Embed presentation
Downloaded 25 times





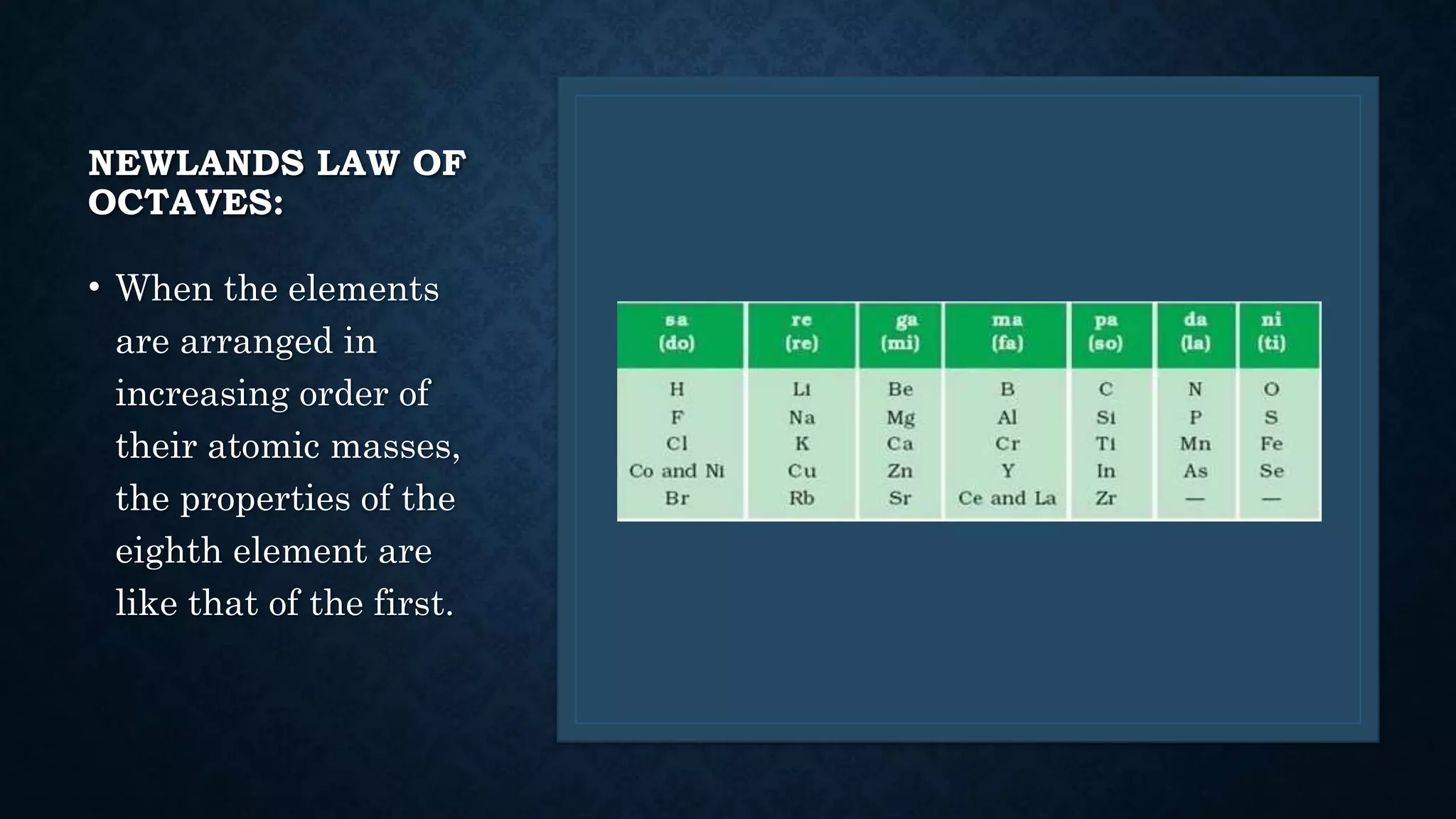


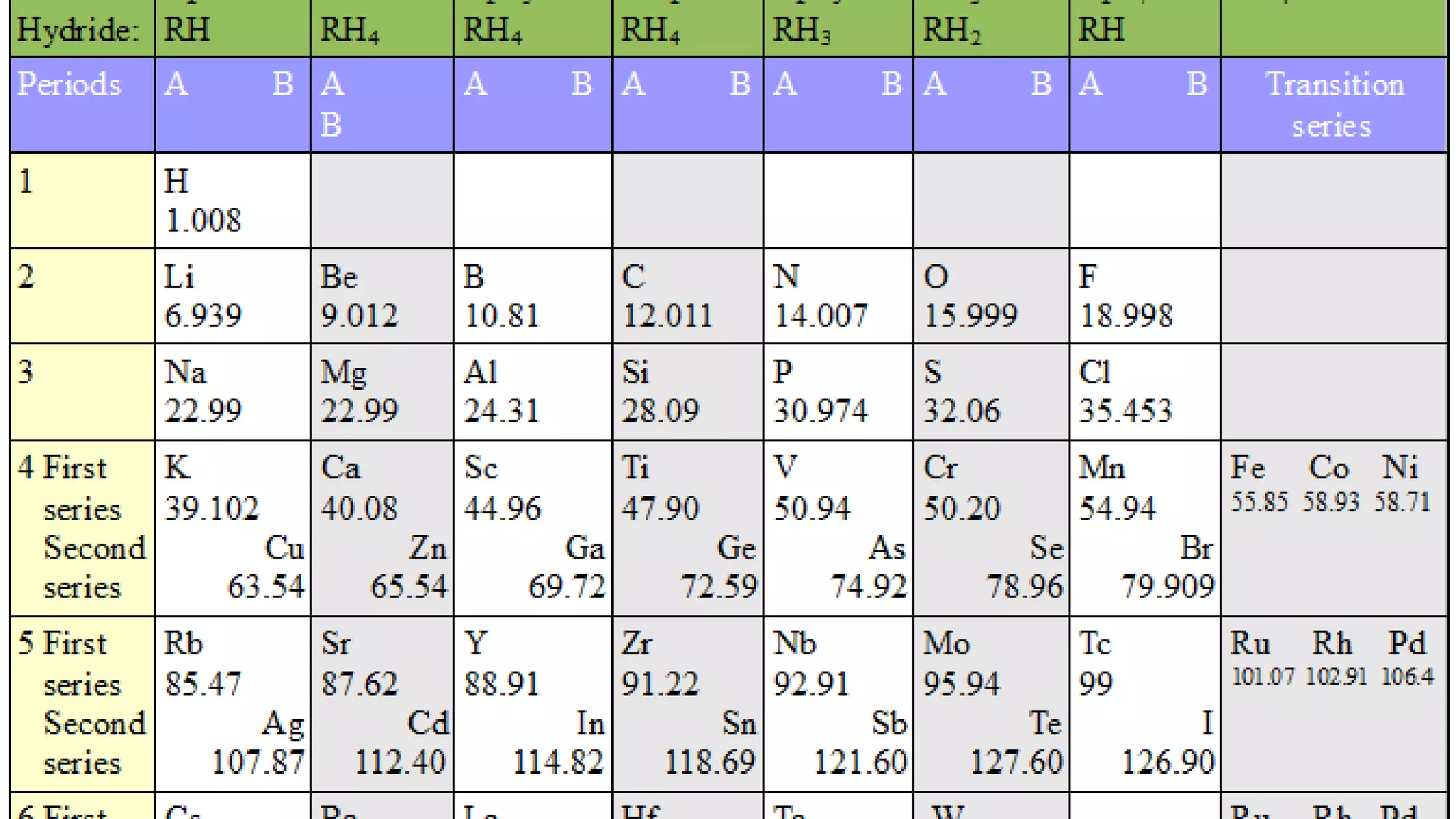
