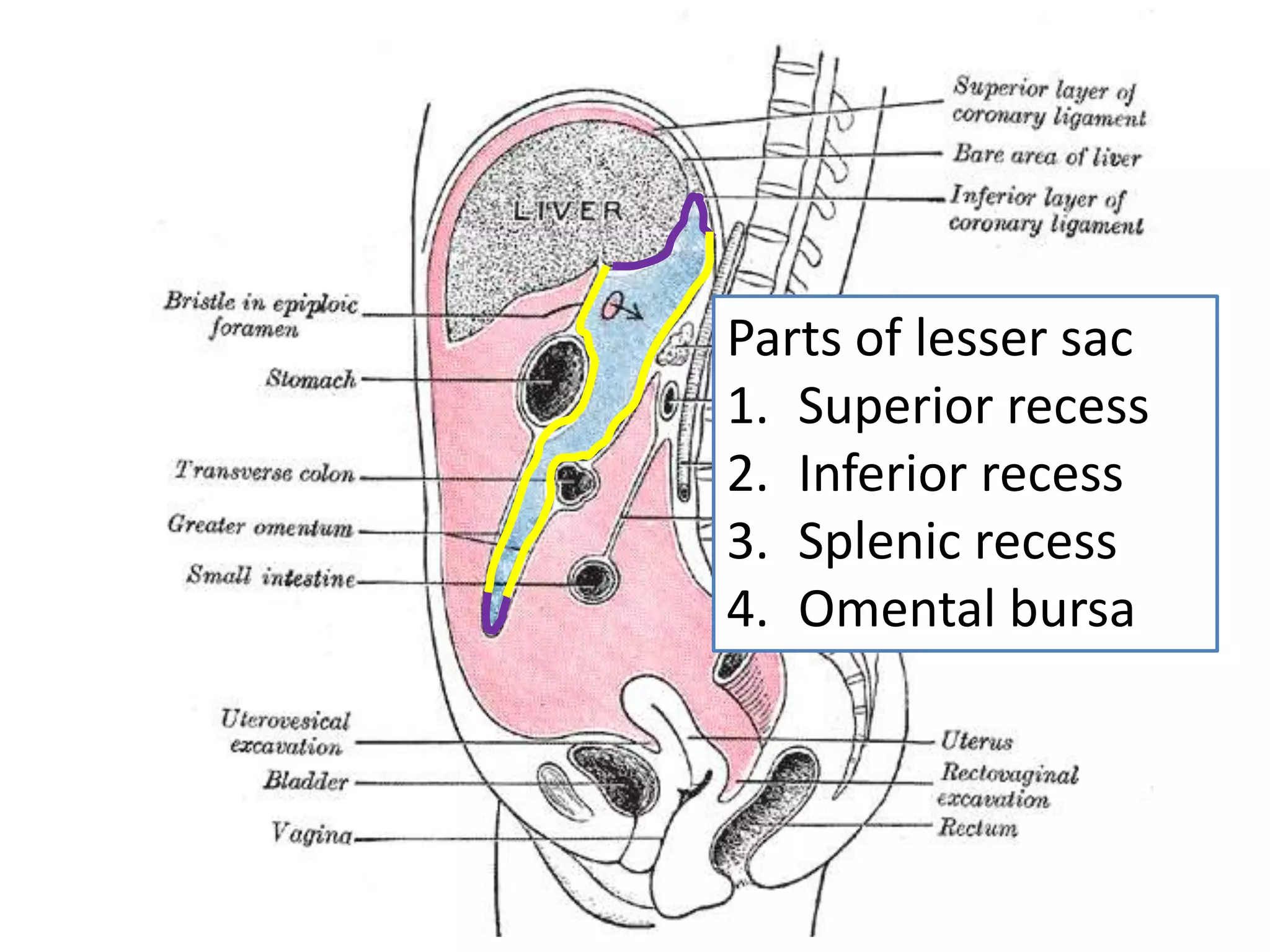
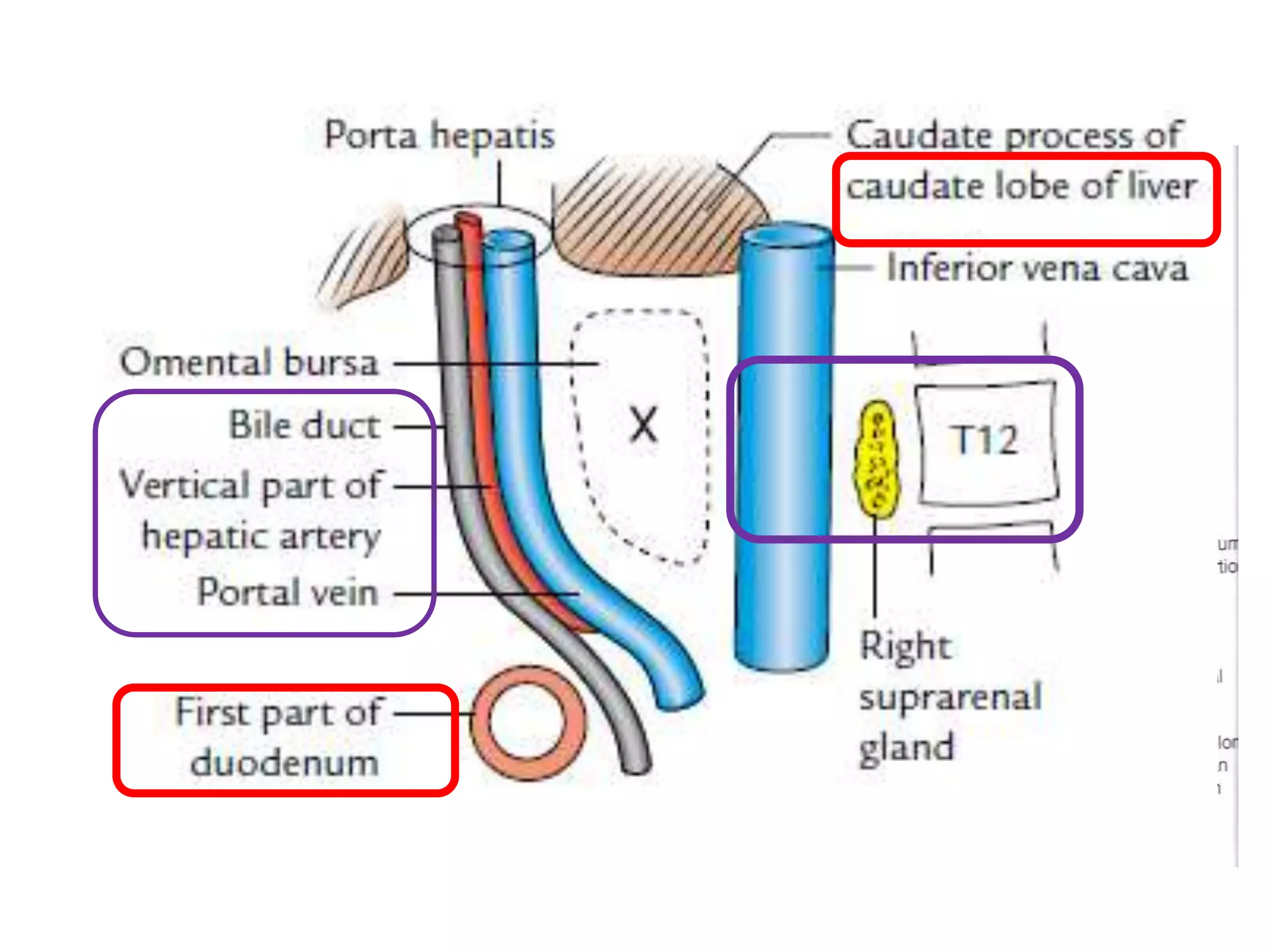
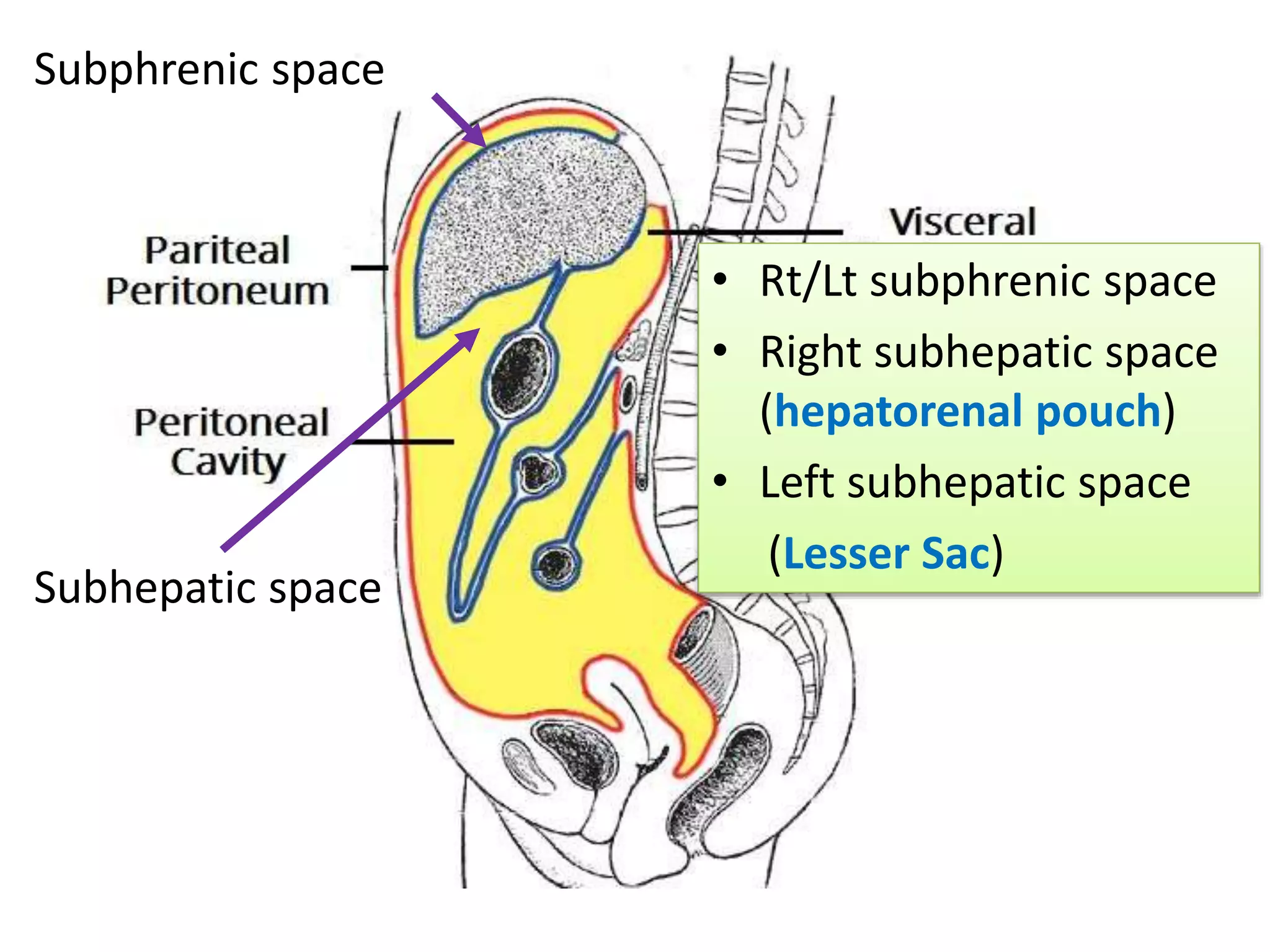
