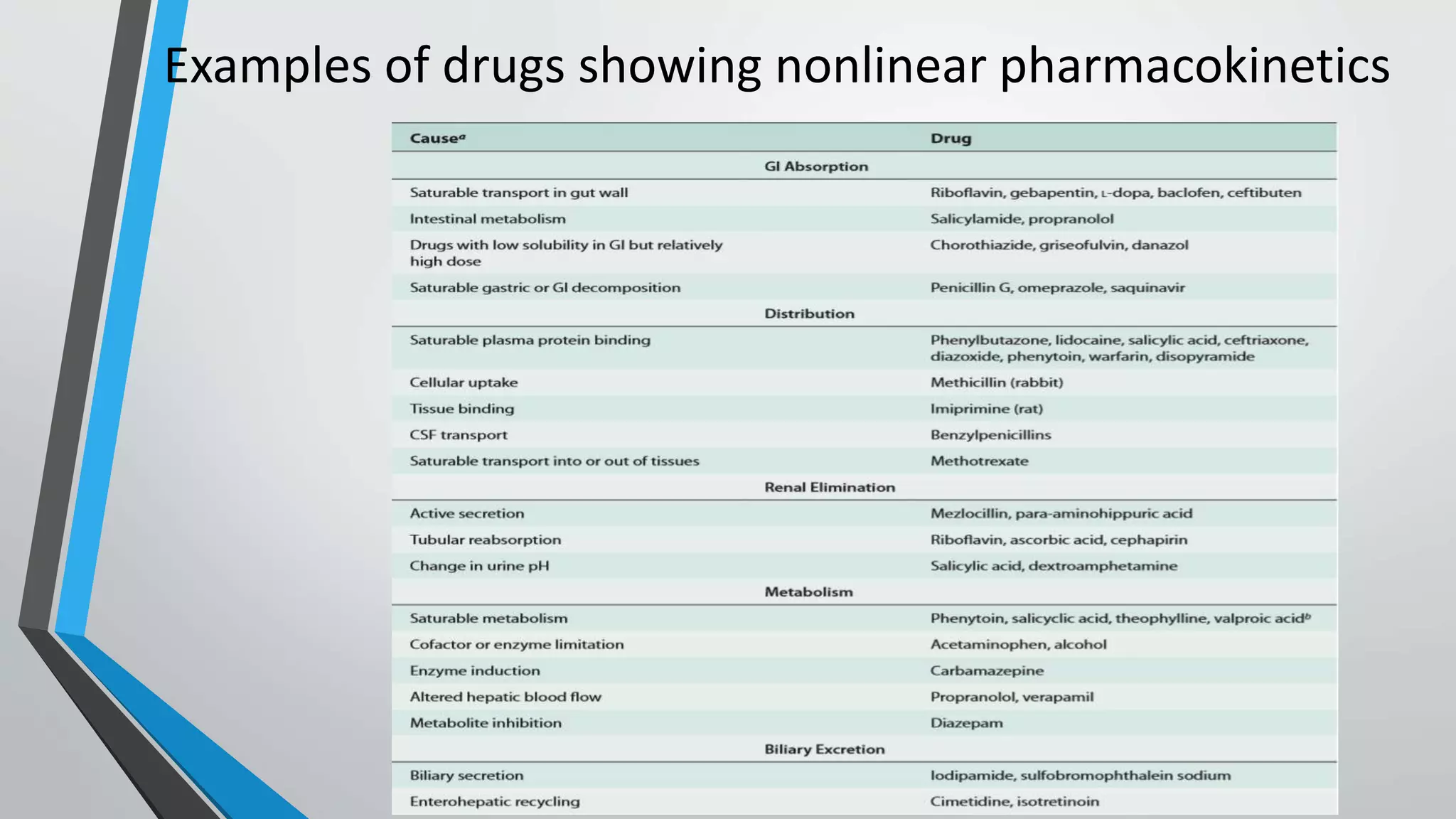
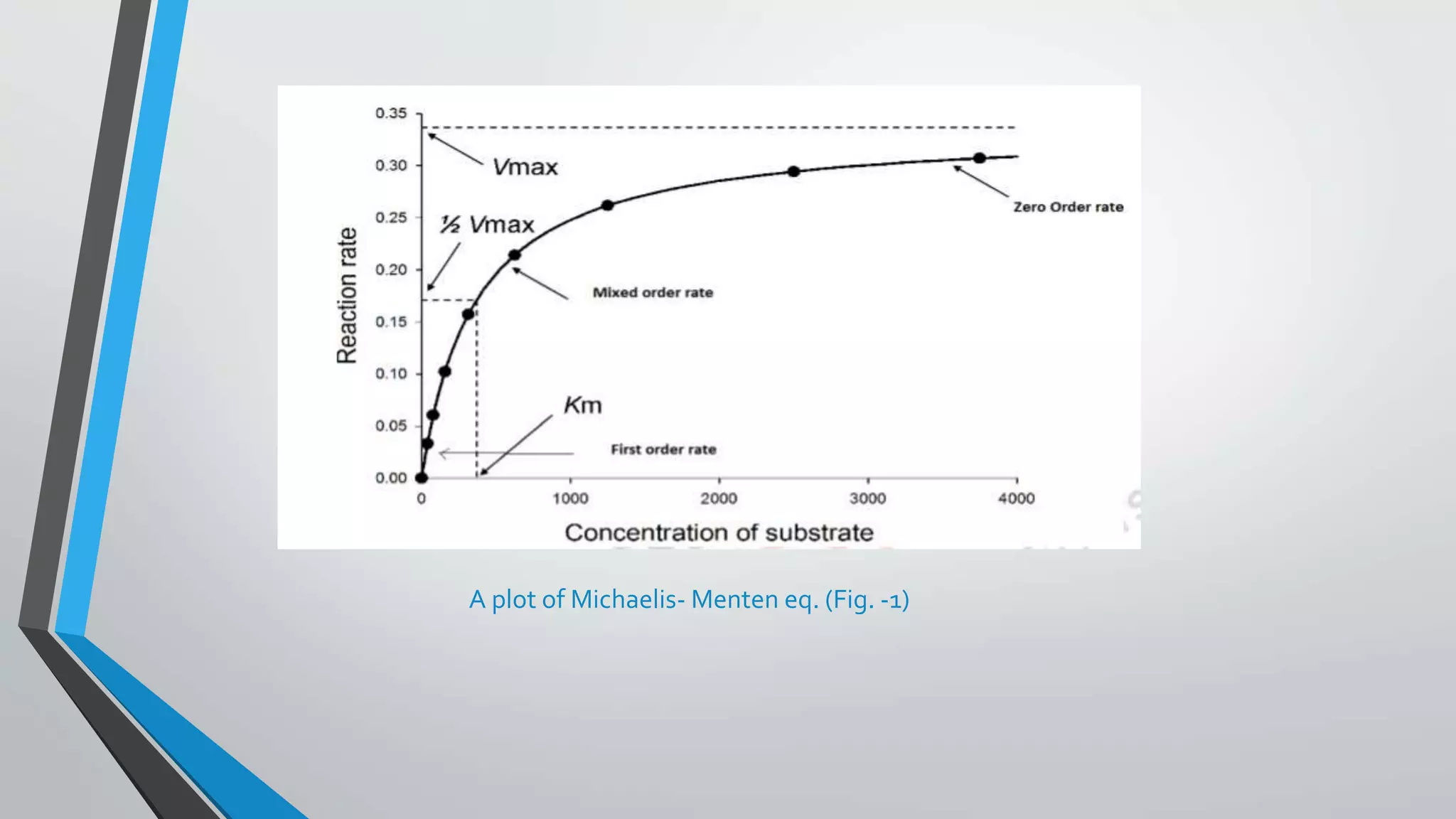
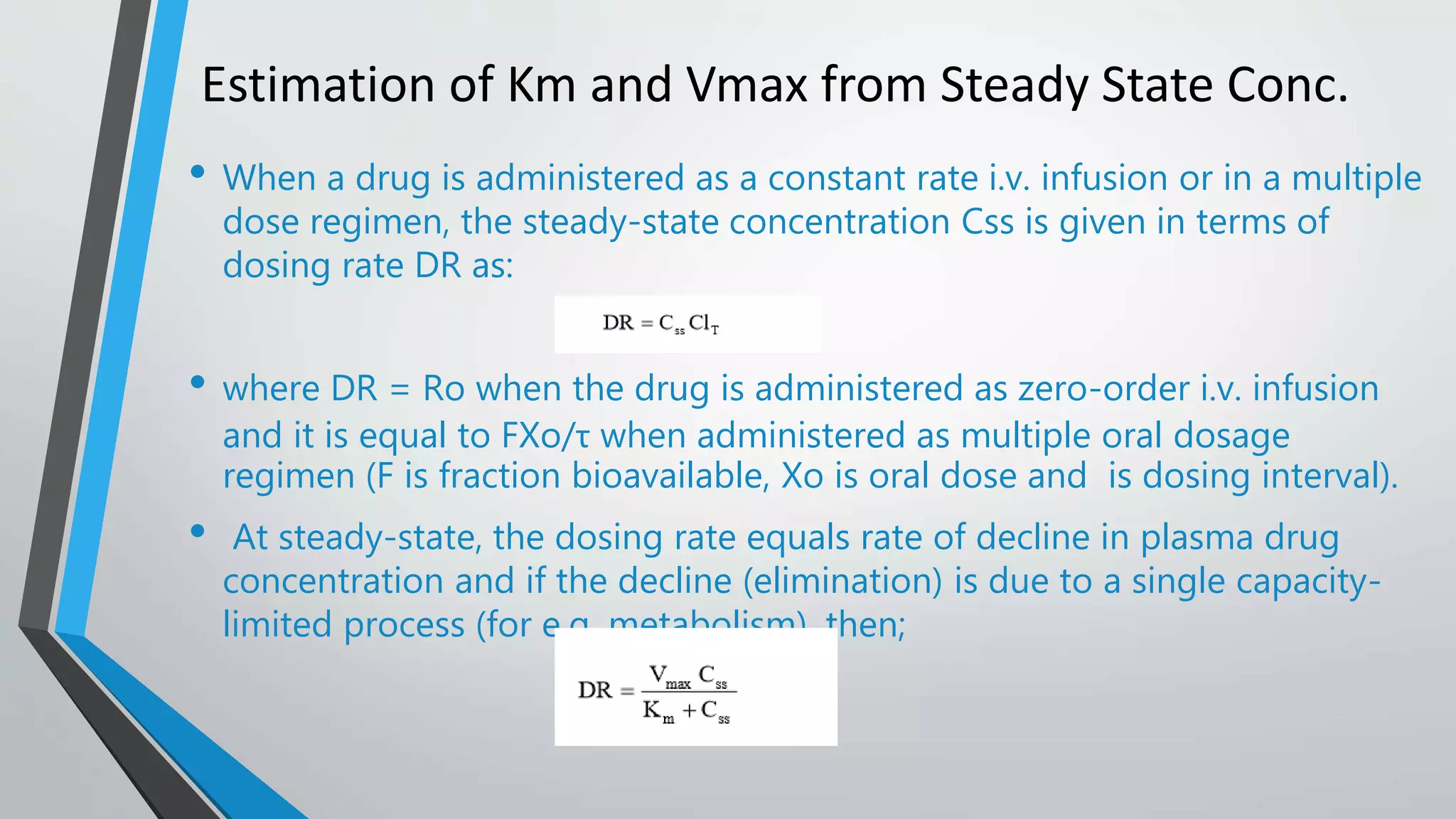
