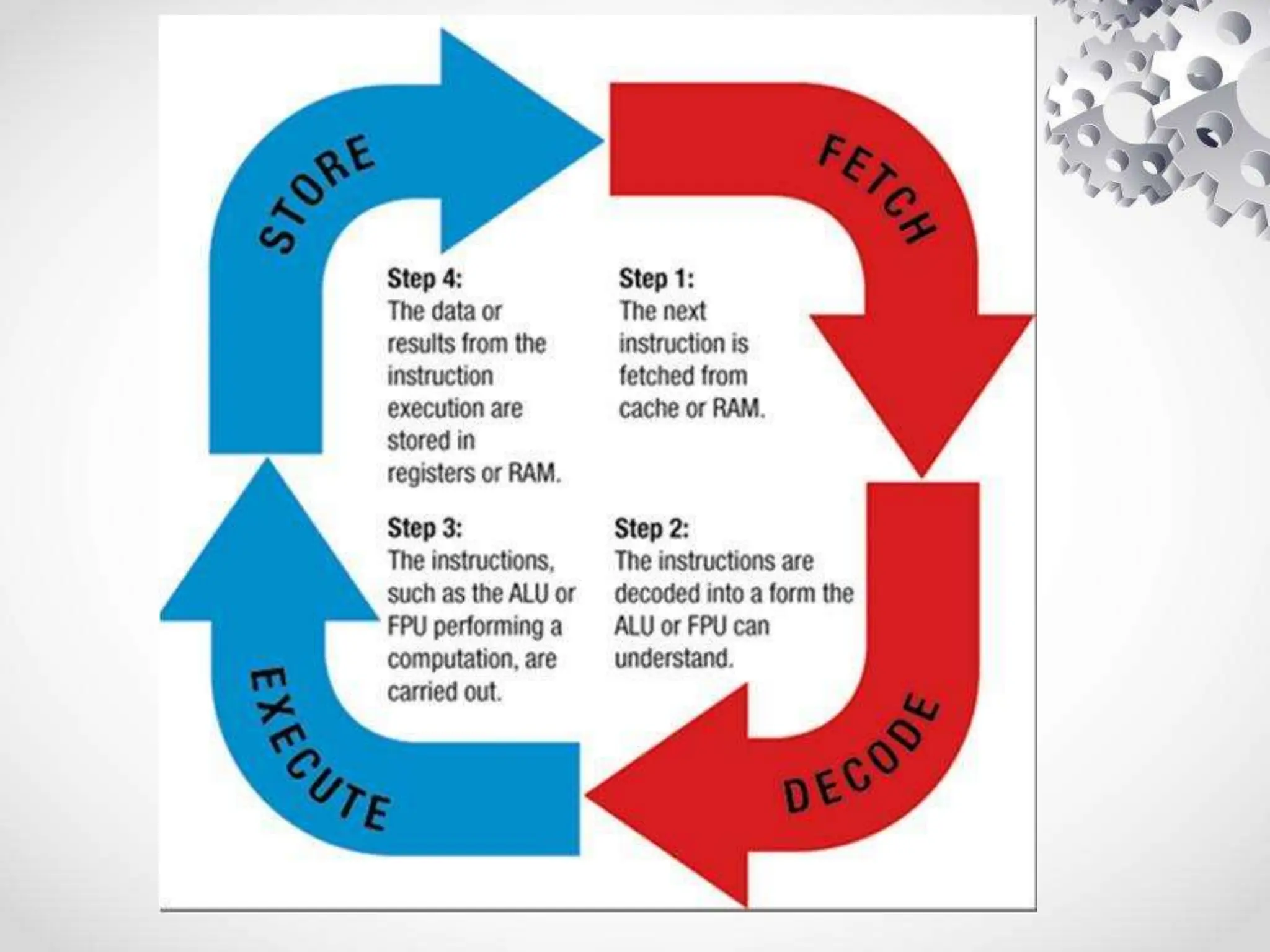
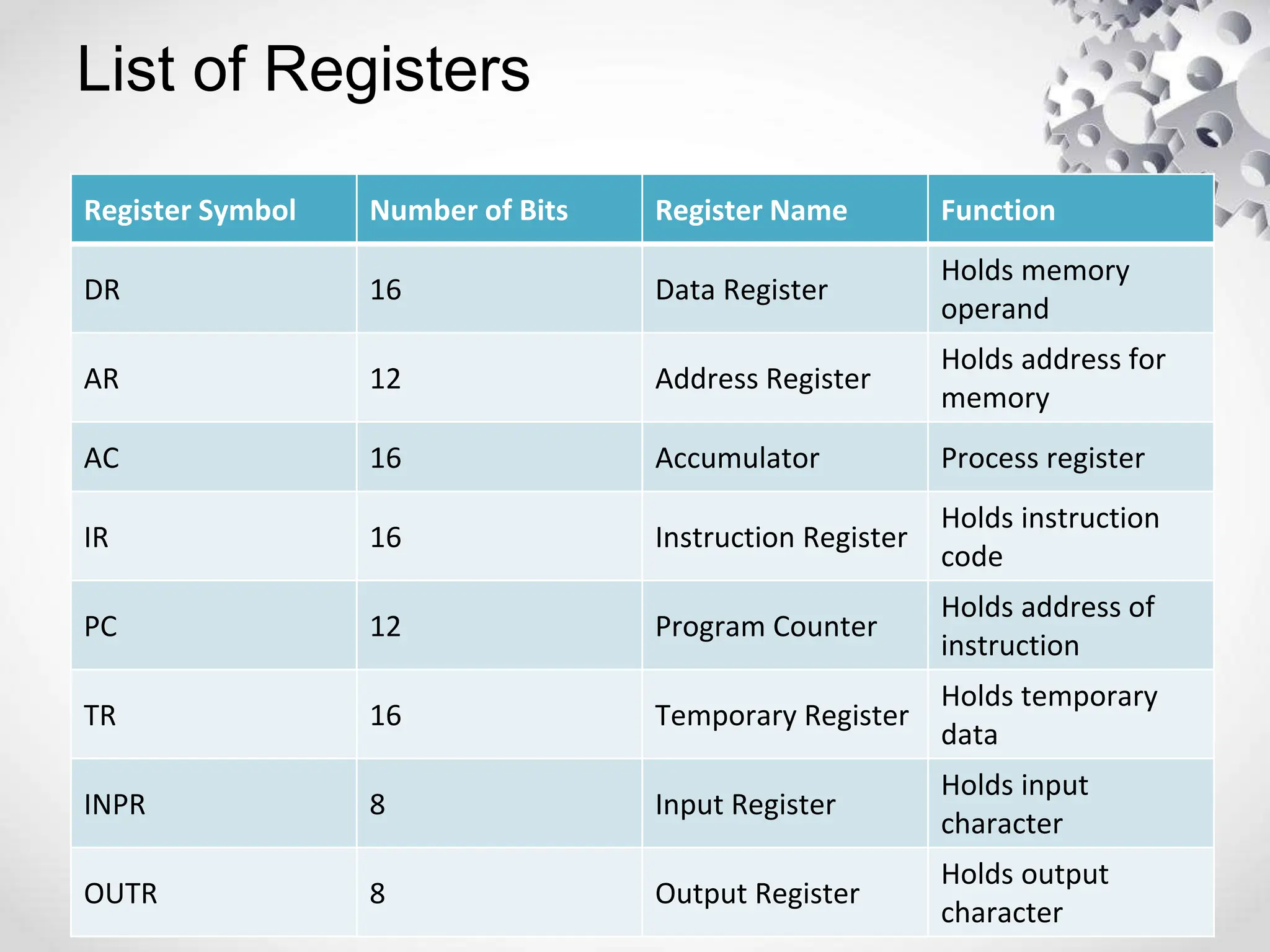
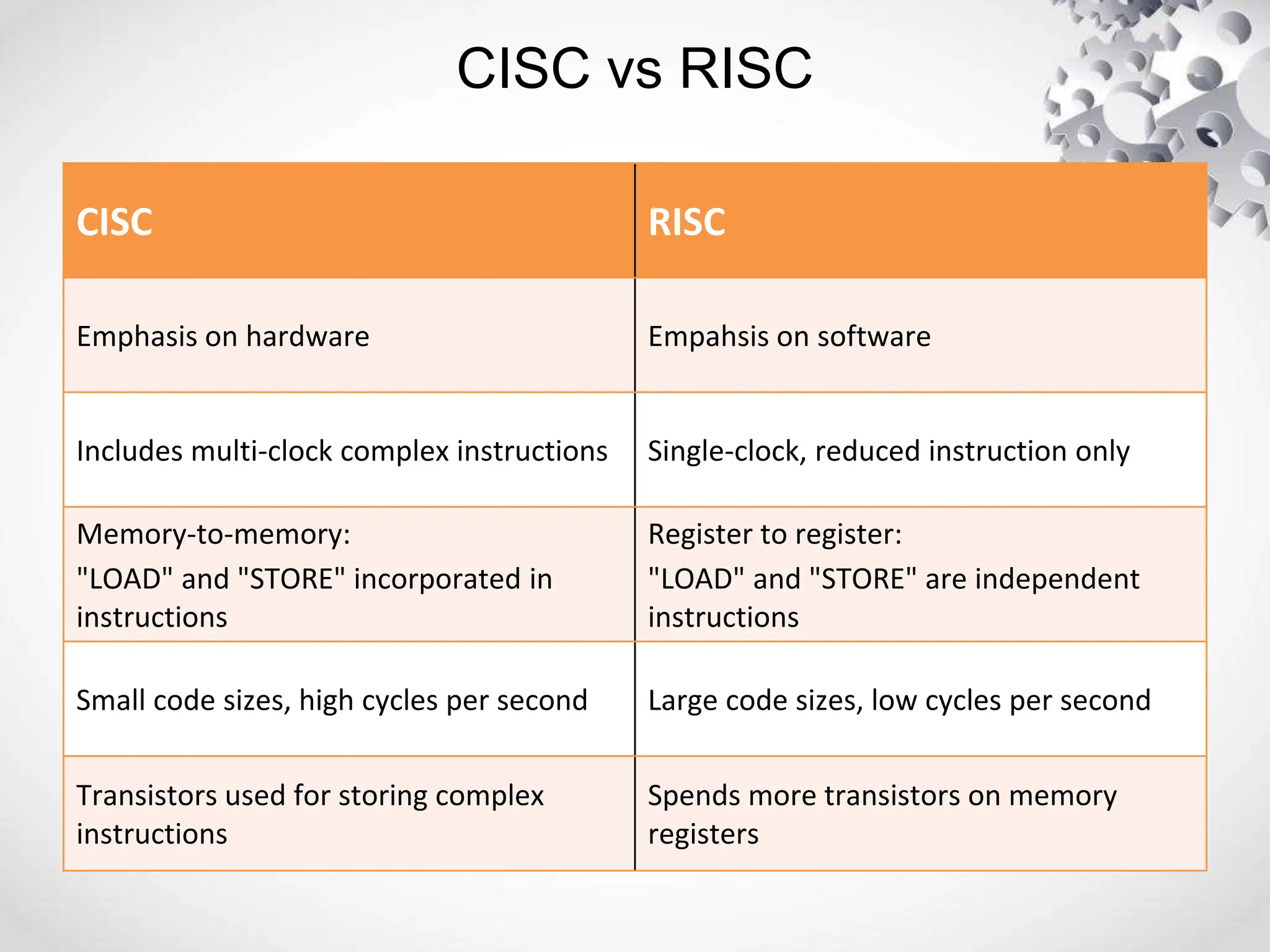
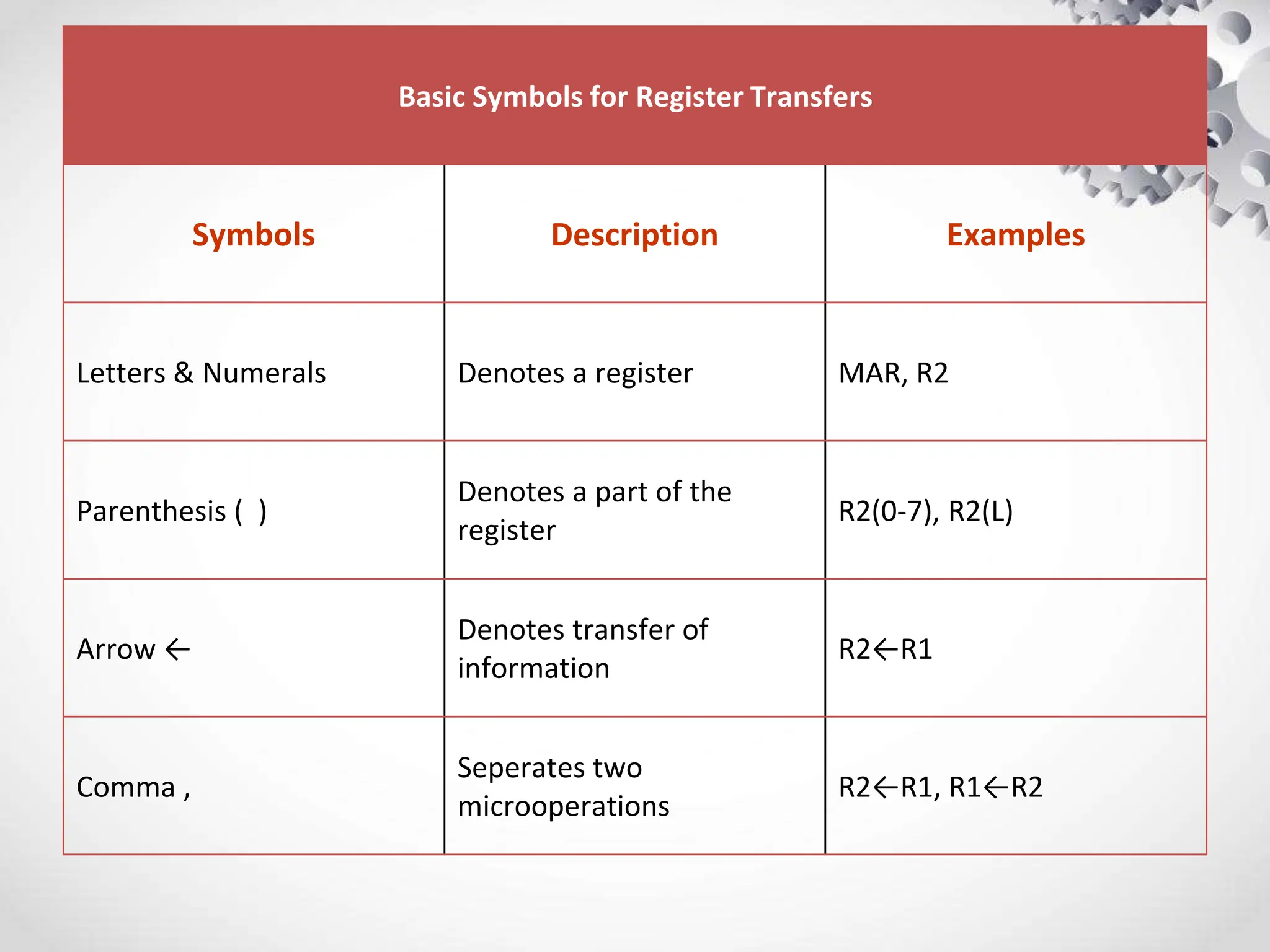
