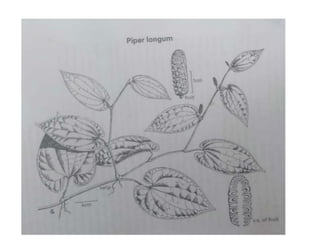
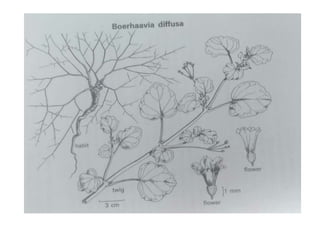
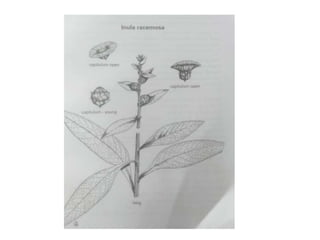
1. The document provides details on four Dravyas - Pippali, Prishniparni, Punarnava, and Pushkaramoola.
2. For each Dravya, it describes their taxonomy, varieties and morphology, chemical constituents, uses mentioned in Ayurvedic texts, self-work examples, and important formulations.
3. The document serves as a reference for BAMS students to learn about these four medicinal plants used in Ayurveda.