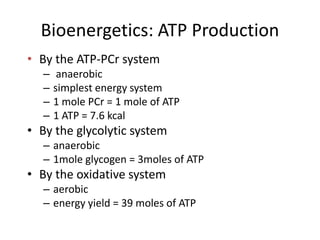
This document discusses physiological adaptations to exercise. It explains that acute adaptations during exercise involve the nervous and endocrine systems regulating muscle, heart, and breathing function. Long-term adaptations provide health benefits like increased endurance. It describes the energy systems of ATP-PCr, glycolysis, and aerobic respiration. Regular exercise leads to adaptations like increased oxygen consumption, ventilation, blood flow, and muscle fiber changes. Factors like intensity, duration, and frequency of training programs influence these adaptations.