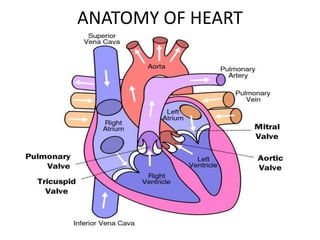
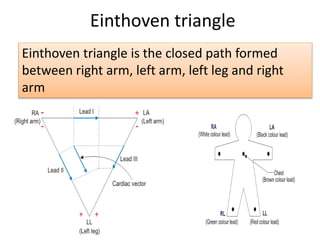
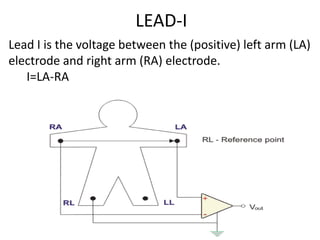
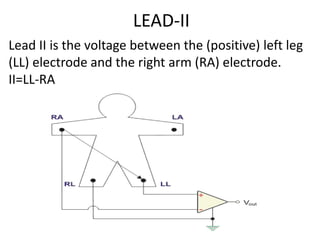
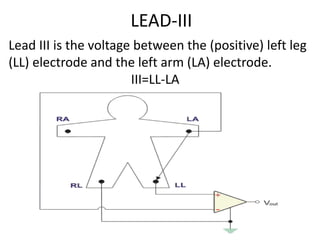
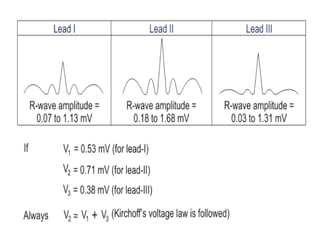
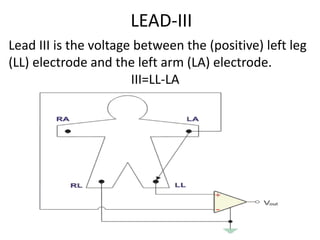
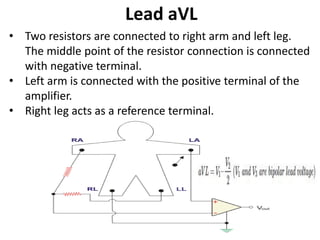
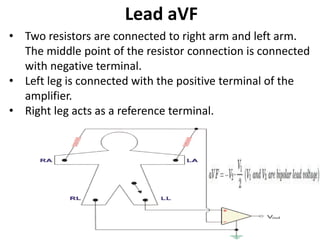
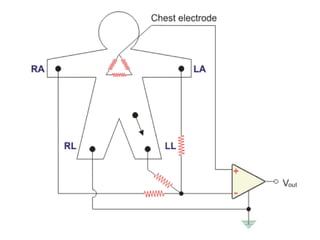
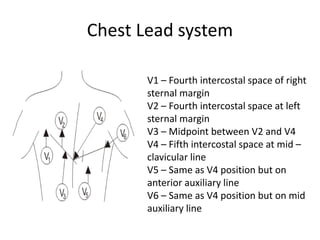
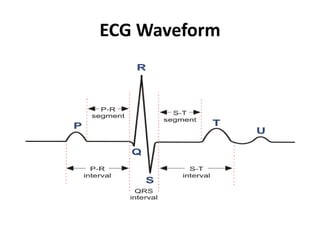
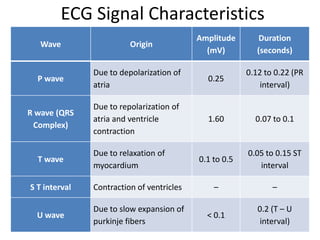
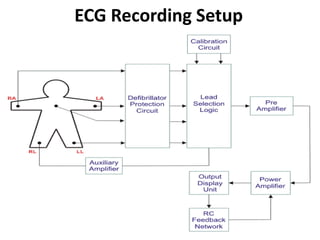
This document provides an overview of electrocardiography (ECG). It defines ECG as the study of the electrical activity of the heart muscles using an electrocardiograph. It describes the anatomy of the heart including its four chambers, four valves, three layers, blood vessels, and dual circulation systems. It also explains the different ECG lead systems including standard bipolar limb leads, augmented unipolar limb leads, and chest leads. Finally, it outlines the basic components of an ECG recording setup including defibrillator protection, lead selection logic, calibration, pre-amplification, power amplification, feedback, and output display.