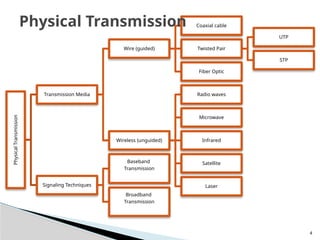
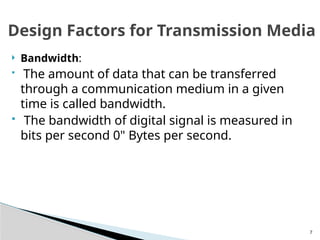
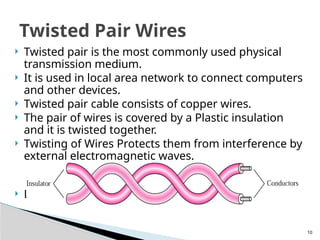
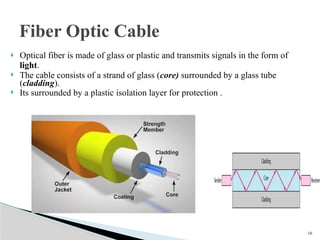
The document discusses physical transmission networking, which involves the transfer of data between computers and devices through various media. It categorizes transmission media into wired (guided) and wireless (unguided), detailing types such as twisted pair, coaxial cable, and fiber optic. Additionally, it highlights the significance of bandwidth, advantages and disadvantages of each medium, and specifies that fiber optic cables offer the highest speed transmission.