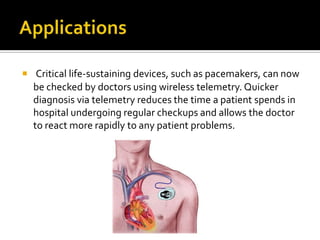
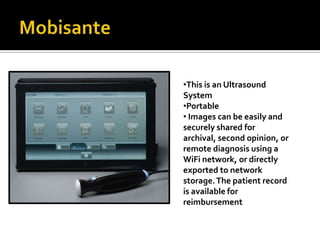
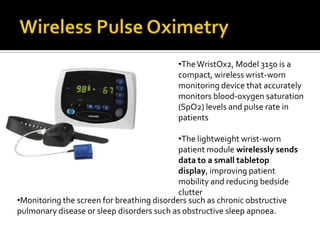
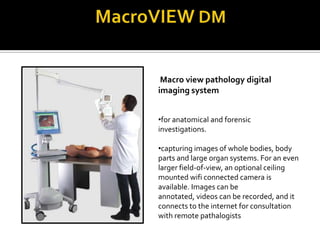
Wireless medical telemetry uses radio frequencies to monitor patient physiological parameters from a transmitter worn by the patient to a central monitoring station, allowing freedom of movement. It has advantages like faster diagnosis and reduced hospital visits. However, signal interference from other wireless devices can be an issue. Standards like WMTS and protocols like Bluetooth address this by establishing exclusive frequency bands for medical use and incorporating security features. New wireless technologies continue to enhance patient mobility and provider access to information.