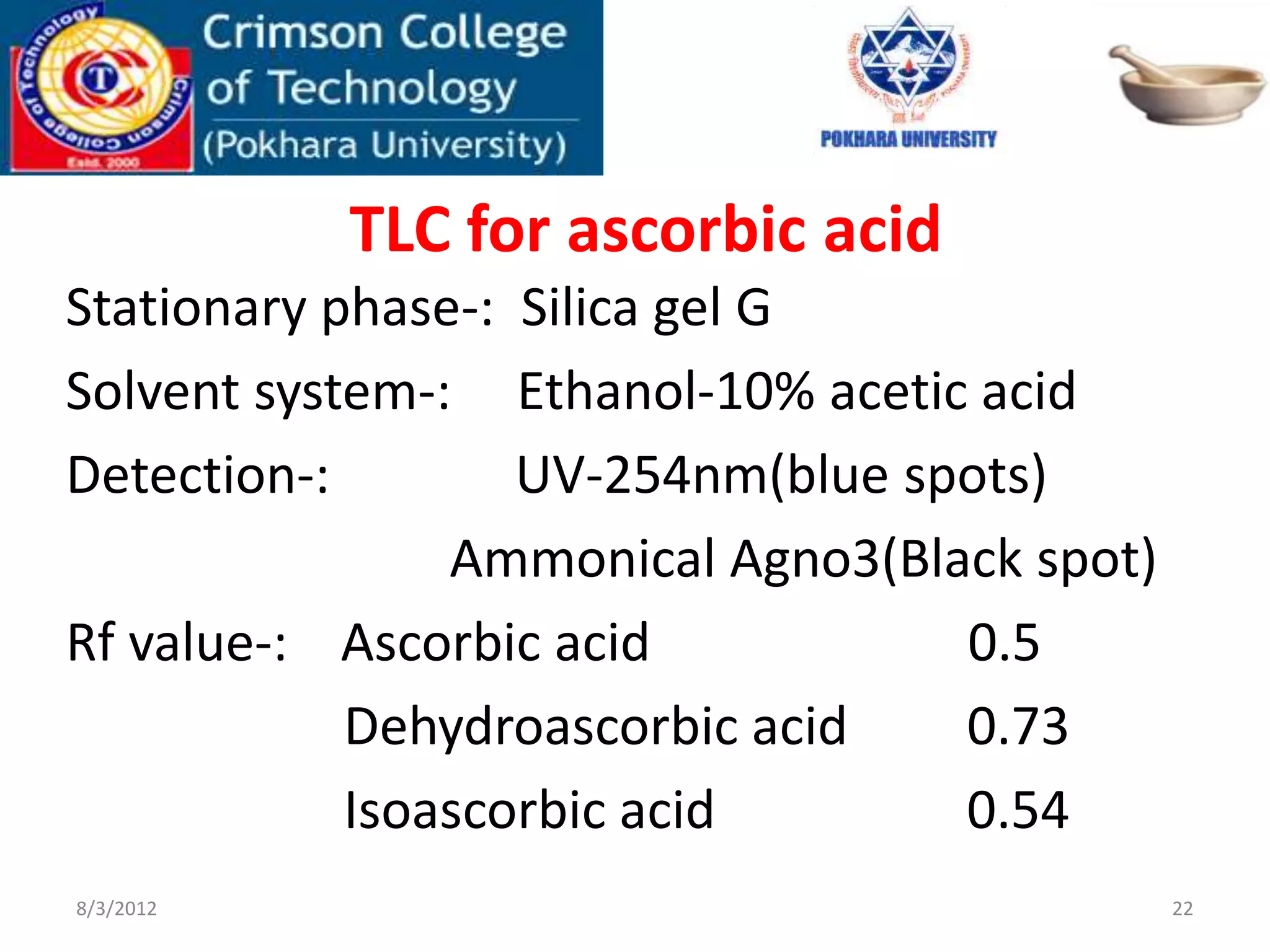
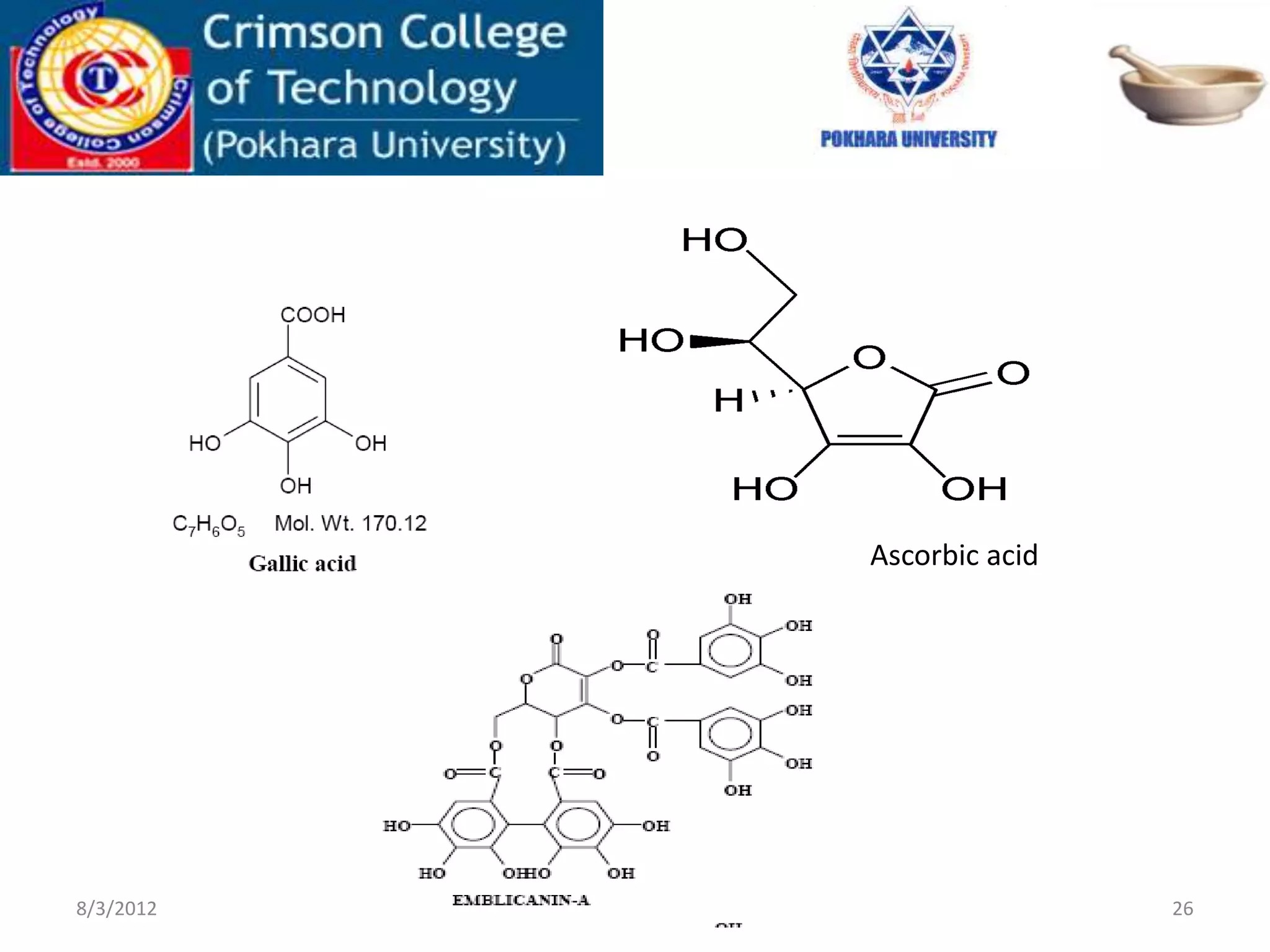
Phyllanthus emblica, commonly known as amla, is a plant native to India and Nepal. The fruit is used in Ayurvedic medicine to treat cough, asthma, digestive issues, and other conditions. It contains high levels of vitamin C and antioxidants. Microscopic analysis of amla fruit shows epicarp, hypodermis, mesocarp tissue with fibrovascular bundles, and seeds containing sclereid cells. The plant is used to treat liver problems, cancer, fever, pain, and memory loss due to its hepatoprotective, antitumor, antipyretic, and antioxidant properties.