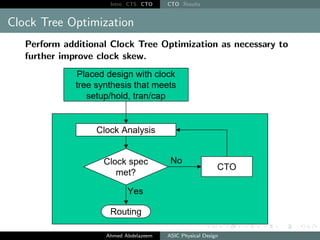
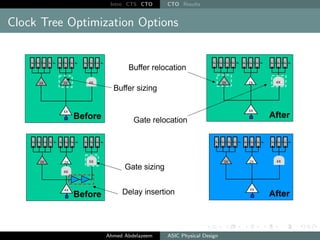
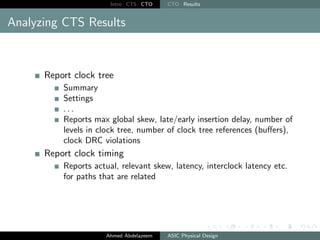
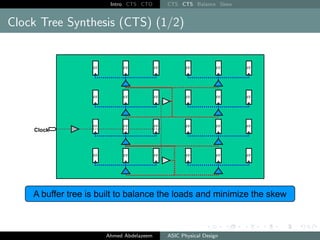
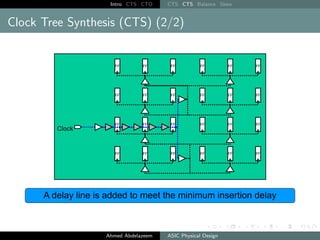
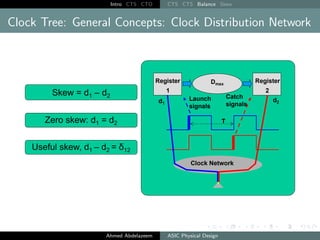
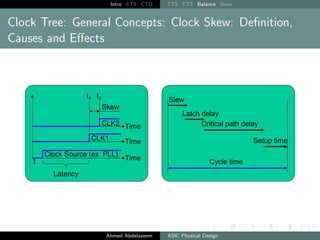
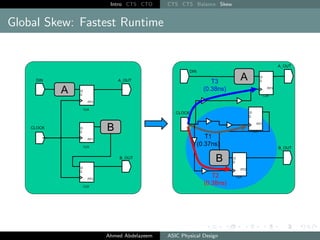
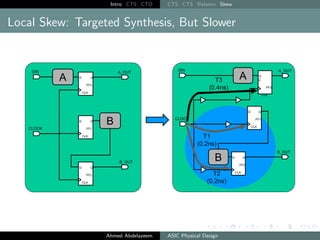
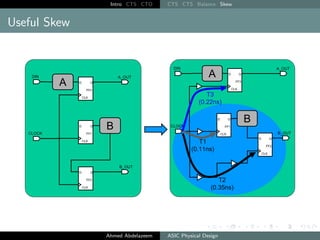
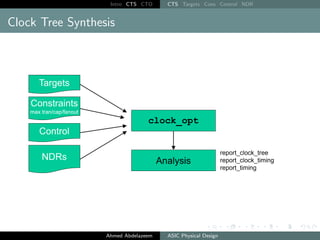
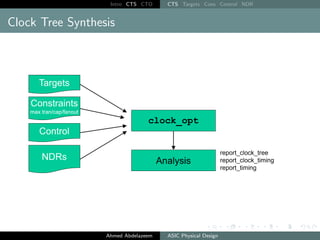
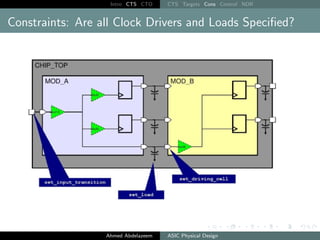
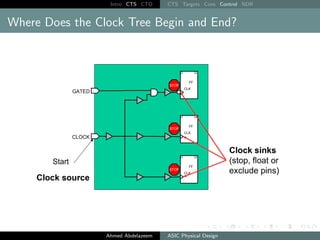
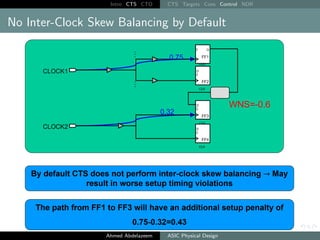
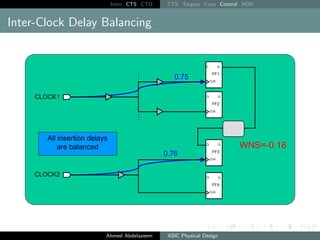
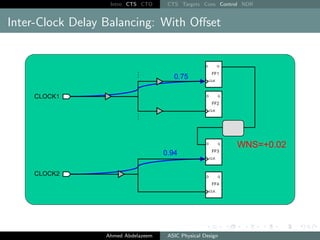
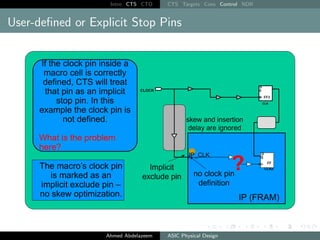
The document outlines the process of Clock Tree Synthesis (CTS) in ASIC physical design, detailing the goals, optimization techniques, and considerations necessary for effective clock distribution. It emphasizes the importance of balancing skew, managing insertion delays, and optimizing clock routing to achieve desired performance metrics. Additionally, it discusses the implications of clock network design choices on overall chip functionality and design efficiency.






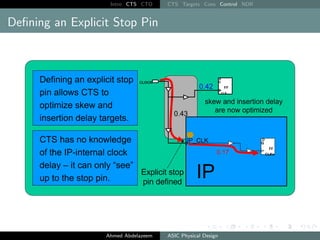
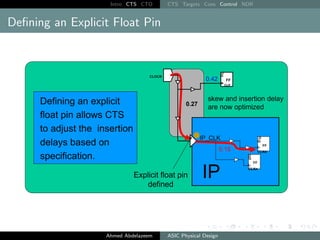


![Intro CTS CTO CTS Targets Cons Control NDR
Put NDR on Pitch for Accurate RC Estimation
Metal traces are always routed “on pitch”
With clock NDR rules, pre-routing RC estimates of
clock nets use NDR width and spacing numbers
If NDR [spacing + width] numbers are not integer
multiples of pitch (i.e. off-pitch), timing estimates
pre-route may not correlate well with post-route timing
Make sure your NDR numbers are on pitch!
Ahmed Abdelazeem ASIC Physical Design](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clocktreesynthesis-240908190739-b7f34dee/85/Clock-Tree-Synthesis-pdf-38-320.jpg)