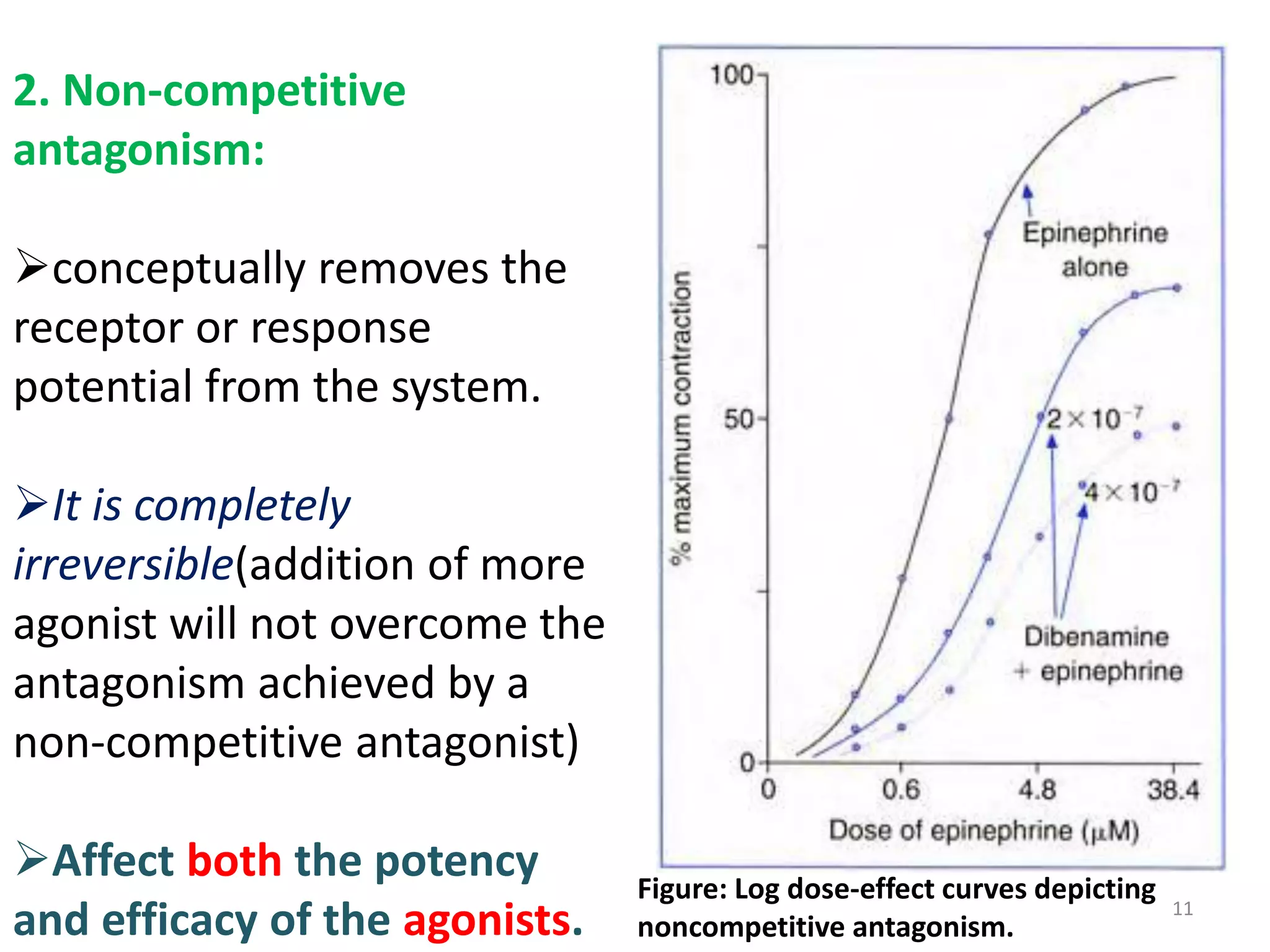
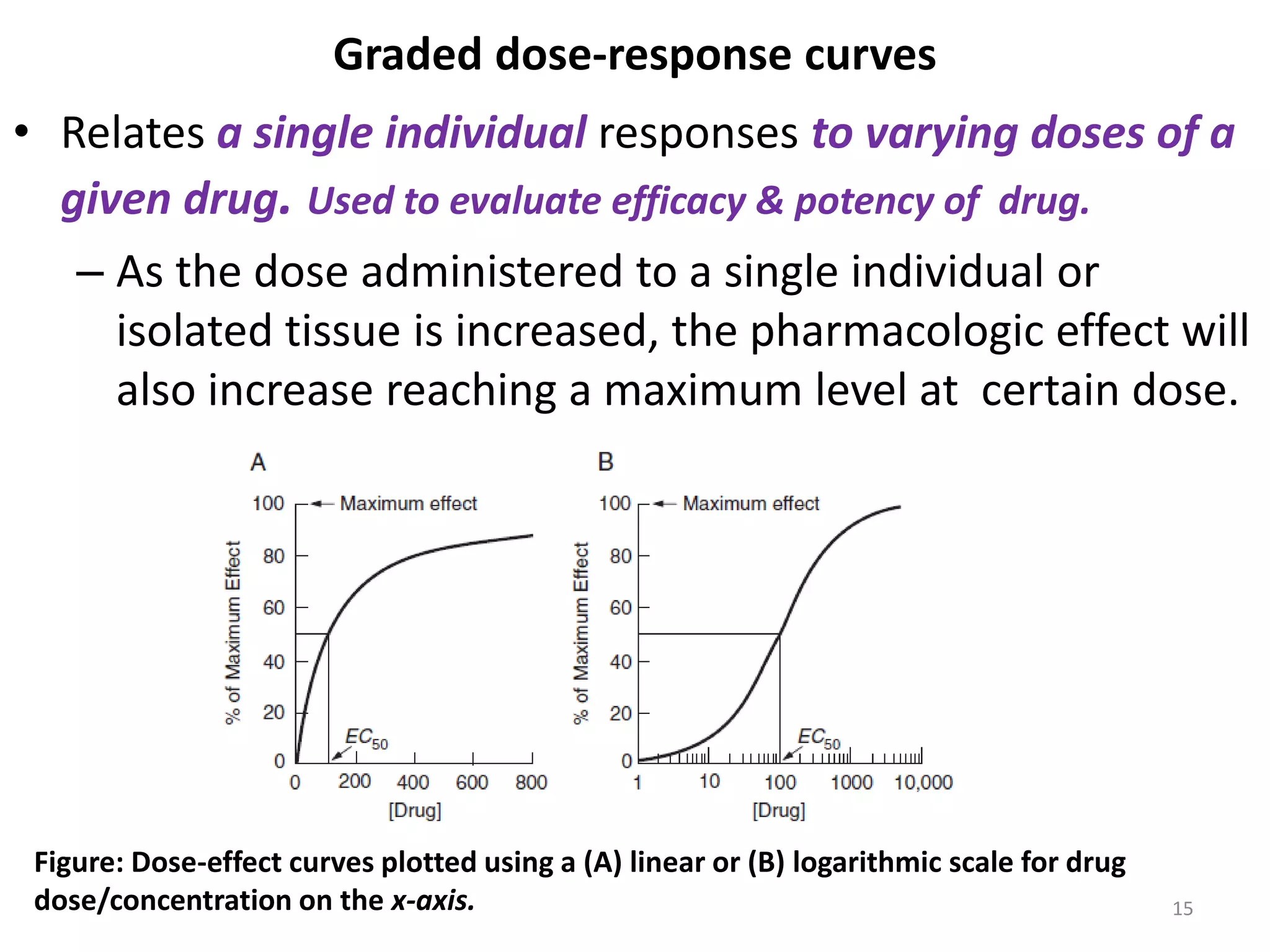
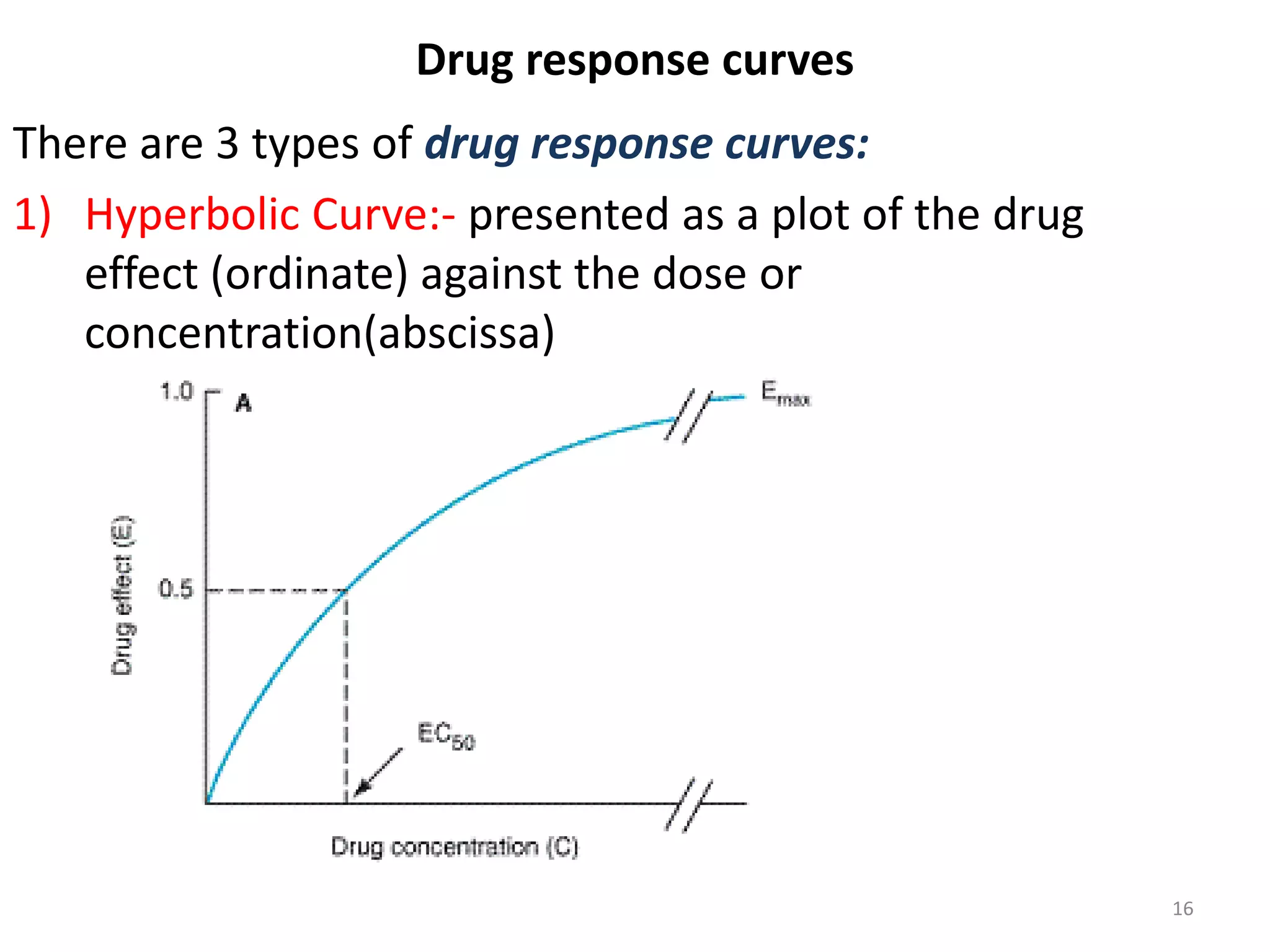
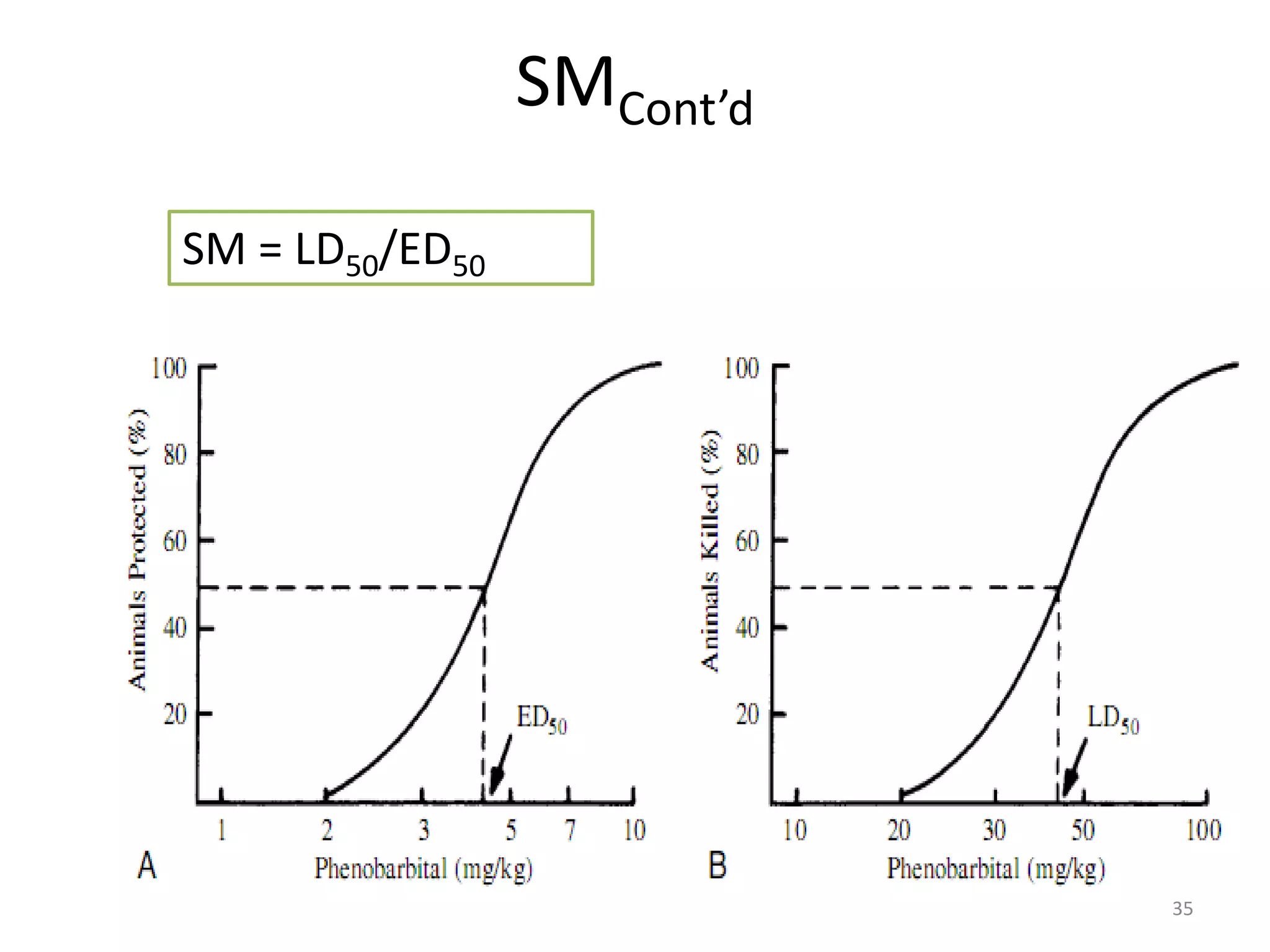
Pharmacodynamics deals with the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs and their mechanisms of action. Drugs act through receptor-mediated or non-receptor mediated pathways. Most drug receptors are proteins that determine drug action selectivity and response. Drug-receptor binding results in a response. Efficacy refers to the maximal response a drug can produce while potency is the dose required to produce a particular effect. Affinity is the tendency of a drug to bind receptors, while occupancy is the fraction of receptors bound. Agonists activate receptors to produce responses while antagonists inhibit agonist binding without efficacy. Dose-response relationships relate effect to dose and can be quantal or graded. Tolerance develops with repeated dosing due