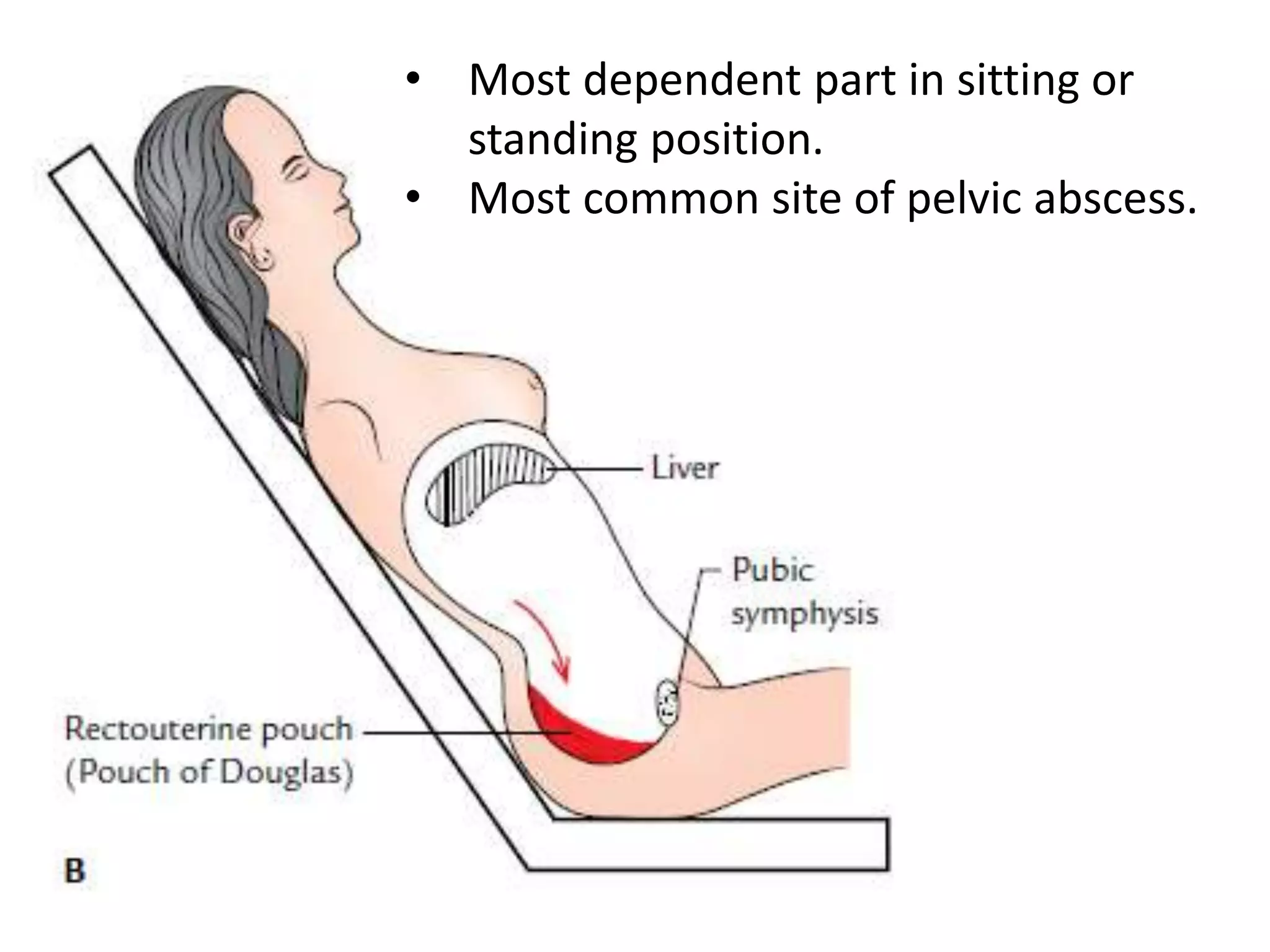
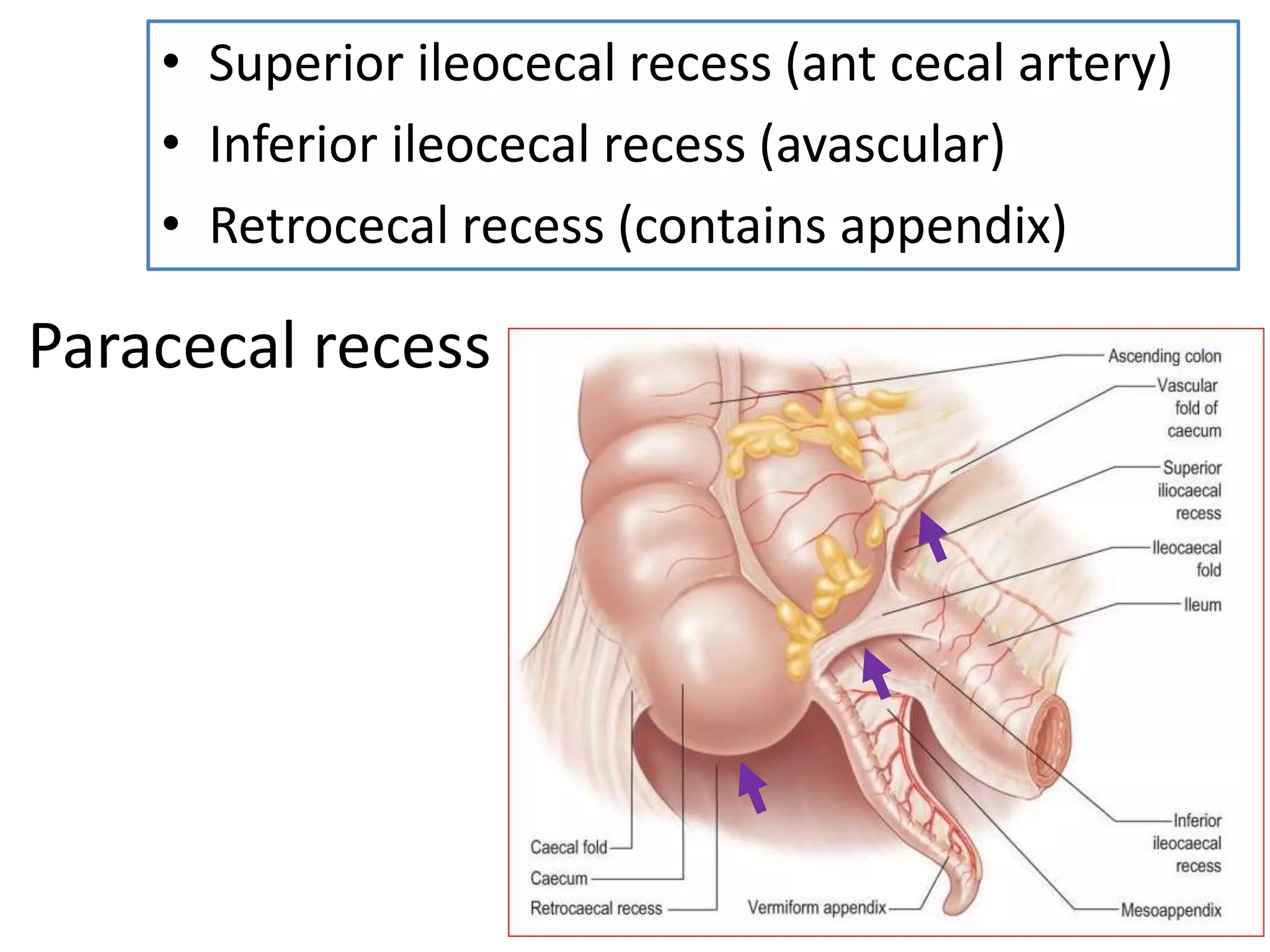
