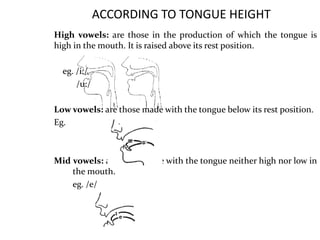
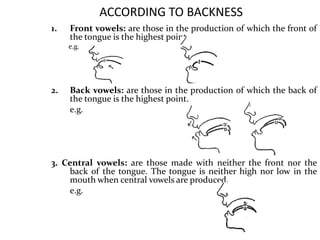
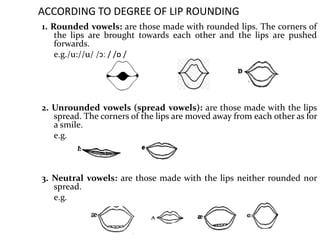
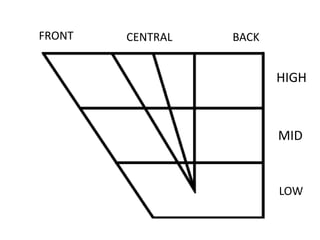
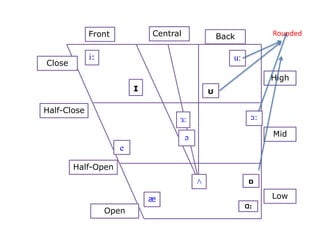
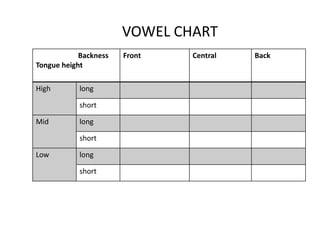
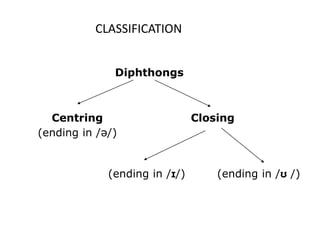
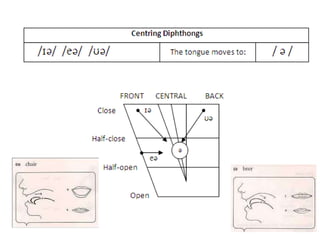
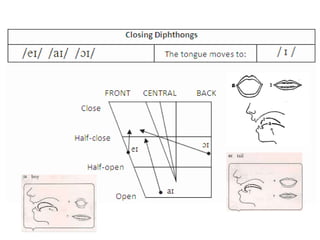
This document provides information about English vowels, including their classification based on tongue height, backness, and lip rounding. It defines vowels and diphthongs, lists the main English monophthongs with examples, and presents the vowel chart showing the positions of vowels in the mouth. Diphthongs are defined as glides between two vowels and are classified as centering or closing depending on whether they end in a schwa or another vowel. Methods for describing and identifying vowels are also outlined.