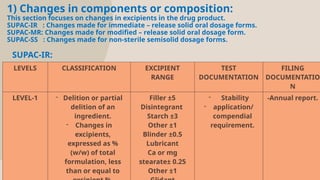
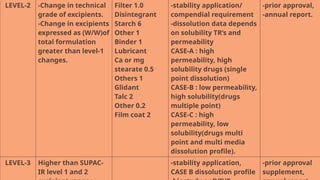
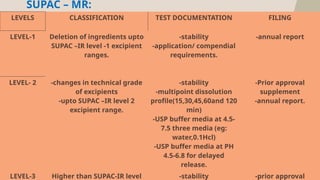
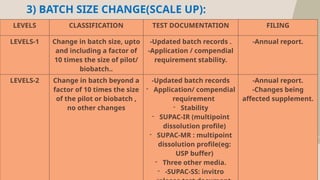
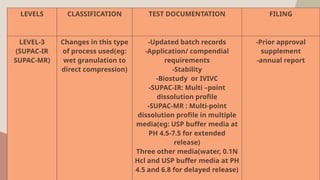
The document presents the SUPAC (Scale-Up and Post Approval Changes) guidelines, which regulate changes in drug manufacturing post-approval, encompassing aspects like composition, manufacturing site, batch size, and processes. It details the historical background, categorization of changes (minor to major), and necessary documentation and testing procedures involved in the scale-up process. Additionally, the document highlights the advantages and disadvantages of these guidelines, emphasizing the importance of maintaining product quality during transitions.