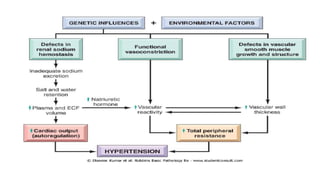
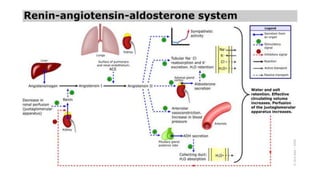
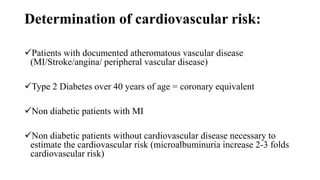
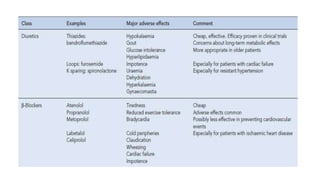
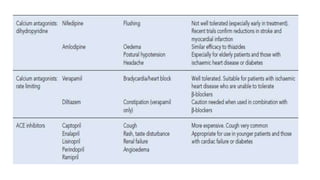
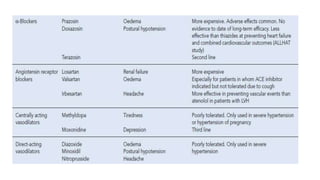
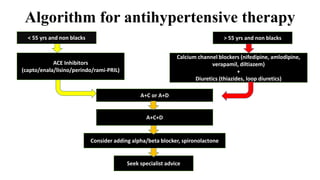
This document discusses hypertension (high blood pressure) including its definition, causes, clinical presentation, assessment, and management. It notes that hypertension is defined as blood pressure above 140/90 mmHg and risks of cardiovascular disease double for every 20/10 mmHg rise. Common complications include stroke, myocardial infarction, heart failure, and renal failure. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications and medication, starting with ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, or thiazides. The goals are to lower blood pressure and reduce cardiovascular risk based on individual patient factors.