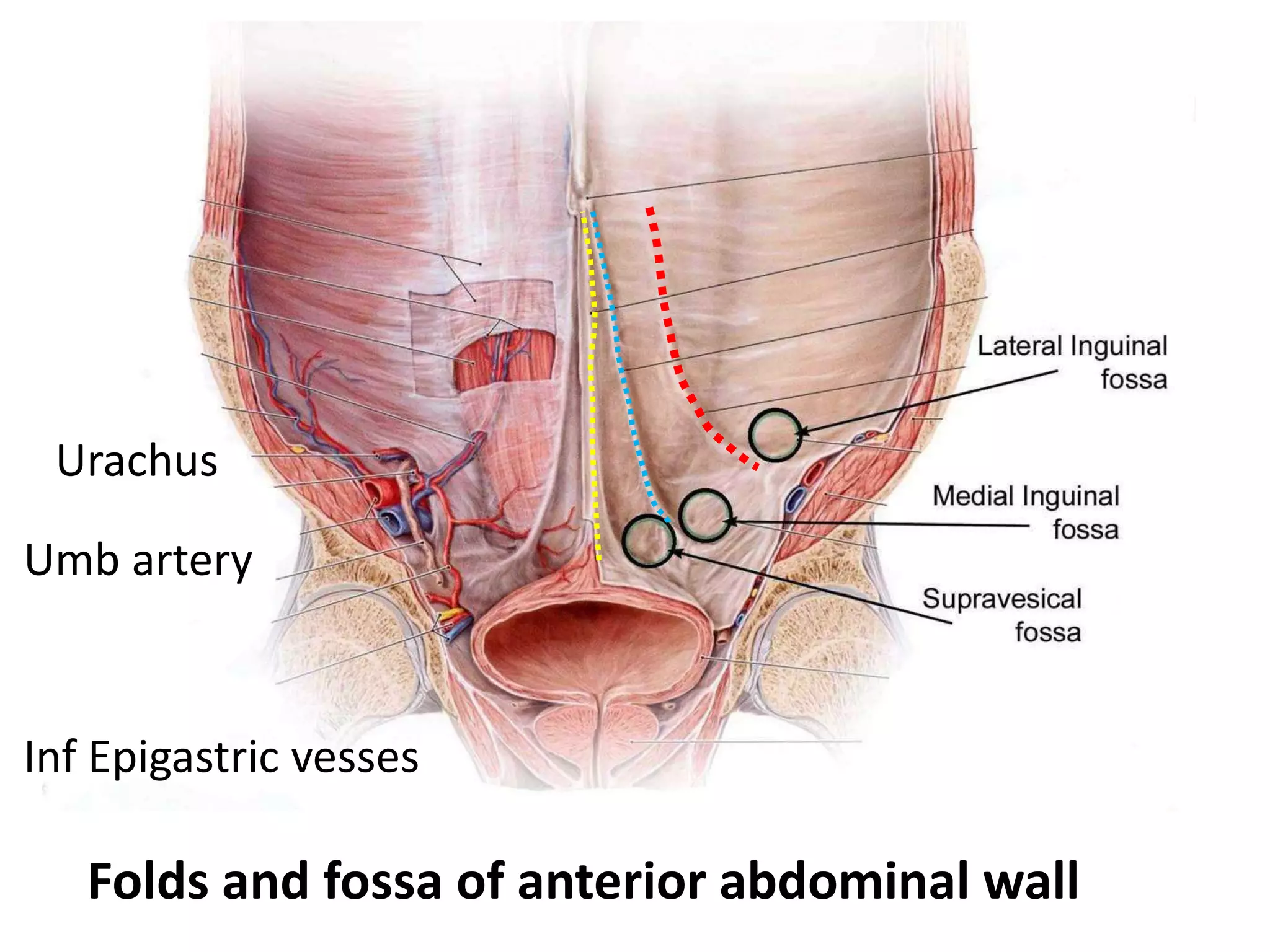
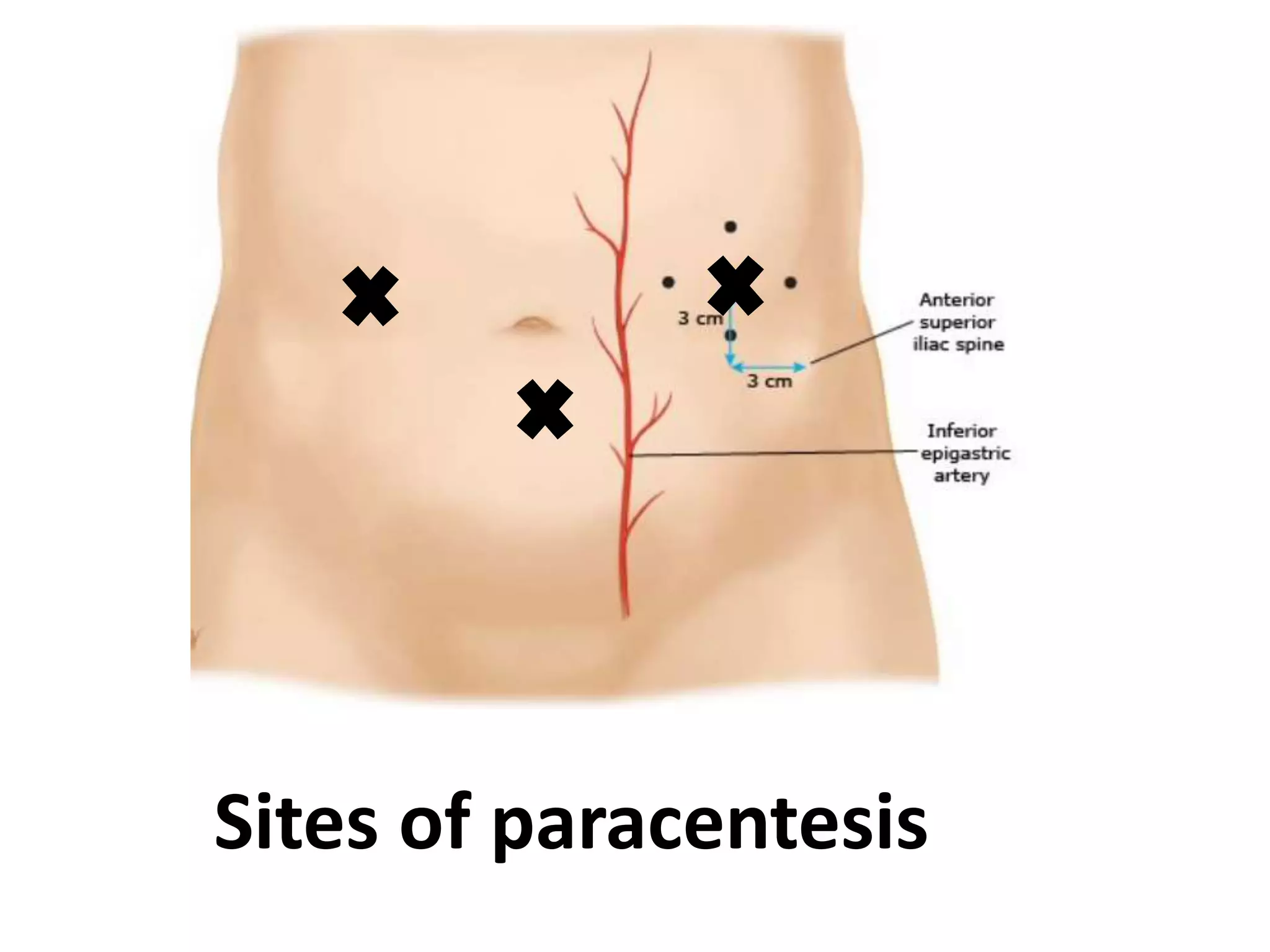
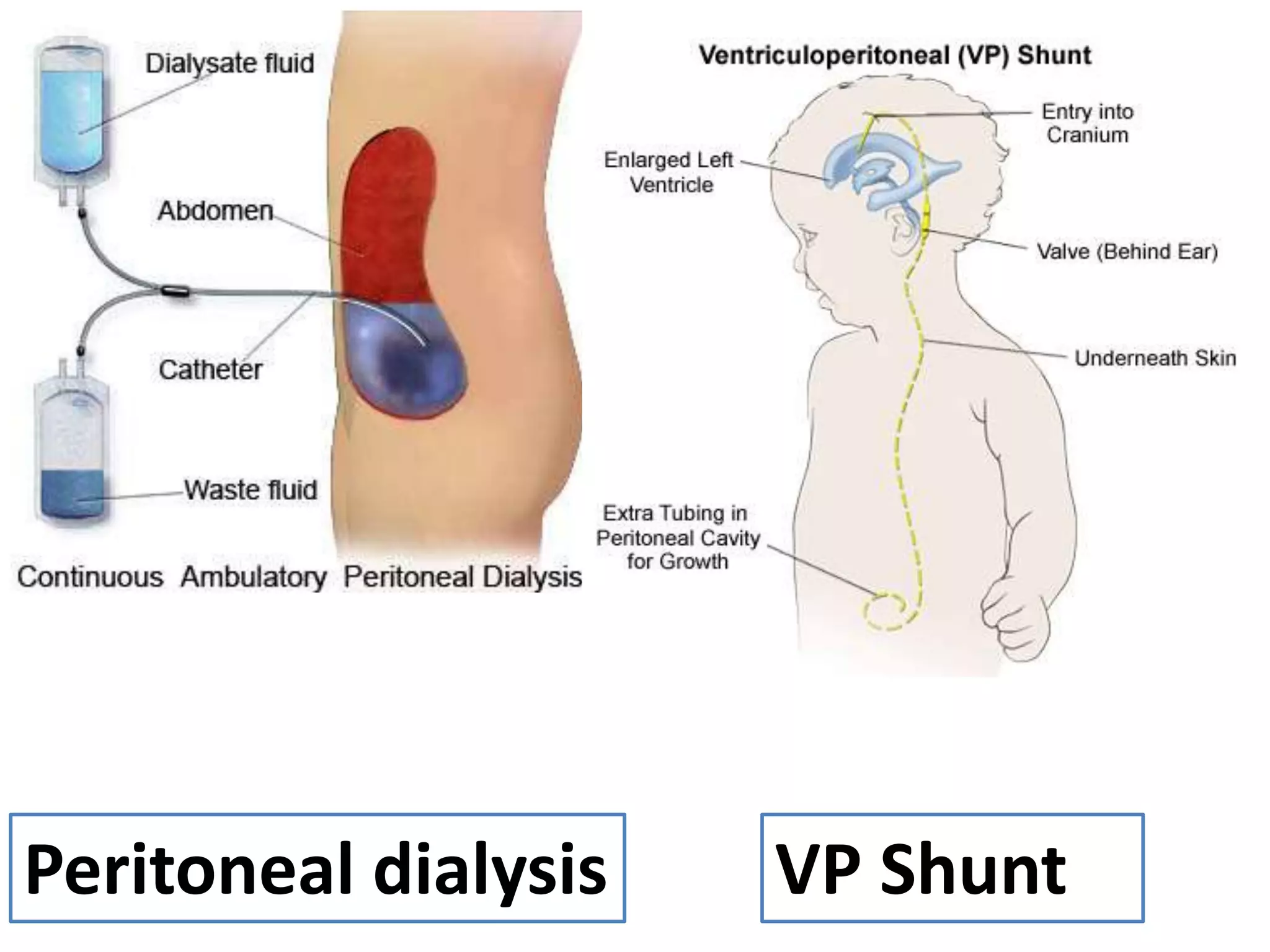
The document covers detailed anatomical information regarding the peritoneum, including derivatives of the dorsal mesogastrium, boundaries of the epiploic foramen, and classifications of peritoneal compartments and their structures. It discusses the supracolic and infracolic compartments, various peritoneal recesses, and importance in clinical contexts such as abscess formation and surgical procedures. Overall, it provides a comprehensive overview for medical students specializing in abdominal anatomy.