Embed presentation

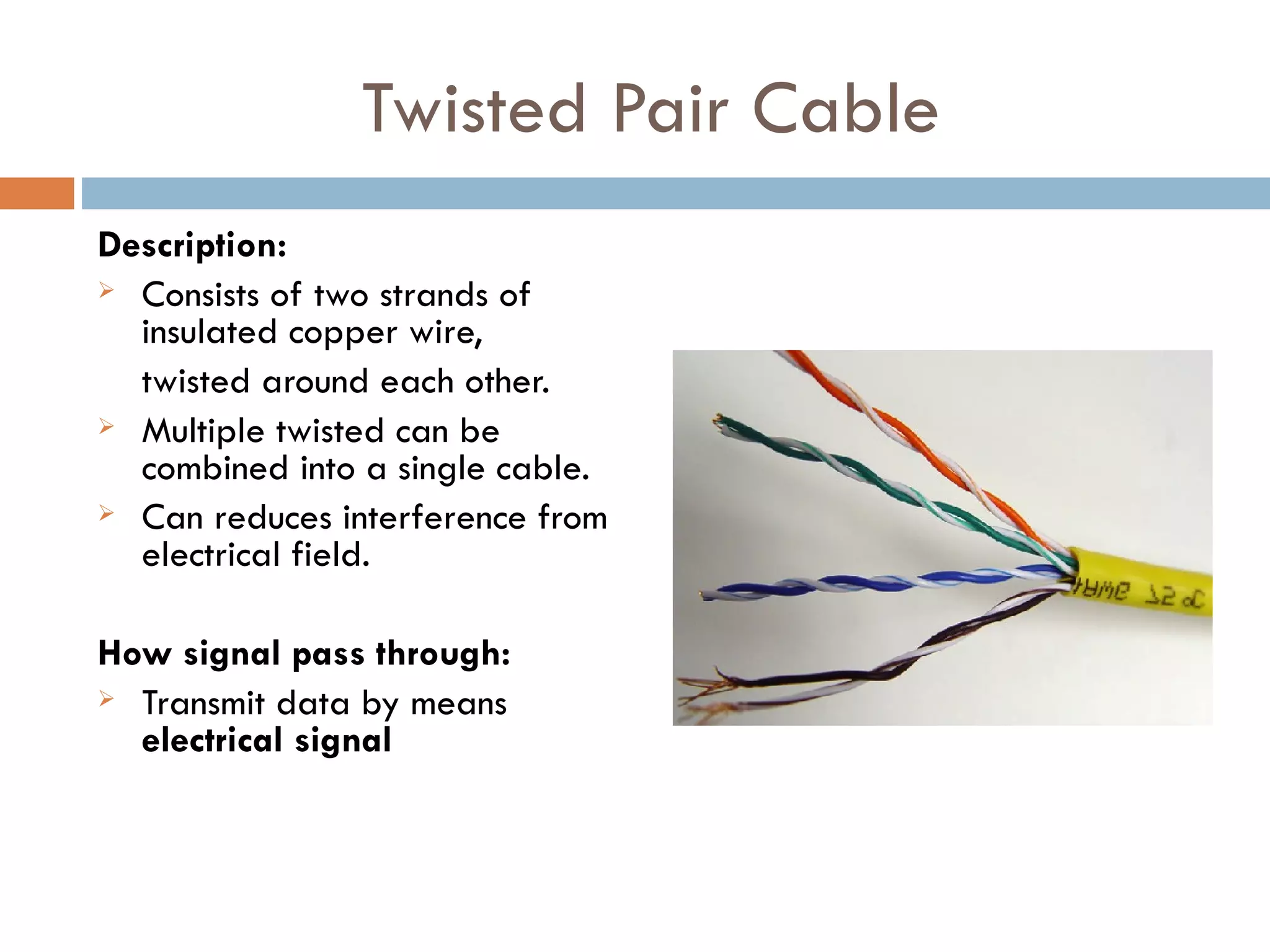
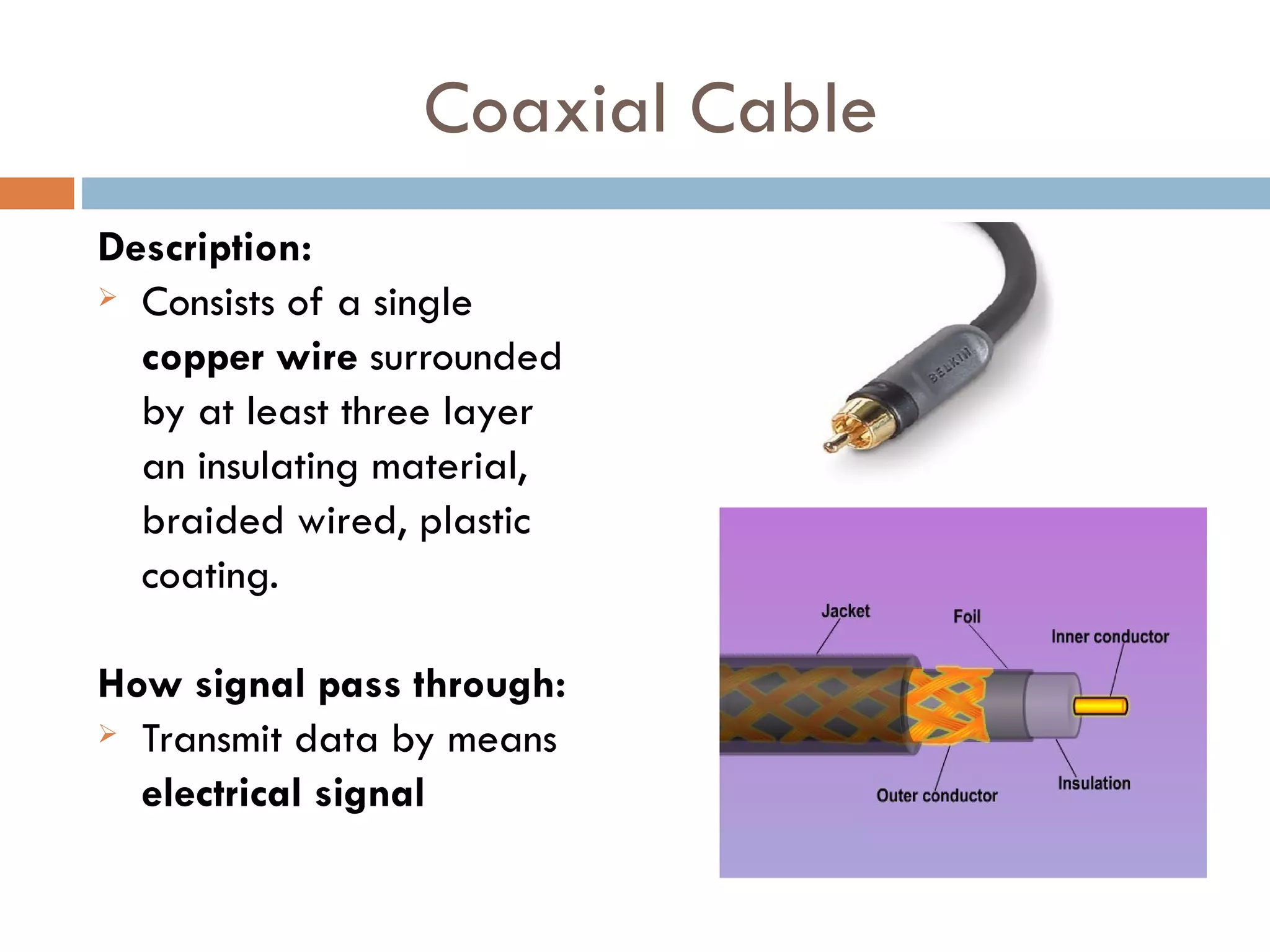
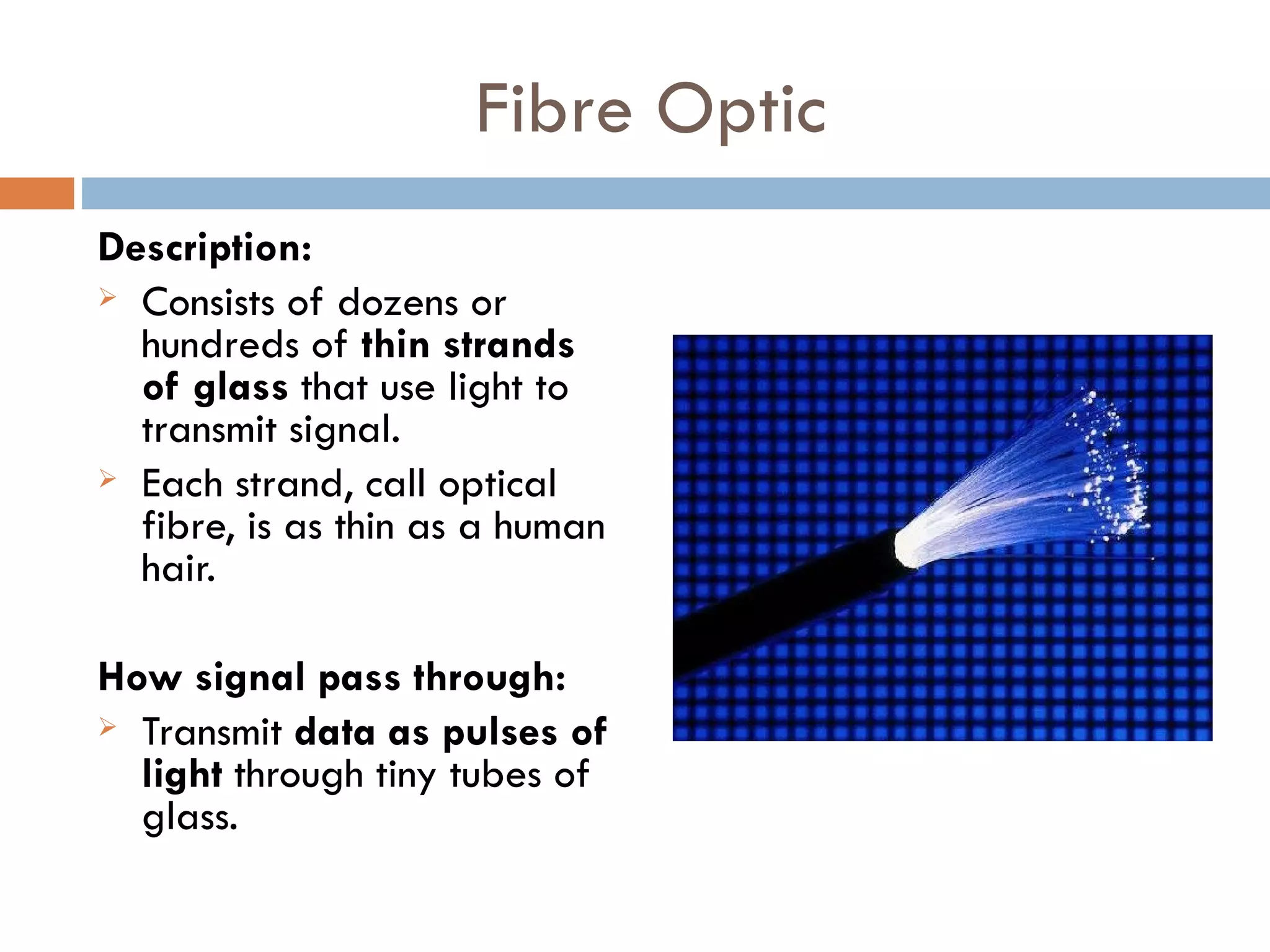
This document discusses three main types of physical transmission media used in computer networks: twisted-pair cable which consists of two insulated copper wires twisted together and can transmit data via electrical signals; coaxial cable which has a single copper wire surrounded by insulating material and braided wires to transmit data electrically; and fibre optic cable which uses thin glass strands to transmit data pulses of light.