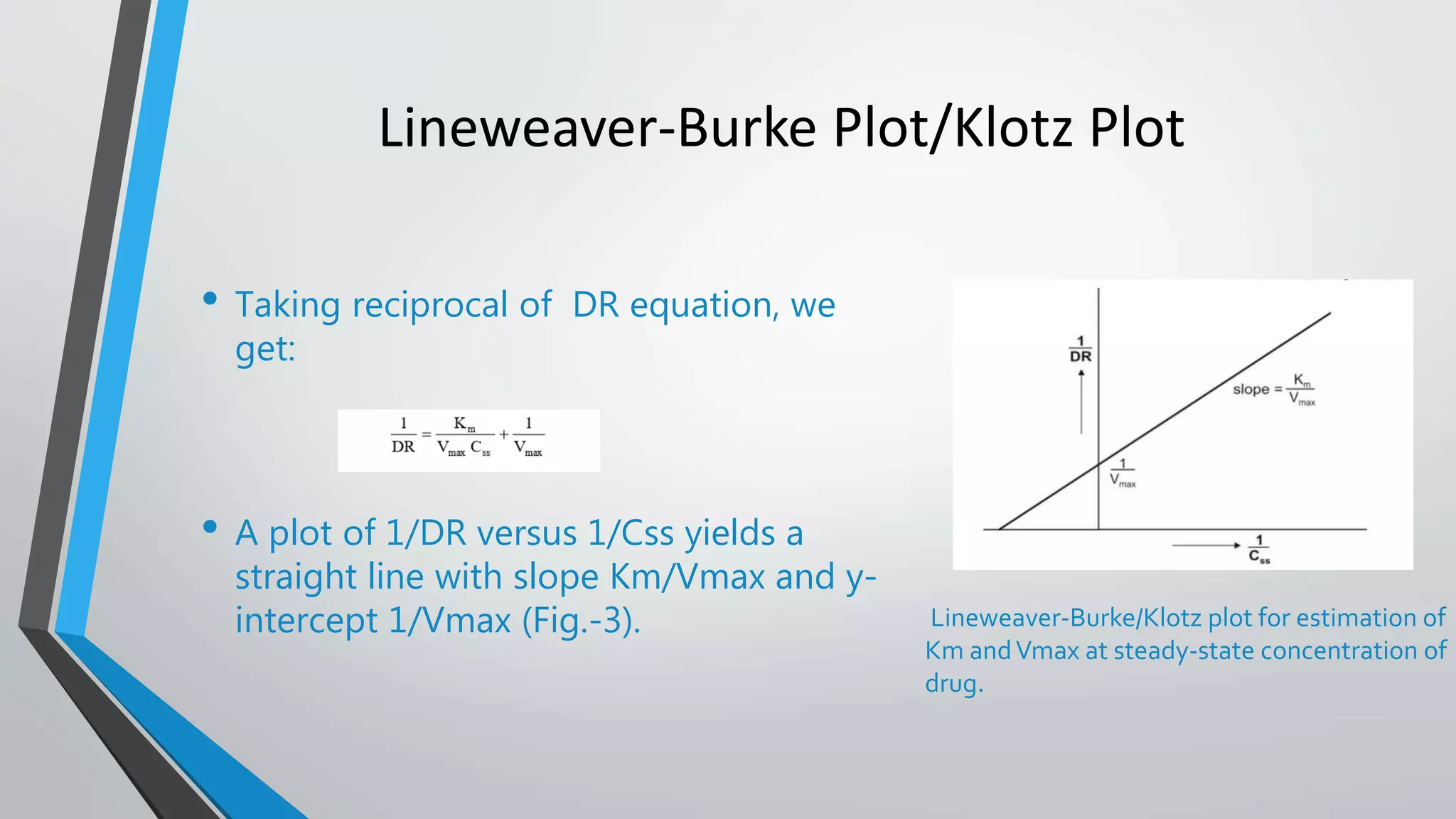
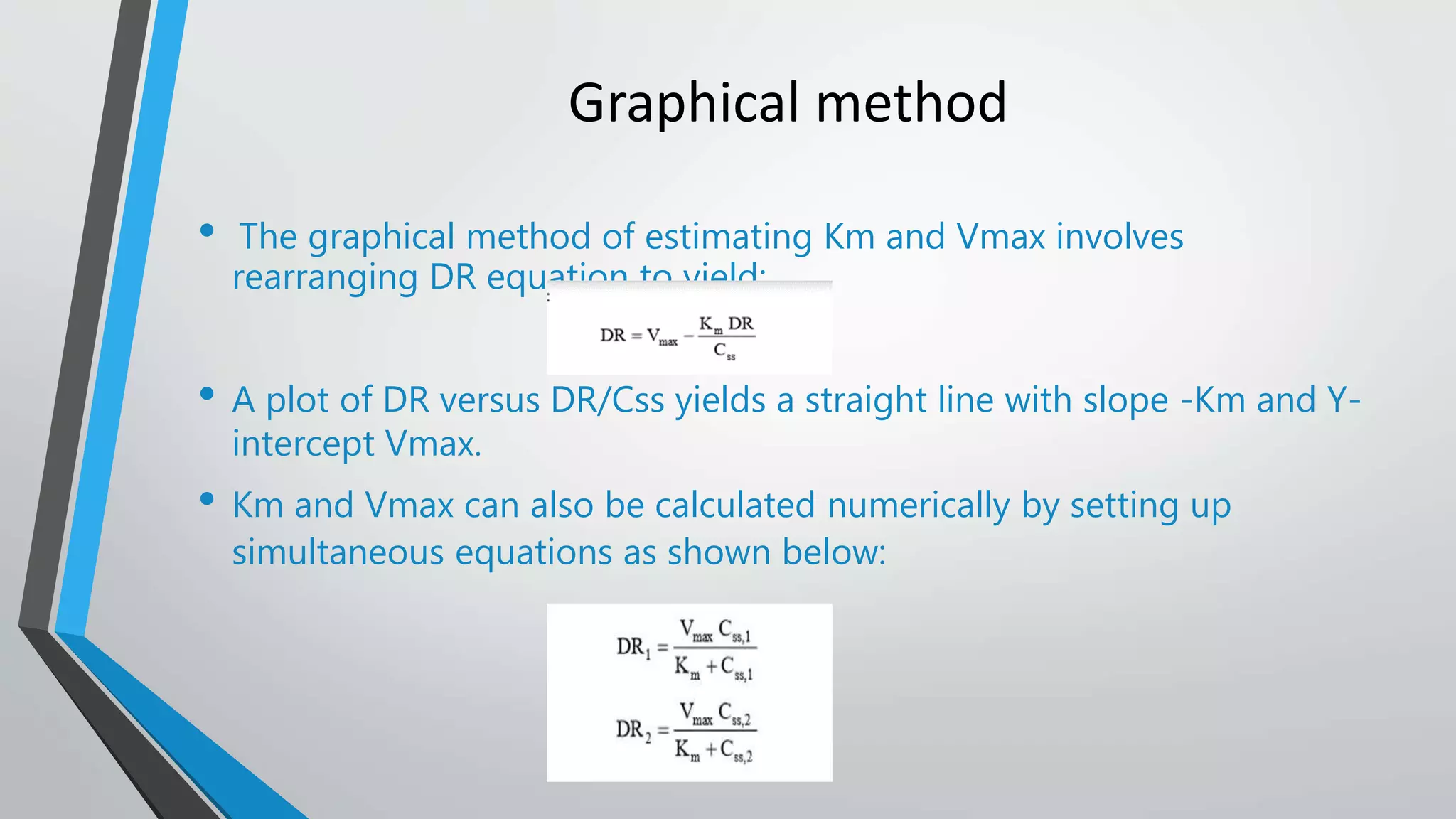
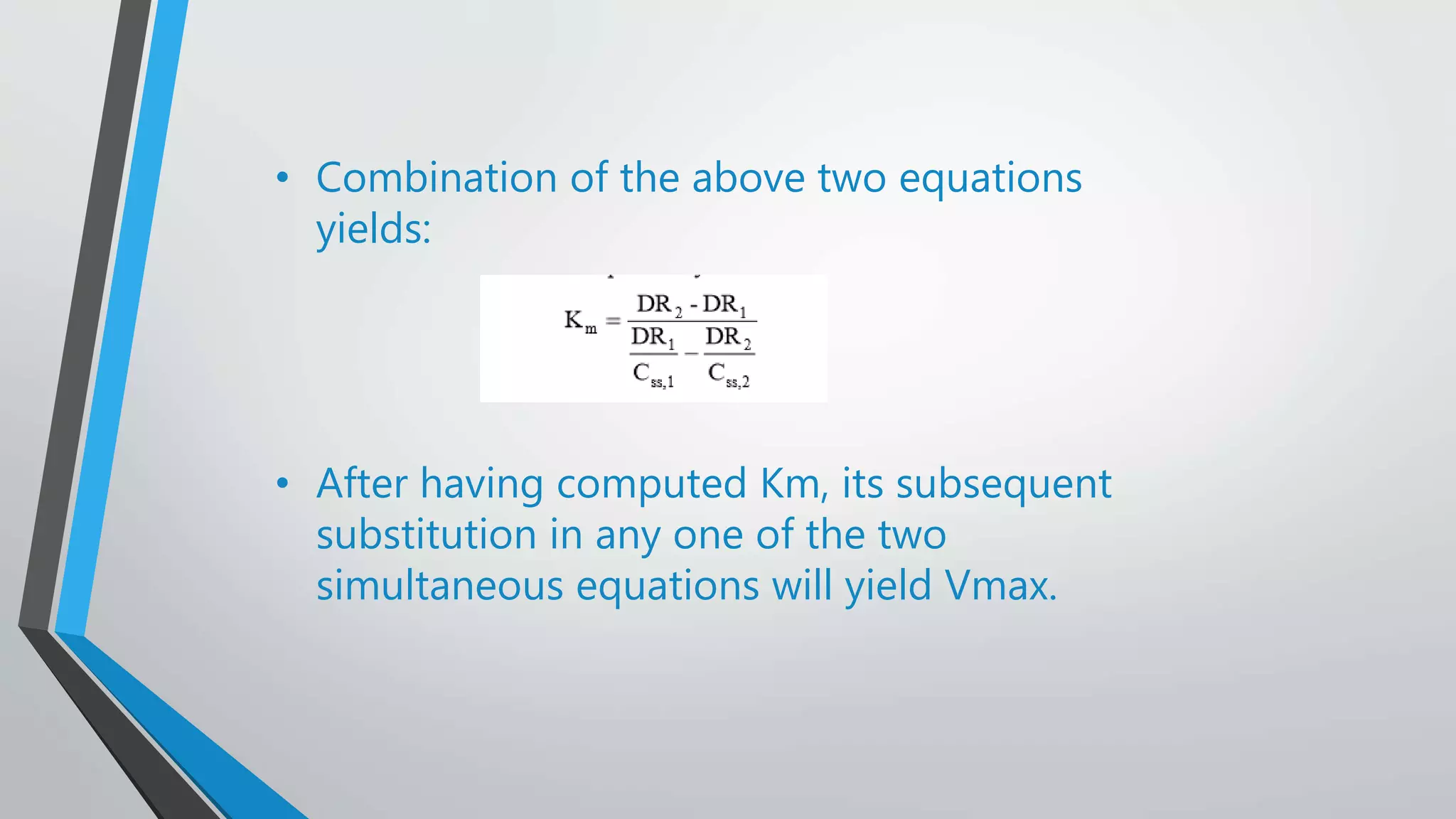
The document discusses non-linear pharmacokinetics, highlighting how drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion can be affected by dose-dependent processes. It explores the Michaelis-Menten equation and examples of drugs that exhibit non-linear kinetics, such as phenytoin, emphasizing the significance of saturation in metabolic processes. Additionally, it outlines methods for detecting non-linearity in pharmacokinetics and factors contributing to it, such as enzyme saturation and binding site limitations.