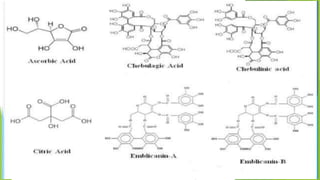
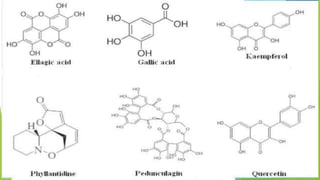
This document summarizes the plant Phyllanthus emblica, commonly known as amla or Indian gooseberry. It provides details on the plant's nomenclature, habitat, cultivation, chemical constituents, traditional medicinal uses, and pharmacological activities. Key points include that amla is native to tropical Asia, grows well in sunny locations, contains antioxidants like vitamin C and tannins, and has traditionally been used in Ayurveda to treat conditions like diarrhea, inflammation, and liver problems. Modern research also supports amla's antioxidant, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective pharmacological activities.