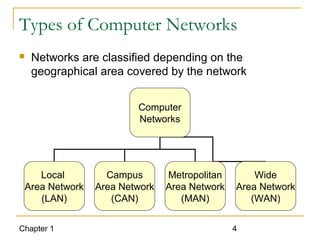
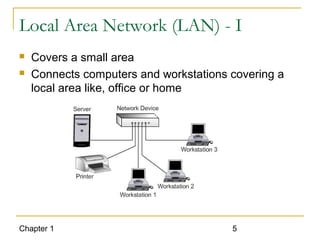
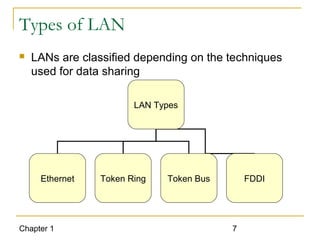
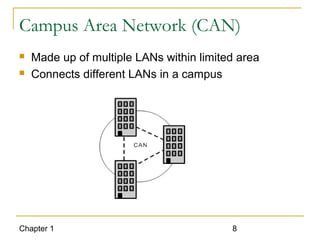
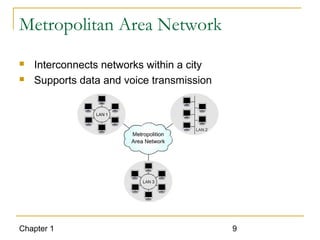
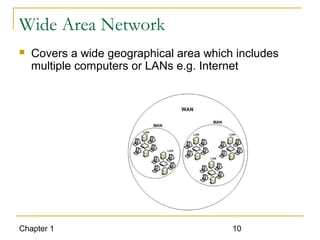
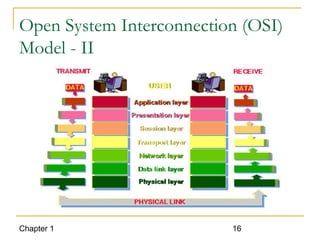
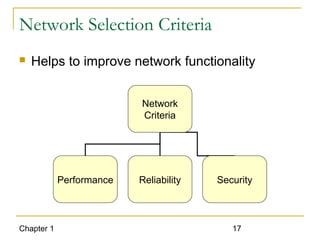
The document introduces computer networks and their types, including LAN, CAN, MAN and WAN. It describes client/server configuration and the 7-layer OSI model. It also covers network selection criteria and standards organizations that develop network standards. Case studies provide examples of using different network types in business scenarios.