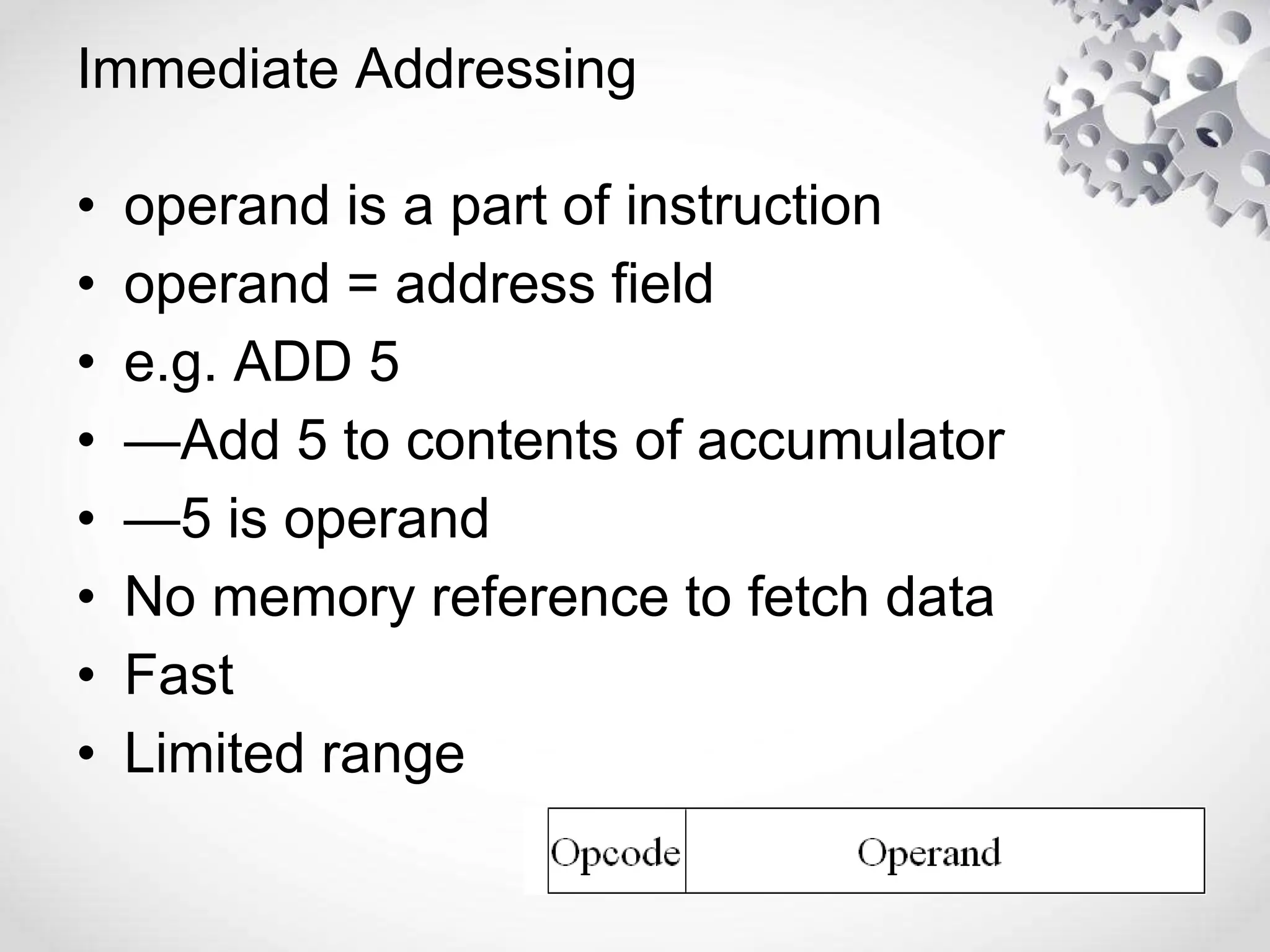
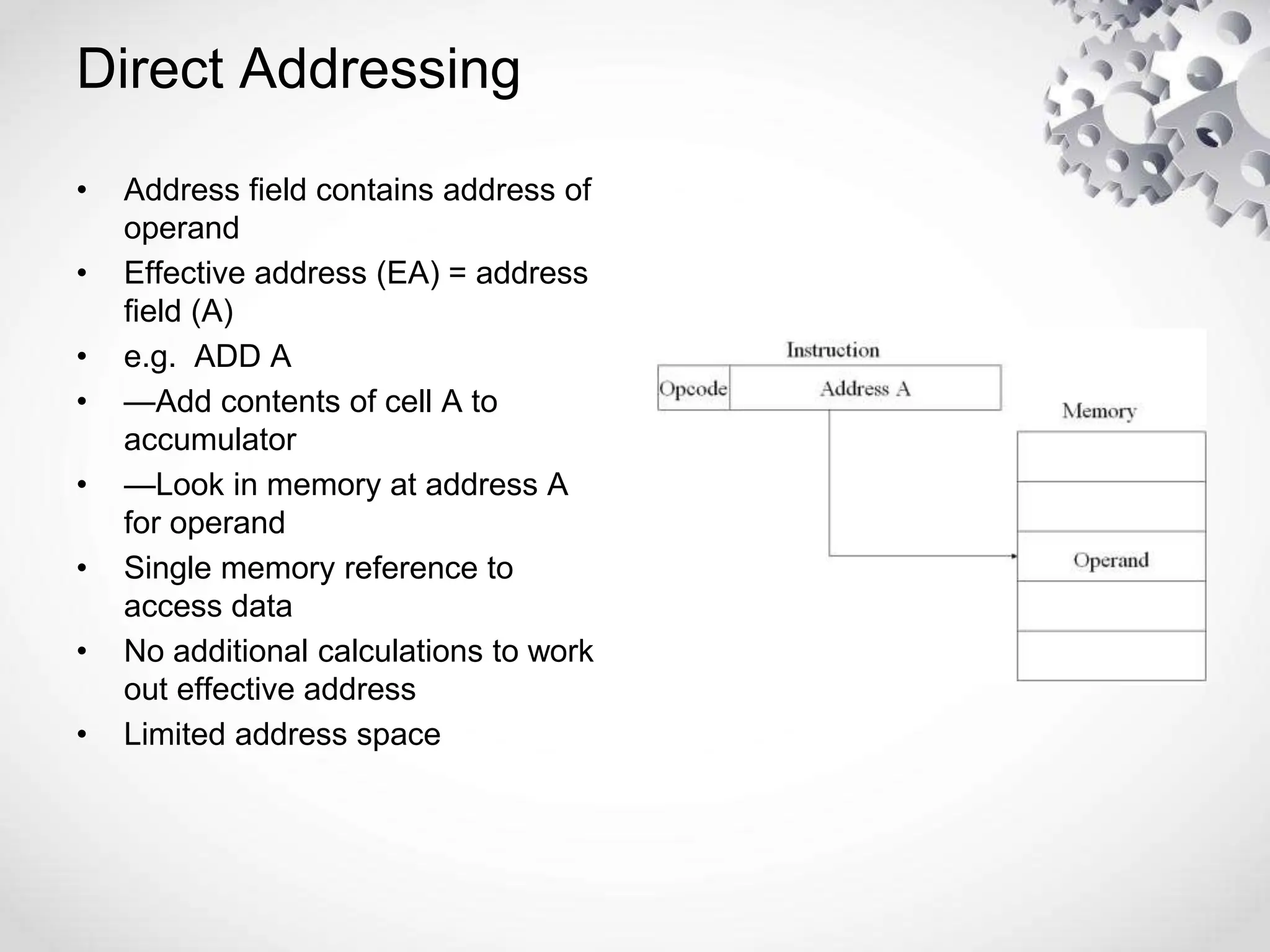
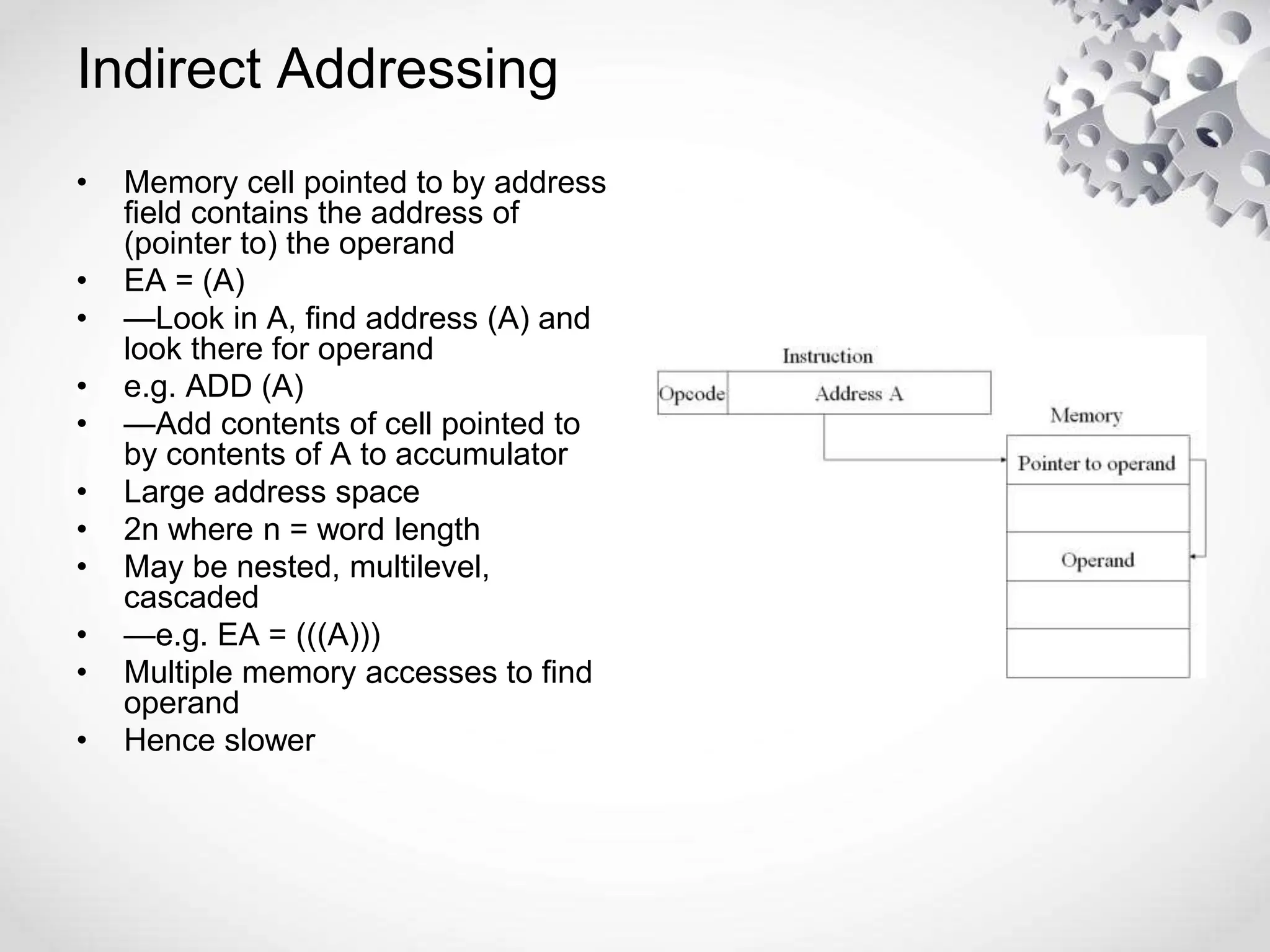
