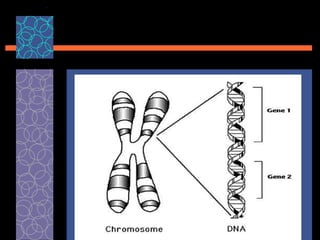
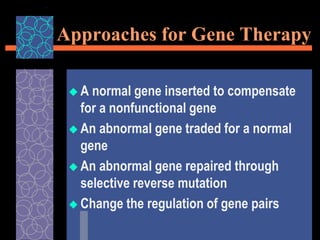
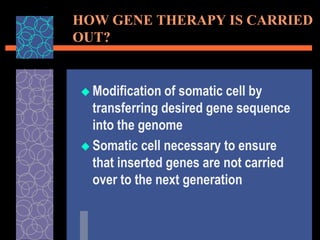
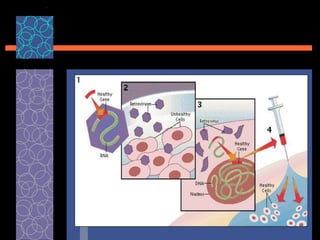
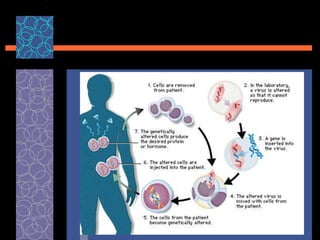
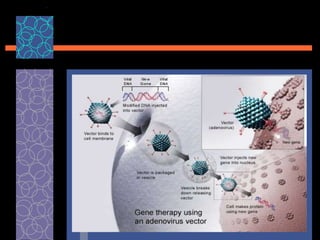
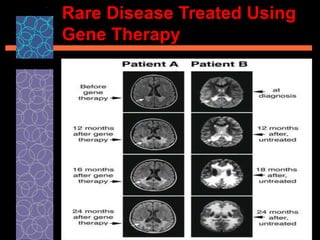
This document provides an overview of gene therapy, including its history, approaches, delivery methods, applications, and challenges. Gene therapy involves introducing a normal gene into cells containing a defective gene in order to correct the underlying genetic disorder. It can be carried out in vivo by using viral vectors to deliver the therapeutic gene directly into patients, or in vitro by manipulating cells outside the body before reintroducing them. Many genetic diseases have been targeted, including immunodeficiencies, cancers, hemoglobinopathies, and rare diseases. While gene therapy holds promise, challenges remain such as short-lived effects, immune responses, and ethical concerns.