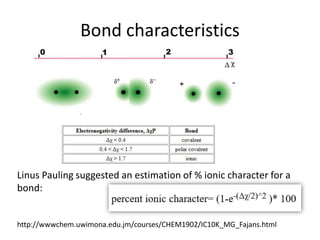
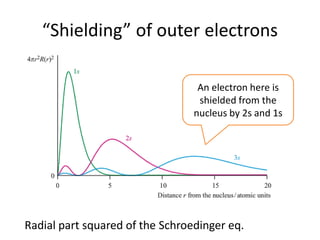
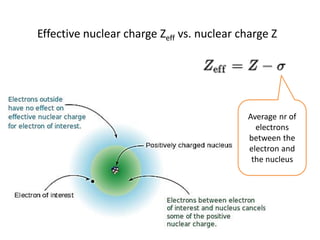
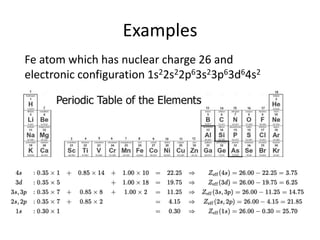
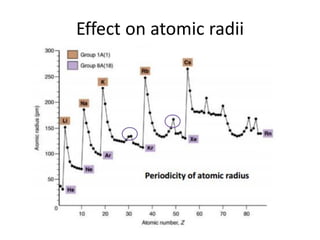
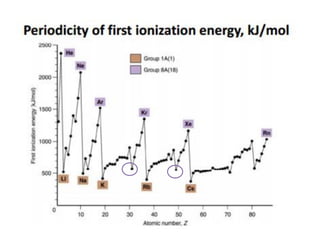
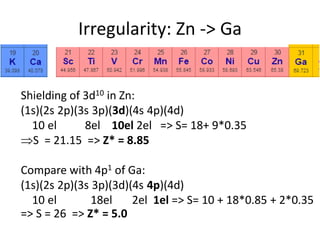
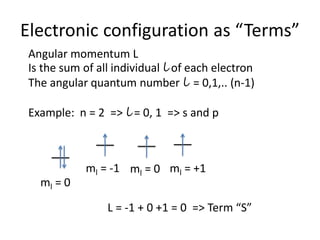
This document discusses atomic structure and electron configuration. It begins by explaining Slater's rules for calculating effective nuclear charge. It then provides examples of applying Slater's rules to determine electron shielding and effective nuclear charge. The document also covers electron configurations, term symbols, Hund's rules, and periodic trends in atomic size, ionization energy, and metallic character across periods and groups. It defines concepts like ionization potential, electron affinity, and electronegativity scales. In summary, the document provides an in-depth overview of theoretical atomic structure concepts.


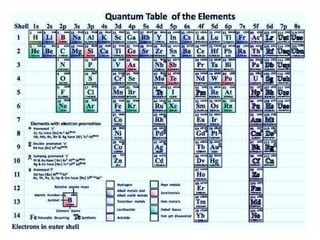
![Slater’s rule
Group el. in the
same
group
el. in same
shell n and
orbital nr < l
el. in shell
n-1
el. in shell
< n-2
[ 1s] 0.30 - - -
[ns np ] 0.35 - 0.85 1
[nd] or [nf] 0.35 1 1 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atomicstructurepart3-160903085810/85/Atomic-structure-part-3-3-5-320.jpg)



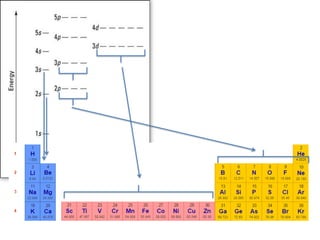
![Solution
Configuration V: (1s) (2s 2p) (3s 3p) (3d) (4s 4p)
[Ar] 4s2 3d3
Shielding for one 4s electron: S = 10 + 11 * 0.85 + 0.35
Z* = 3.30
Shielding for one 3d electron: S = 18 + 2 * 0.35
Z* = 4.30
=> The 4s electrons are less attracted than 3d](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atomicstructurepart3-160903085810/85/Atomic-structure-part-3-3-10-320.jpg)





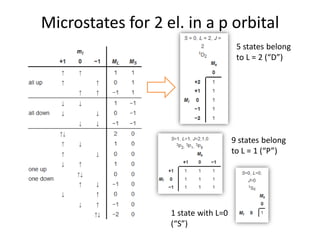
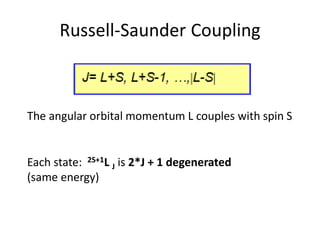
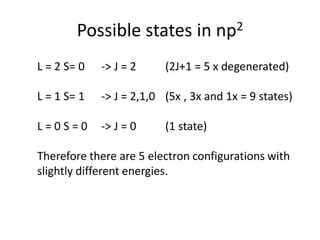
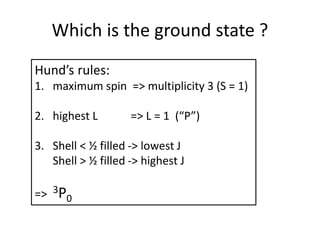











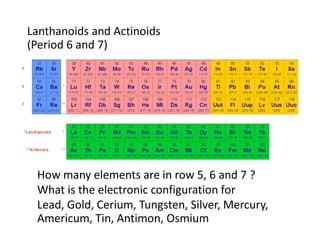
![Exceptions from Aufbau Principle
La (Z=57) should have configuration:
but has: [Xe] 4f0 5d1 6s2
Ac (Z=89) should have configuration:
but has: [Rn] 5f0 6d1 7s2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atomicstructurepart3-160903085810/85/Atomic-structure-part-3-3-43-320.jpg)