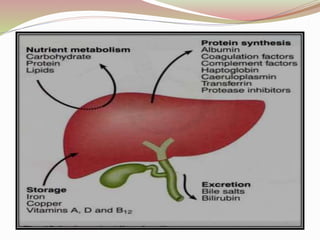
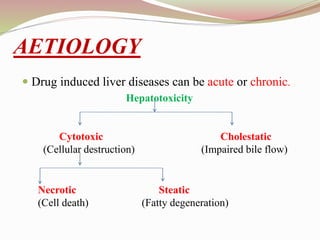
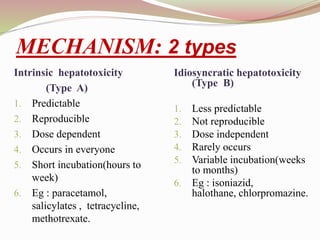
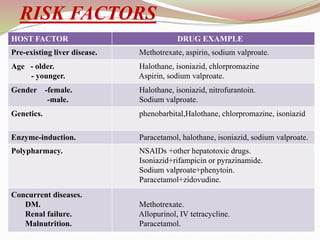
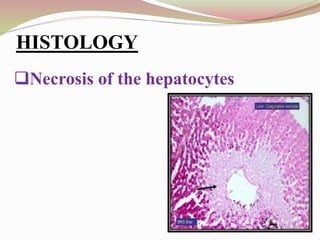
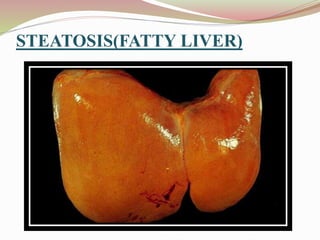
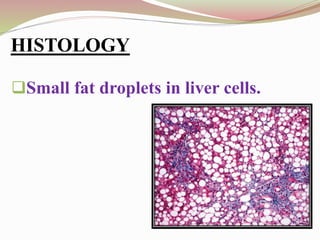
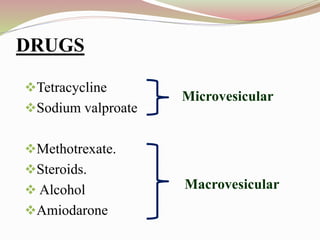
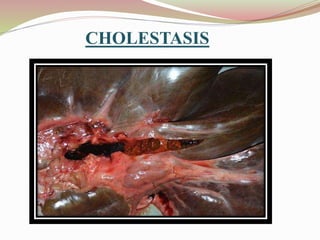
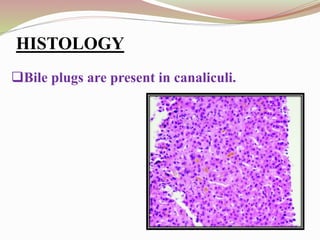
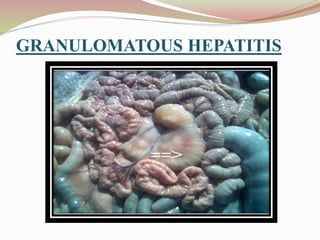
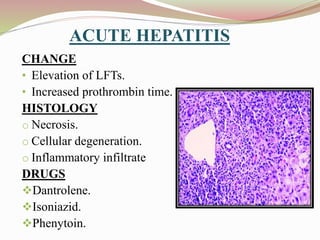
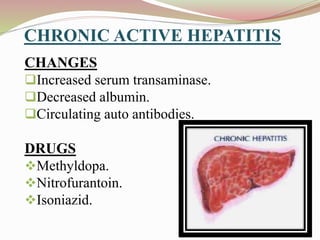
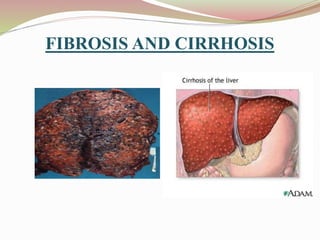
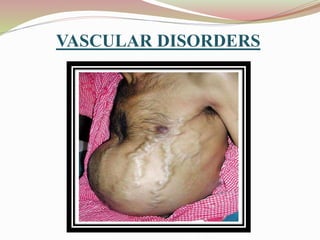
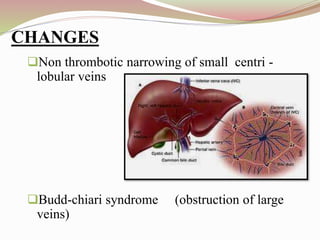
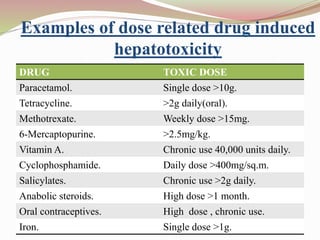
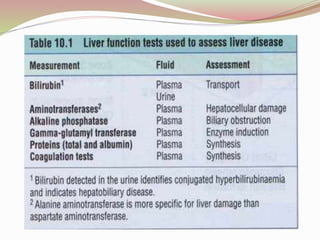
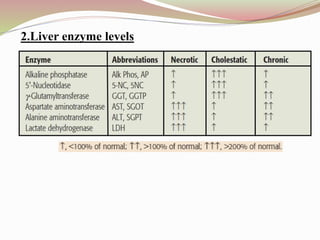
This document provides an overview of drug-induced liver disease (DILD). It defines DILD and discusses its epidemiology and risk factors. Two main mechanisms of hepatotoxicity are described - intrinsic and idiosyncratic. Various types of DILD are outlined including hepatocellular necrosis, steatosis, cholestasis, granulomatous hepatitis, and fibrosis/cirrhosis. Clinical manifestations, investigations, and treatment approaches are summarized. Assessment involves a patient history, liver enzyme levels, biopsy, and nutritional status evaluation. Treatment focuses on diagnosis, drug withdrawal, supportive care, and use of antidotes/corticosteroids if needed.