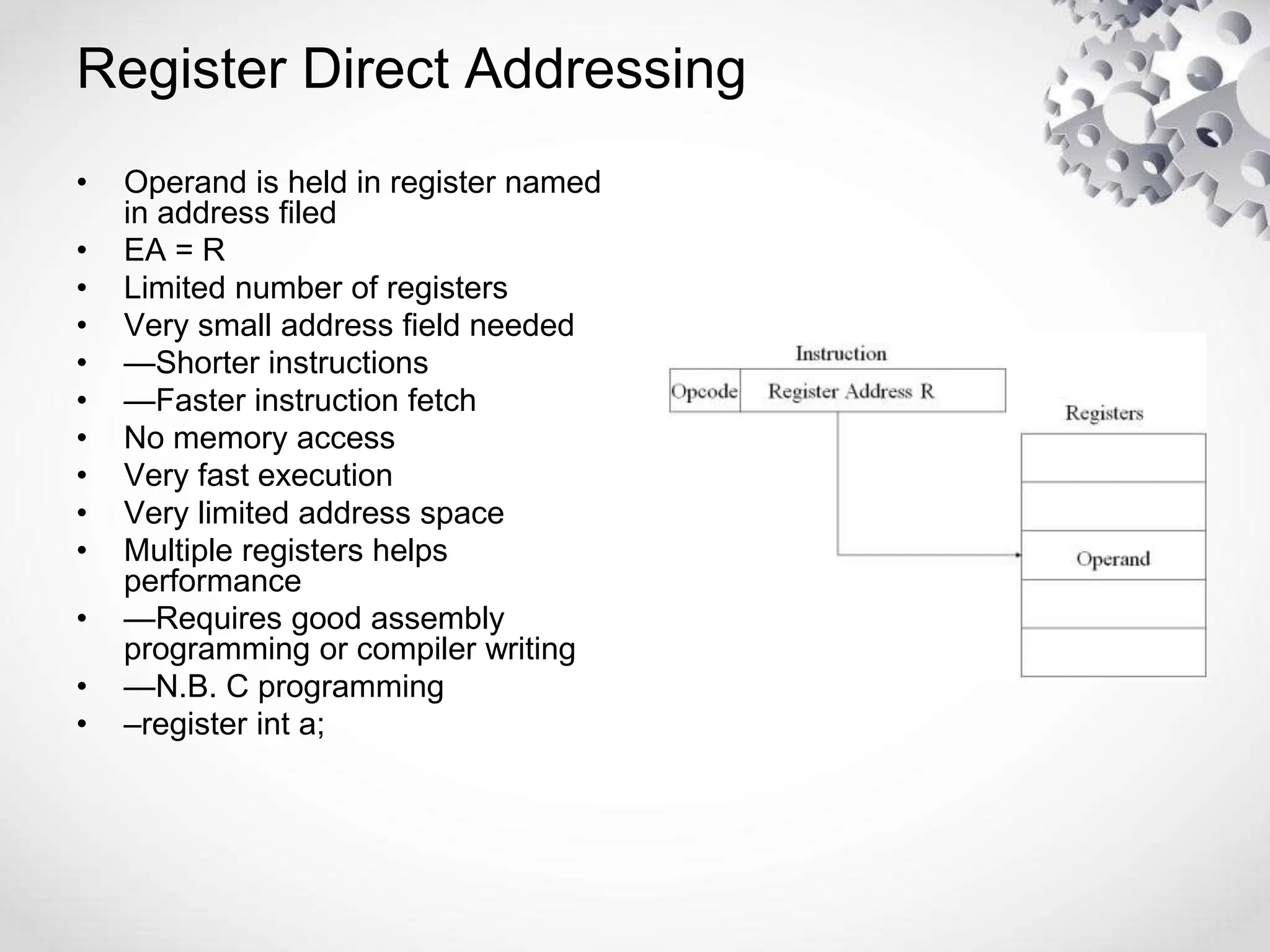
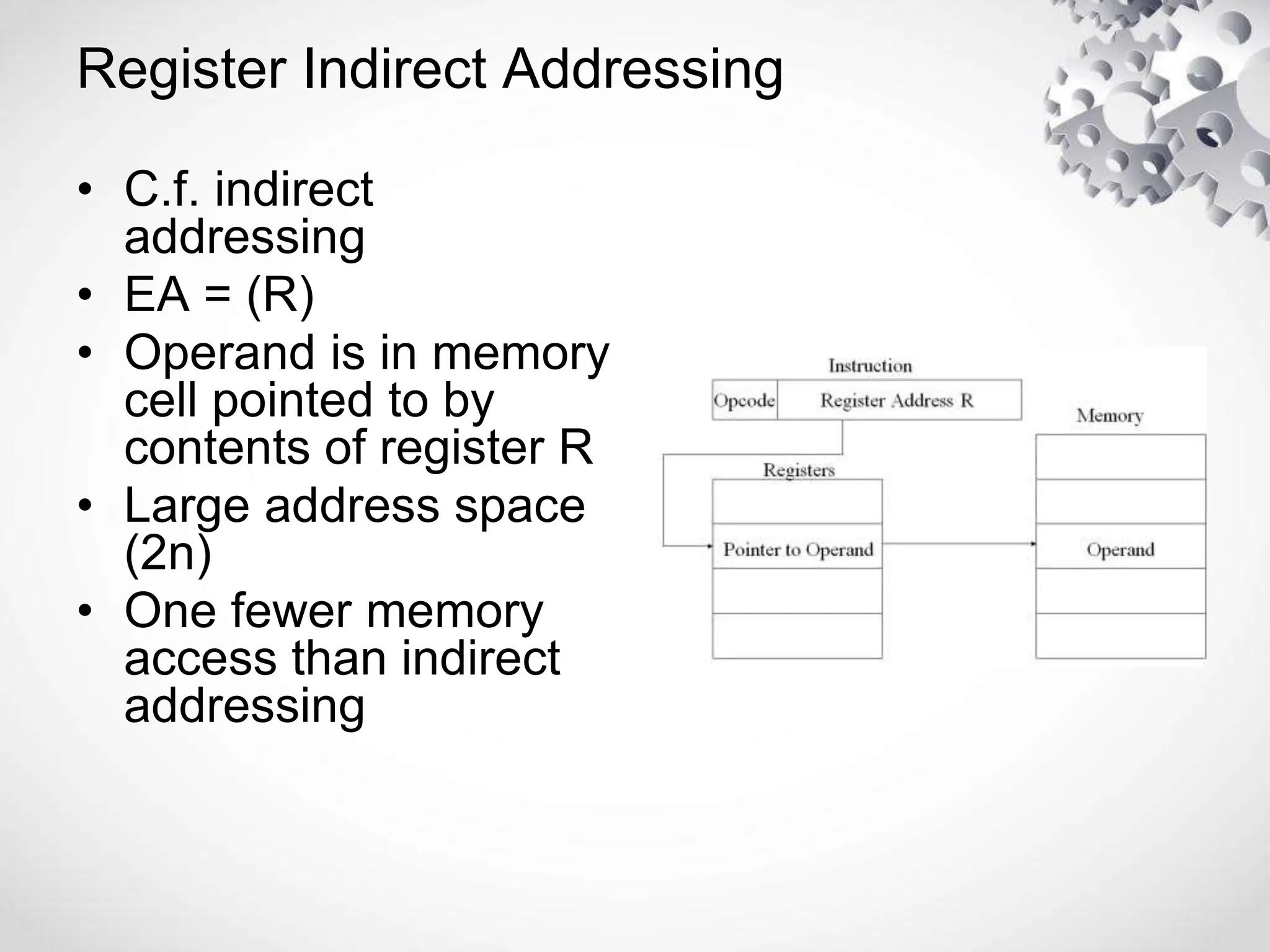
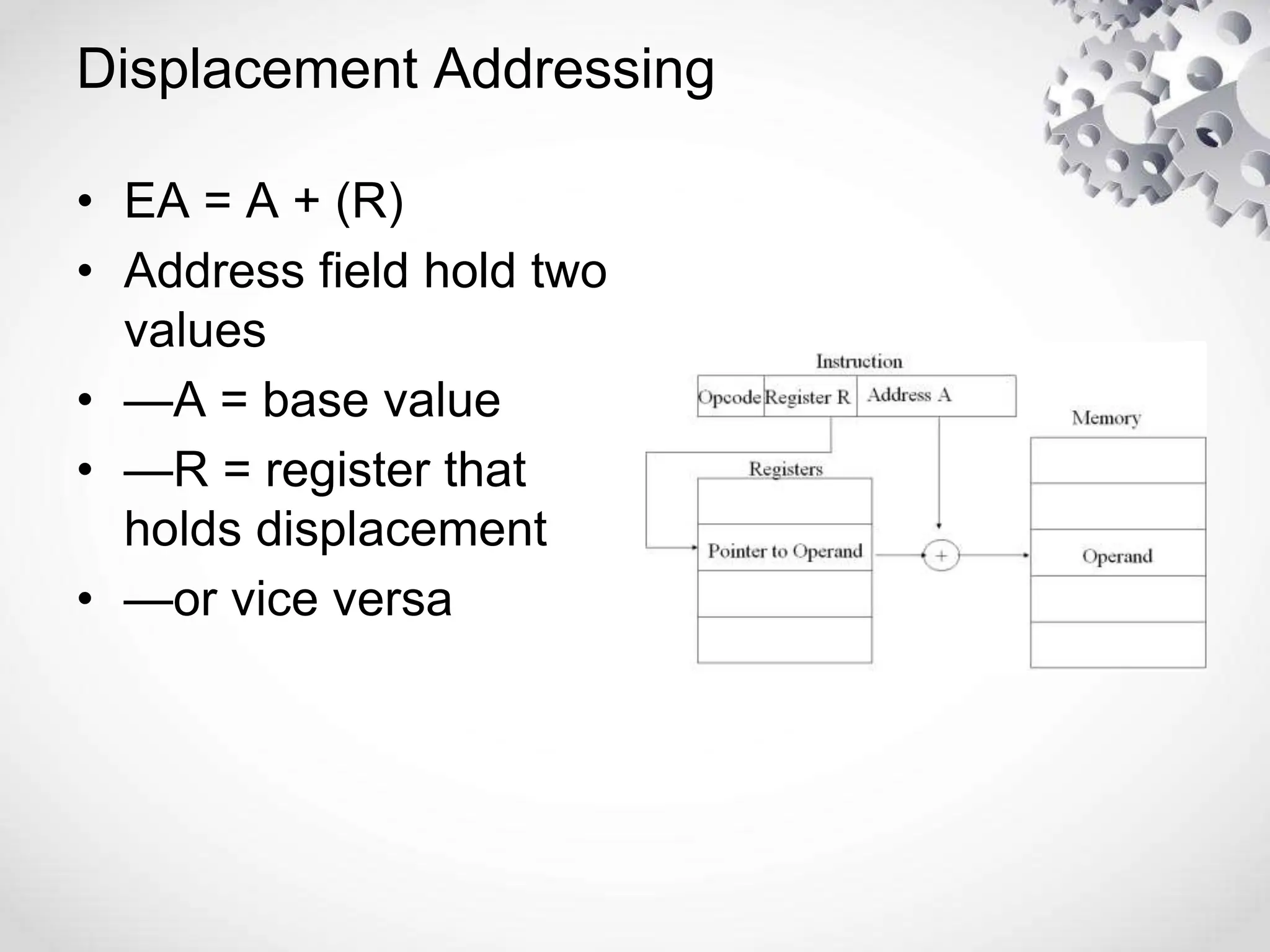
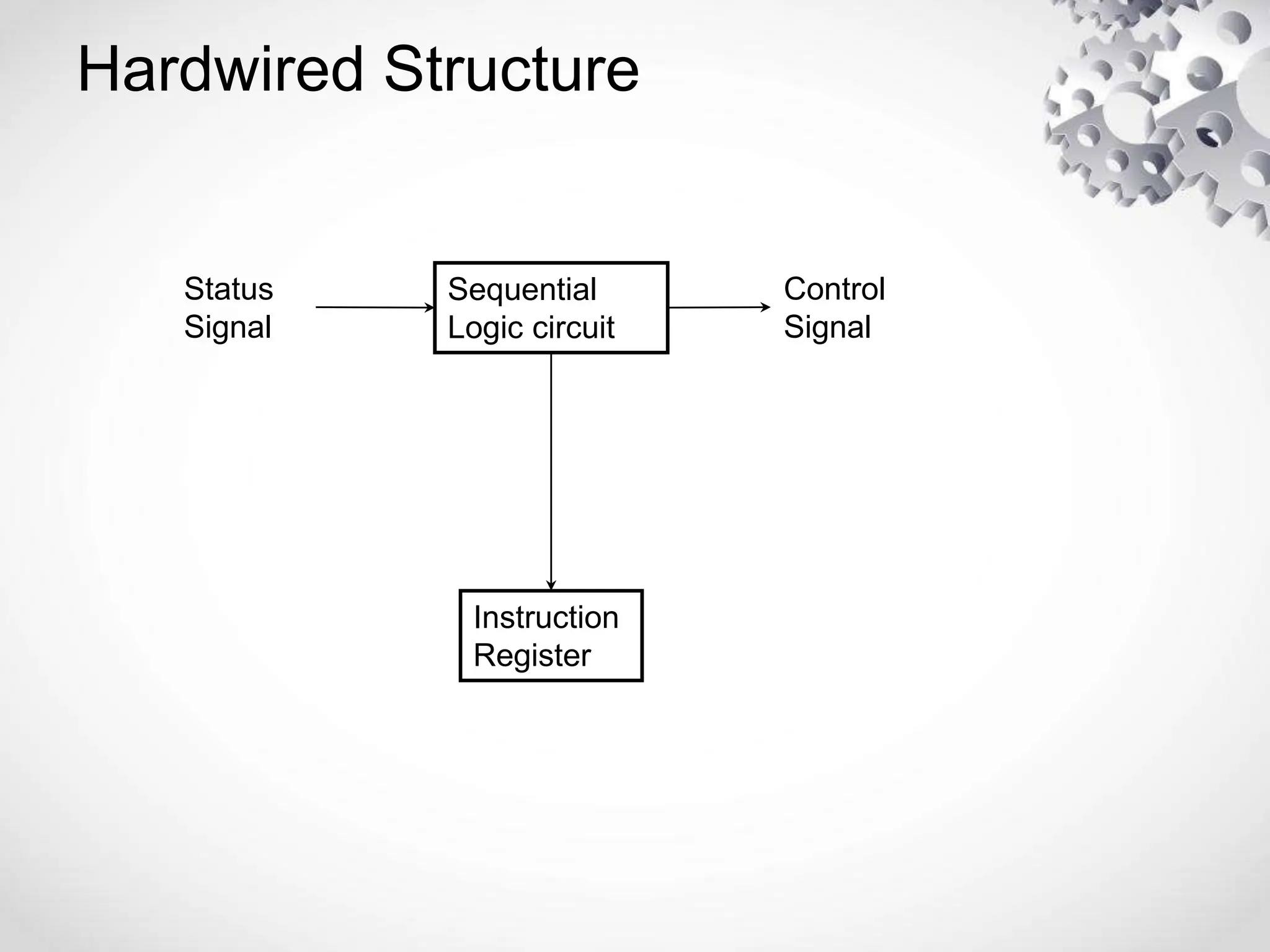
The CPU or central processing unit is the brain of the computer and performs data processing. It has three main components - the arithmetic logical unit (ALU) which performs calculations, the control unit which directs operations, and registers which temporarily store data. The CPU fetches instructions from memory, decodes them, executes the operations, and stores the results. It has different modes like user mode for programs and supervisor mode for the operating system kernel. Interrupts can cause a break in program execution from events internal or external to the CPU. Computer instructions vary between complex instruction set computers (CISCs) and reduced instruction set computers (RISCs).