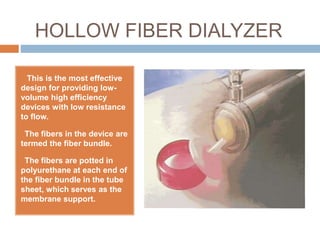
A dialyzer is a device that uses diffusion and convection to remove waste and regulate electrolytes from the blood of patients with kidney failure. It contains hollow fibers that separate the blood compartment from the dialysate compartment. Blood flows through the hollow fibers while dialysate flows around them. Wastes diffuse across the semipermeable fiber membranes into the dialysate. The hollow fiber dialyzer is now the most popular design as it provides high clearance with a small, compact size and reduced risk of leaks compared to earlier designs like coiled and parallel plate dialyzers.