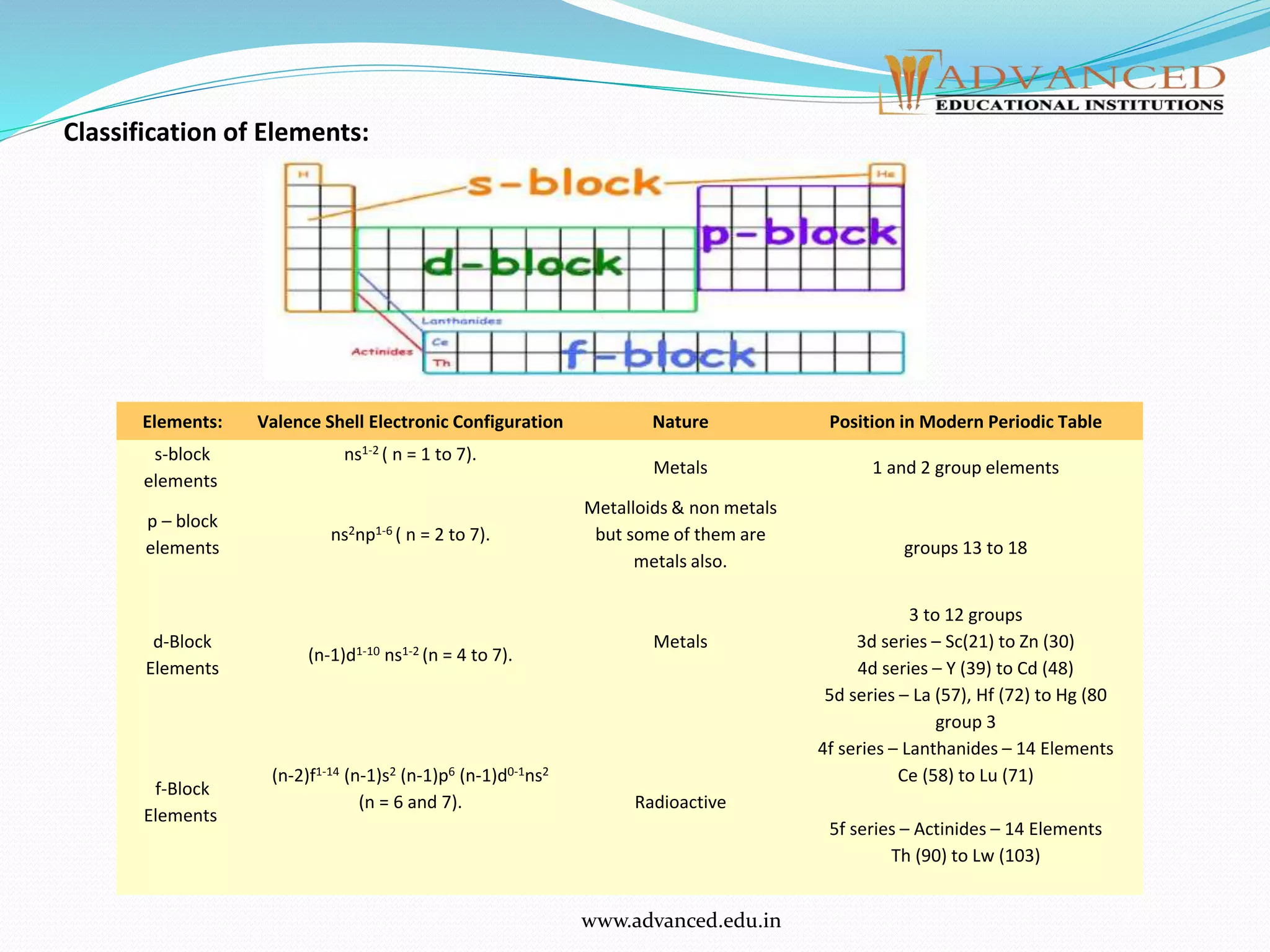
The document discusses the modern periodic law and periodic trends in atomic properties. It can be summarized as follows:
1. The modern periodic law states that the properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers. Elements are arranged in the periodic table based on increasing atomic number and similar outer electron configurations that repeat at regular intervals.
2. The periodic table is divided into blocks based on orbital types. Elements show trends in properties within periods and down groups, including decreasing atomic radius and increasing ionization energy with increasing atomic number. Electron affinity also tends to decrease down groups.
3. Successive ionization energies increase as more energy is required to remove additional electrons. Stability of half-filled and fully-filled