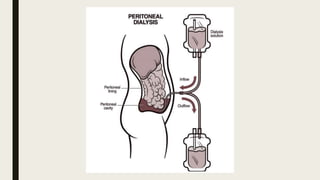
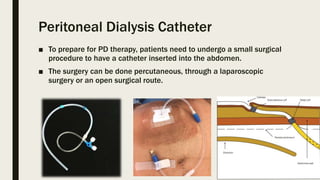
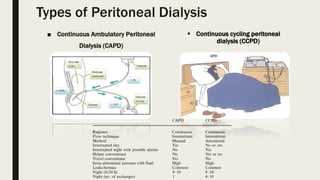
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a treatment that uses the peritoneum as a filter to remove waste from the body, requiring the assistance of a care partner. The process involves a catheter inserted into the abdomen and utilizes osmosis and diffusion to remove excess water and waste products. There are different types of PD, including CAPD and CCPD, with specific indications, contraindications, and potential complications.