This document discusses temperature transducers, including:
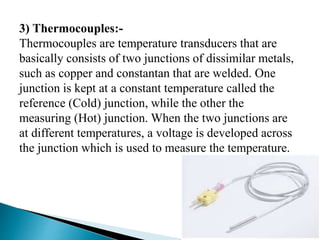
1) It defines a temperature transducer as a device that converts thermal quantity into other physical quantities like pressure or electrical signals. Thermocouples produce voltage based on temperature difference.
2) It describes contact and non-contact temperature sensors, with contact sensors directly measuring temperature via conduction and non-contact via convection.
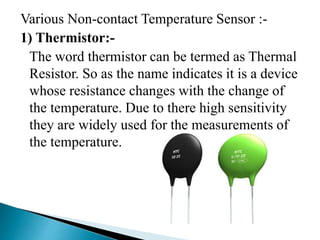
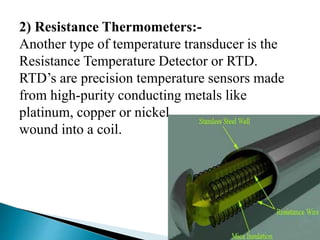
3) It provides examples of non-contact sensors like thermistors, resistance thermometers, thermocouples, and integrated circuit temperature transducers.