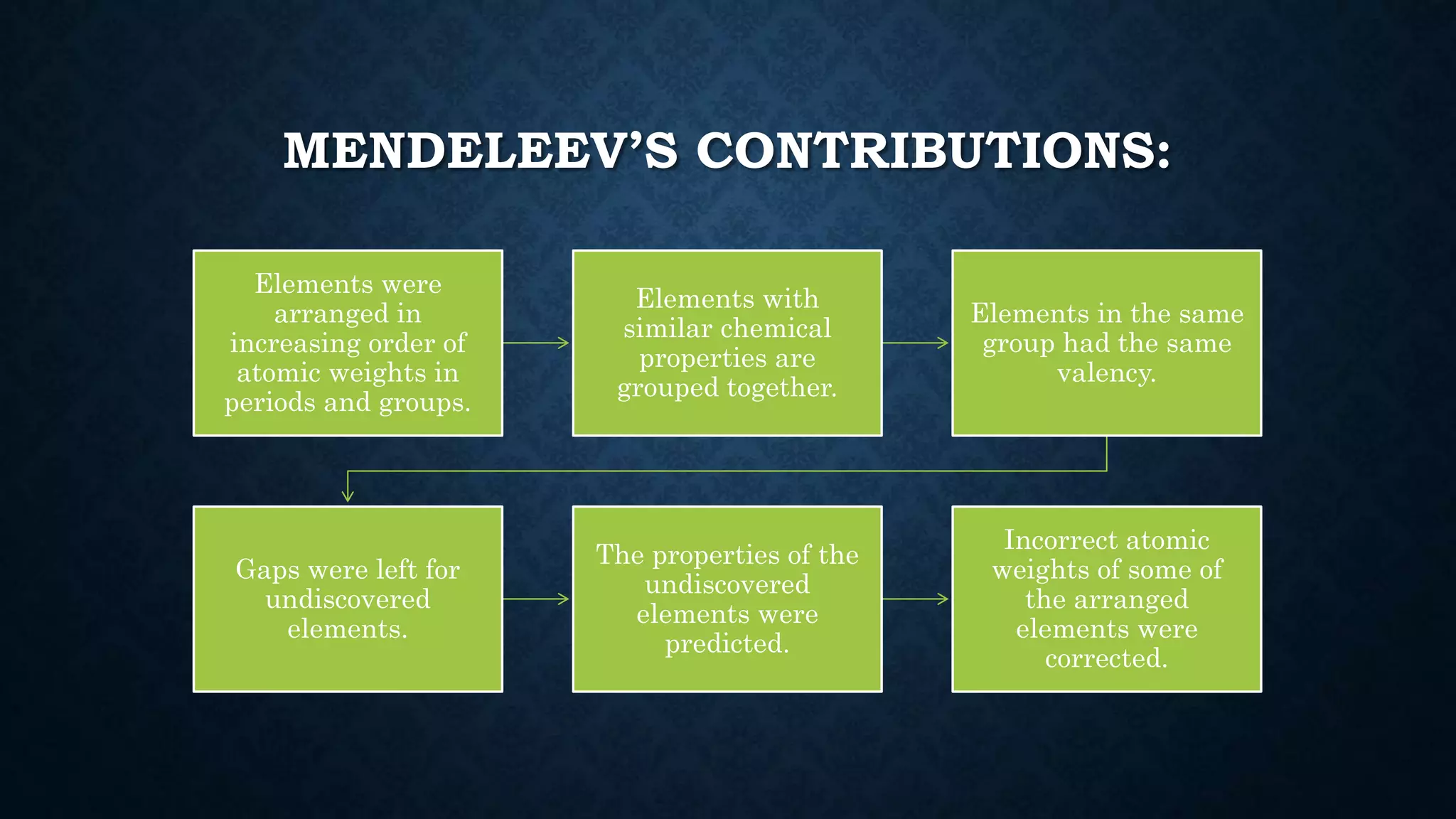


