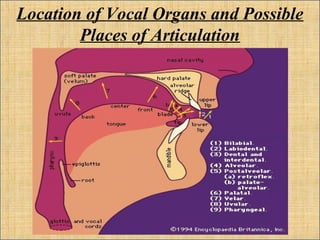
Phonetics is a branch of linguistics focused on the production, nature, and reception of speech sounds, including articulatory, acoustic, and auditory subfields. In contrast, phonology studies the systems and patterns of speech sounds within a specific language. The document outlines the differences between phonetics and phonology, emphasizing their distinct focuses on speech sounds and their characteristics.