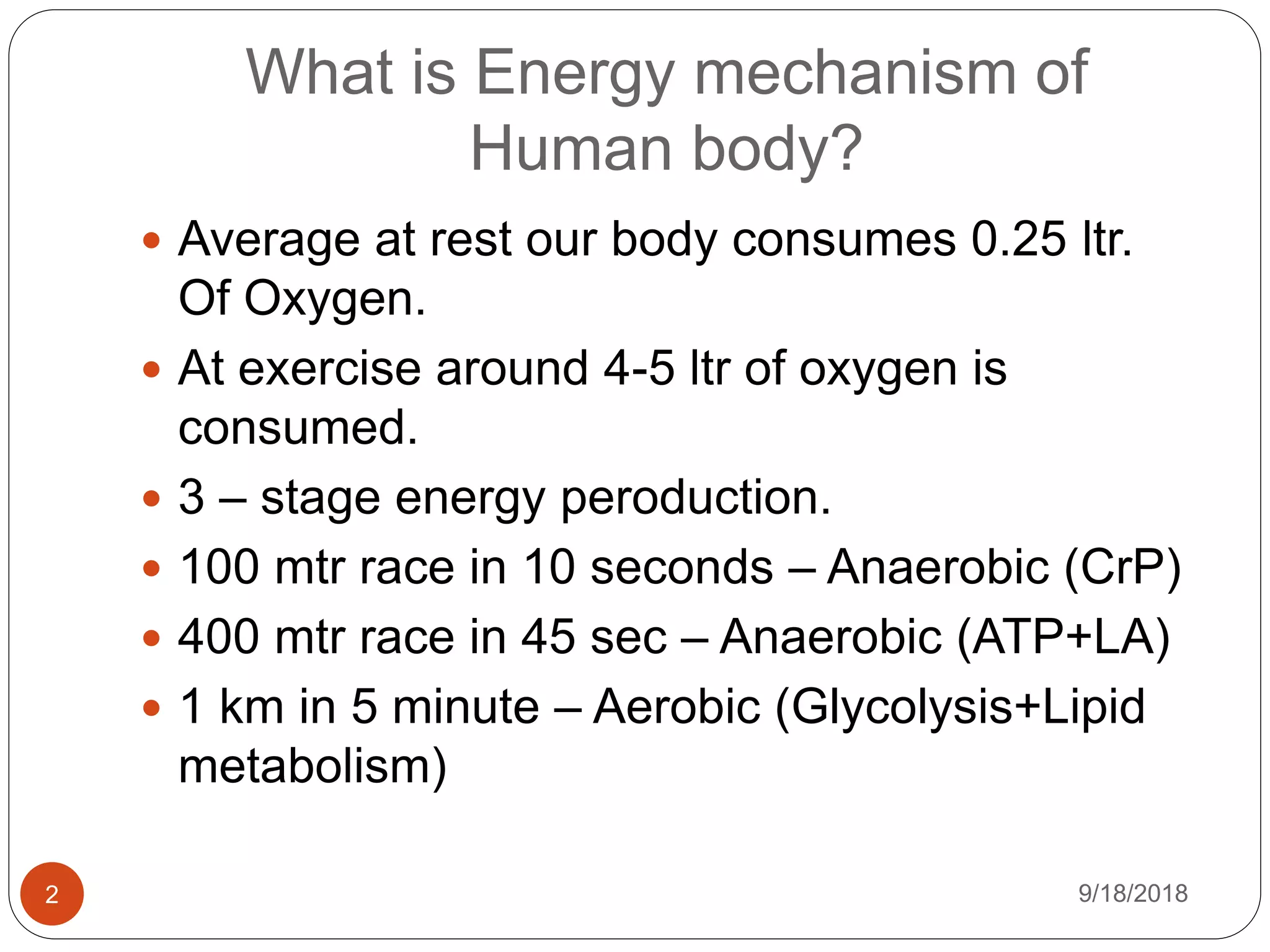
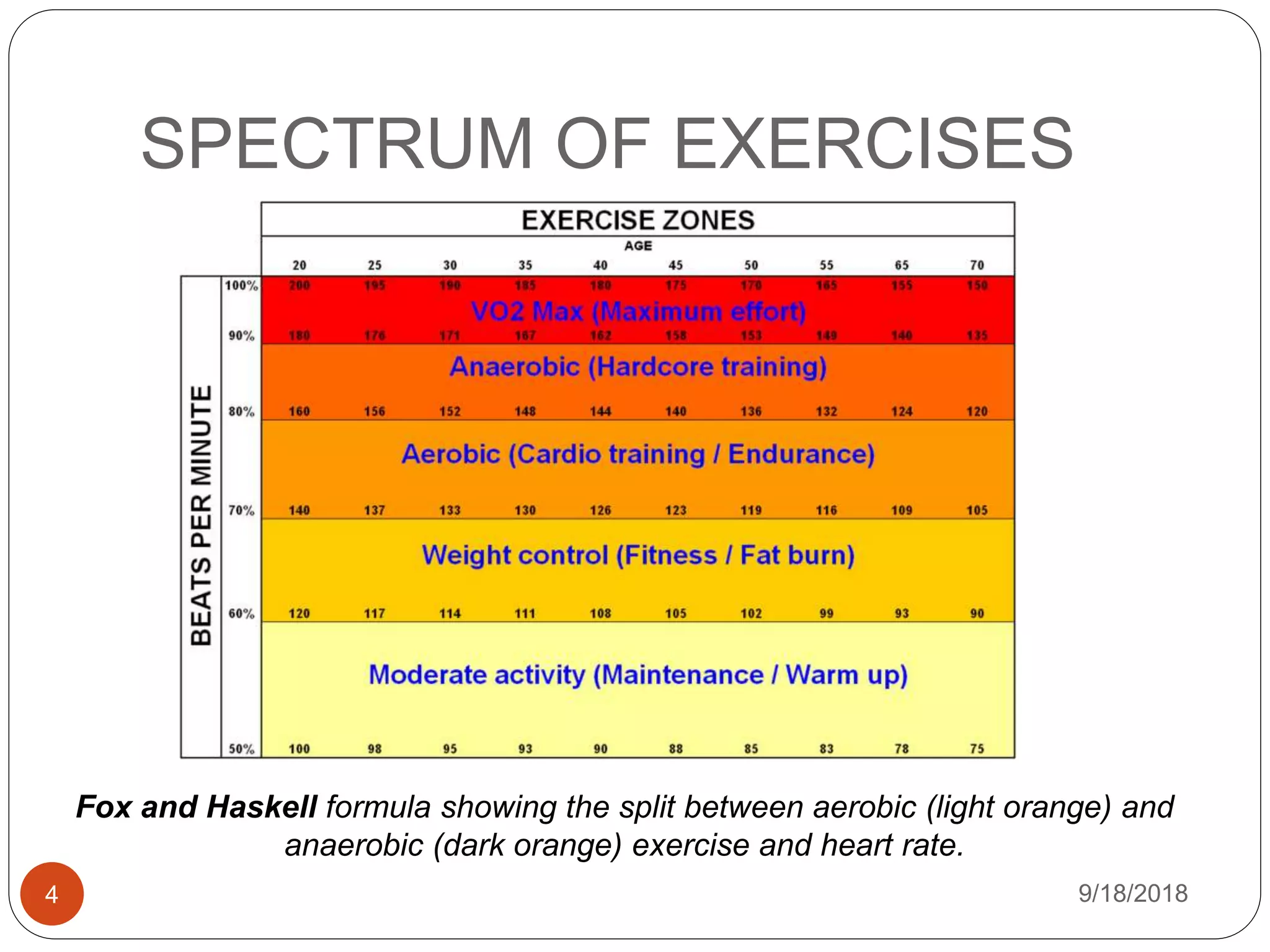
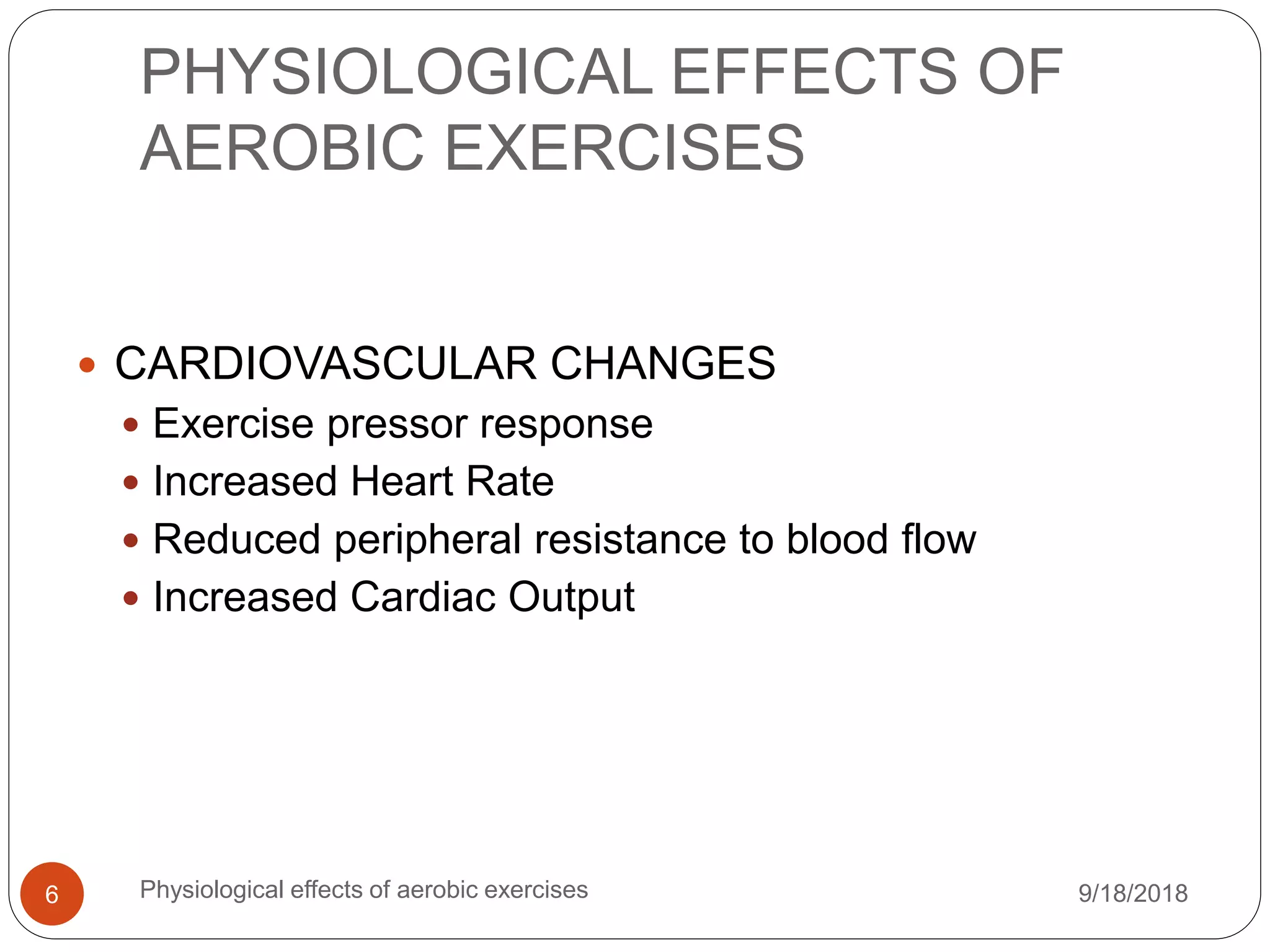
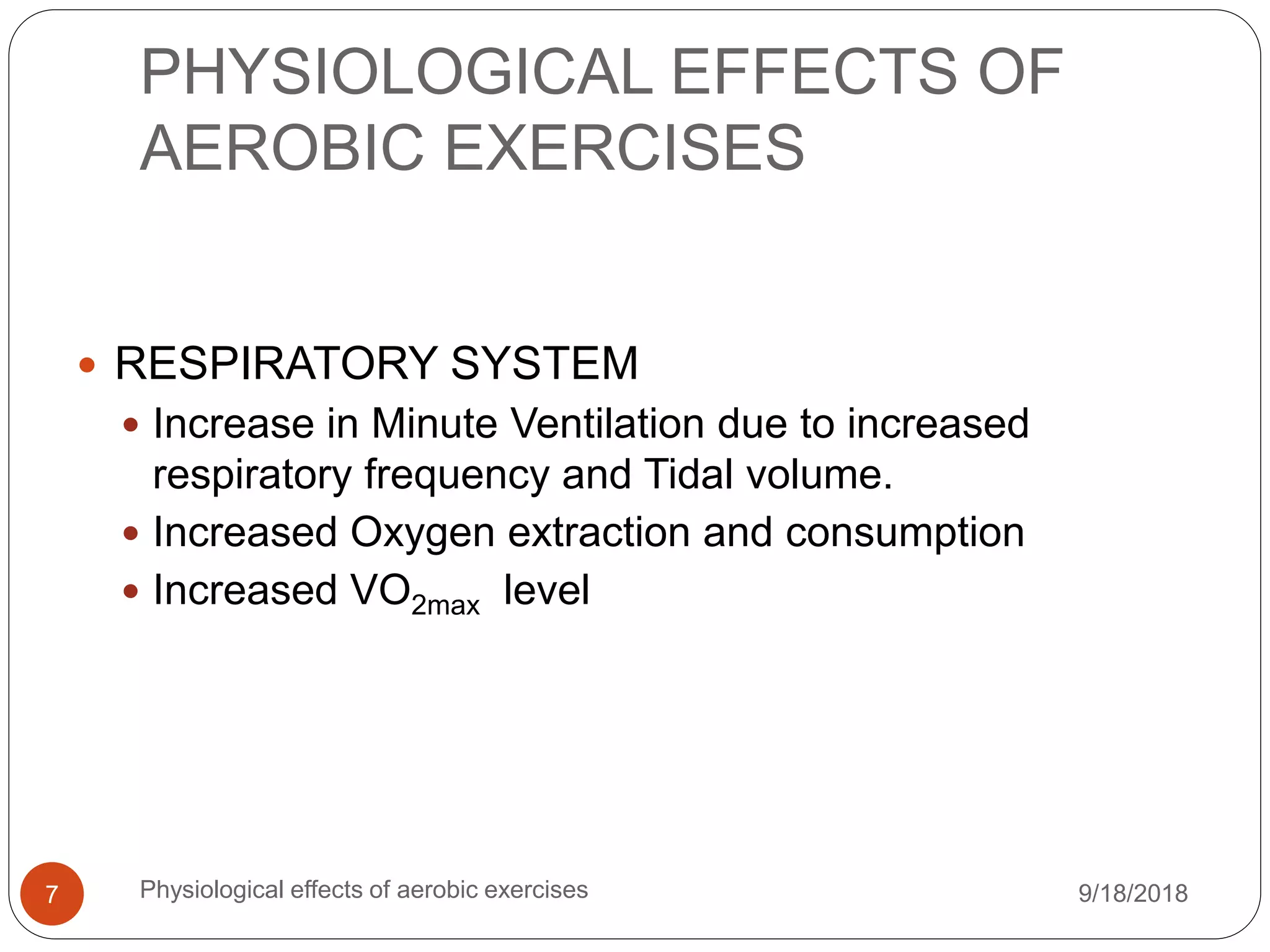
The document outlines the physiological effects of aerobic exercises, highlighting their impact on energy consumption, cardiovascular health, respiratory efficiency, metabolic changes, and musculoskeletal benefits. It describes the types of aerobic activities, their adaptations in the body during exercise, and their applications in managing conditions like diabetes and hypertension. Overall, it emphasizes the importance of aerobic exercise in enhancing physical fitness and health.