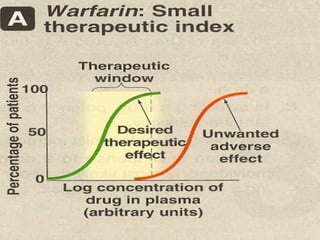
This document discusses pharmacodynamics concepts including graded dose response curves, potency, efficacy, therapeutic index, and types of antagonism. Graded dose response curves plot the magnitude of drug responses against increasing doses to determine efficacy, potency, and therapeutic index. Potency refers to the amount of drug needed to produce an effect, while efficacy refers to the magnitude of response. Therapeutic index is the ratio of lethal dose 50 (LD50) to effective dose 50 (ED50), and indicates a drug's safety margin. Antagonism can be chemical, physiological, pharmacological (competitive or noncompetitive), or biochemical in nature.