The sounds [w] and [ʍ] in the given words are allophones of the same phoneme. They are in complementary distribution, with [w] occurring after vowels and [ʍ] occurring word-initially. The phonological rule is that the phoneme is realized as [w] in the environment of _V (after a vowel) and as [ʍ] elsewhere, specifically word-initially. As they do not contrast meaningfully in any context, [w] and [ʍ] are considered variants of the same underlying phoneme.




![Distinctive and Non-distinctive Sounds
Distinctive (contrastive) Sounds: make a difference in
meaning; e.g. /p/ & /b/ in pin, bin.
Non-distinctive (non-contrastive) Sounds:
Do NOT make a difference in meaning; e.g. [ph] in pin & spin.
Example:
/t/ in : top [thɒp]
stop [stɒp]
little [liɾ l]
kitten [kiʔn] (n is syllabic here)
hunter [hʌ nr]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phonologychapter8-151209130046-lva1-app6891/85/Phonology-chapter-8-5-320.jpg)
![Phoneme and Allophone
A phoneme: a class of speech sounds that are identified
by a native speaker as the same sound; e.g. /t/;
unpredictable (given “in” in pin like the example above
we CANNOT predict which sound can come before it like
bin, tin, din, kin, gin, fin, thin, sin, shin, chin)
A phoneme: a class of speech sounds that are identified
by a native speaker as the same sound; e.g. /t/;
phonemes are unpredictable
A phoneme is an abstract representation & cannot be
pronounced (it is not a speech sound)
A phone: the actual phonetic segment produced by a
speaker & has been classified as belonging to some
phoneme; e.g. [th]; predictable
An allophone: a variant of a phoneme, e.g. /t/ = [ʔ], [ɾ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phonologychapter8-151209130046-lva1-app6891/85/Phonology-chapter-8-6-320.jpg)
![Phoneme and Allophone
The phonological system of a language has two levels:
1- the more concrete level which involves the physical
reality of phonetic segments, the allophones represented
by square brackets [ ] (greater number).
2- The abstract (underlying) level which involves phonemes
represented by / / slanted brackets (small inventory).
/p/ has 3 allophones ([p], [ph], [p̚ ])
Similar to natural sciences (H2O is realized as ice,
water, & water vapor); different realizations/forms of the
same thing.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phonologychapter8-151209130046-lva1-app6891/85/Phonology-chapter-8-7-320.jpg)


![Kinds of Phonemic Distribution
Overlapping Distribution: when the sets of phonetic environments
in which two sounds occur are partially or completely identical.
bait [bet] date [det]
lobe [lob] load [lod]
knobs [nabz] nods [nadz]
Two Kinds:
1- Contrastive distribution (give different meanings= belong to
different phonemes = appear in minimal pairs)
2- Free Variation (never cause a contrast in meaning = allophones
of the same phoneme = no minimal pairs)
mat mat maʔ can be released, unreleased or a glottal stop
either iðər aiðər – neither niðər, naiðər –
tomato təmætə, tometə - data dæta , deta](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phonologychapter8-151209130046-lva1-app6891/85/Phonology-chapter-8-10-320.jpg)
![Kinds of Phonemic Distribution
Complementary Distribution (mutually exclusive, non-
overlapping): when sounds DON’T occur in the same
phonetic environment
English
spat [spæt] pat [phæt]
spool [spul] pool [phul]
speak [spik] peek [phik]
No minimal pairs for such sounds
Phones in Complementary Distribution are allophones of
a single phoneme
The appearance of one allophone or the other is
PREDICTABLE.
In Thai and Korean [p] and [ph ] are separate phonemes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phonologychapter8-151209130046-lva1-app6891/85/Phonology-chapter-8-11-320.jpg)


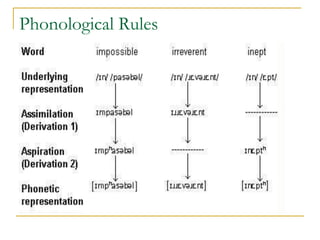
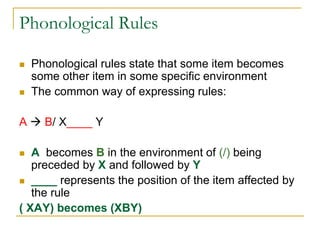
![Phonological Rules
Example from English:
˷ ˷
[fæn]: /æ/ /æ/ /____/n/
A vowel is nasalized whenever it immediately
precedes a nasal stop
[+ syllabic] [+nasal]/ __ [+nasal]
A +syllabic sound (= a vowel) becomes + nasal (= nasalized)
when it comes before a + nasal sound (= m, n, ŋ)
The above captures a generalization about all
vowels not only [æ] and all nasals not only [n].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phonologychapter8-151209130046-lva1-app6891/85/Phonology-chapter-8-16-320.jpg)

![Choosing the Underlying Form
How do we decide on the representation at the
phonemic level?
We can use an arbitrary number like 3 or Fred = harder to
read the rules
Using /p/ tells us that the allophones associated with /p/ all
share some features like [voice, continuant, anterior,
coronal].
/p/ is the simplest of the 3 phonetic forms with nothing
added to its ‘p-ness’ like being aspirated or being
unreleased: /pʰ/ and /p̚/
Use the form with the widest distribution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phonologychapter8-151209130046-lva1-app6891/85/Phonology-chapter-8-18-320.jpg)
![7.13 p. 104
Form with the widest distribution:
Take the case of the devoicing of liquids and
glides following voiceless consonants
kwit, flei, trap, pjur, swaip (all are devoiced)
jɛs, wiʃ, bɔƗ, sk^ri, brik glas, fiƗθ, fiƗm
If the [–voice] allophone were chosen to
represent then our rule(s) would specify
many environments thus the rule would be:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phonologychapter8-151209130046-lva1-app6891/85/Phonology-chapter-8-19-320.jpg)


![Phonetic Naturalness
& Phonological Analysis
Natural means “to be expected”, “frequently found
across languages”
Does NOT mean “English-like”
No words in English begin with onset clusters like
[ps], [pn], [pt].
These clusters appear word initially in other
languages like German, Greek, & French.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phonologychapter8-151209130046-lva1-app6891/85/Phonology-chapter-8-22-320.jpg)
![Phonetic Naturalness
& Phonological Analysis (cont)
What applies to one language is not necessarily true
of other languages.
English /p/ has unaspirated p and aspirated p as
allophones
Thai /p/ and /ph/ are two phonemes:
paa ‘forest’
ph aa ‘to split’
English has /p/ and /b/
Arabic has /b/ with two allophones [b] and [p]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phonologychapter8-151209130046-lva1-app6891/85/Phonology-chapter-8-23-320.jpg)
![Phonetic Similarity
To choose the phonemic form, we have to consider
phonetic similarity.
Example: [h] occurs syllable-initially [hæ m]
[ŋ ] occurs only syllable-finally [brɪ ŋ]
Not allophones of the same phoneme
They lack phonetic similarity
[h]: non-nasal, obstruent, continuant
[ŋ] nasal, sonorant, non-continuant](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phonologychapter8-151209130046-lva1-app6891/85/Phonology-chapter-8-24-320.jpg)
![Pattern Congruity
Phonologists consider the consequences of choosing
one phoneme over the other
Pattern Congruity: the systematic organization of the set
of phonemes and their distribution.
Choosing an allophone depends on the overall patterns
found in the phonological system (pattern congruity)
For example:
In English: obstruent clusters have uniform voicing
Either all members of the cluster are [+ voice], or [- voice].
‘Mixed voice clusters’ DON’T occur phonemically](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phonologychapter8-151209130046-lva1-app6891/85/Phonology-chapter-8-25-320.jpg)

![Process Naturalness
In choosing the underlying form, the linking processes
should be considered
pass [ph æs] pass you [ph æʃ ju]
this [ðɪs] this year [ðɪʃjiə ]
[s] appears in more environments so it makes sense to
choose it as the underlying form instead of vice versa
Assimilation:
[s] alveolar [+coronal, +anterior] becomes
[ʃ] palato-alveolar [+coronal, - anterior] when followed by
[j] palatal [+ coronal, - anterior]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phonologychapter8-151209130046-lva1-app6891/85/Phonology-chapter-8-27-320.jpg)


![Chapter 7 Exercises
Exercise 1 page 110/130
Consider the distribution of [w] and [ʍ] in the following data.
Are the phones allophones of the same or different phonemes?
Why? If they are allophones of a single phoneme, give a rule to
account for the distribution.
a. ʍa’e why h. we way
b. ʍɪʧ which i. weð^r weather
c. ʍ^ɪt white j. wɔnt want
d. ʍeƗz whales k.wɪʧ witch
e. ʍɪp whip l. ʍ^ɪp wipe
f. əʍ^ɪl awhile m. weƗz Wales
g. ʍɛð^r whether n. əʍɔʃ awash](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phonologychapter8-151209130046-lva1-app6891/85/Phonology-chapter-8-30-320.jpg)