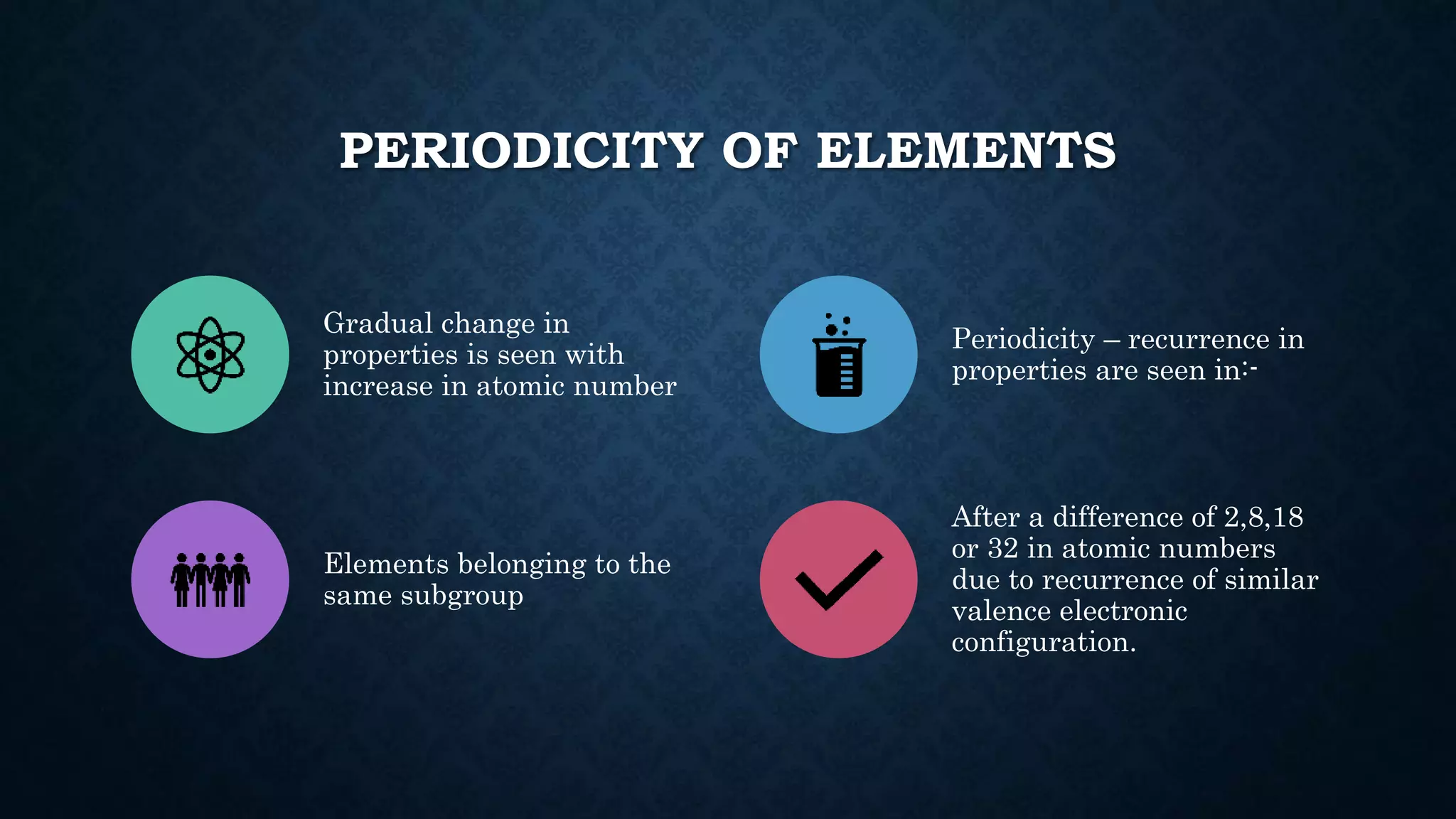




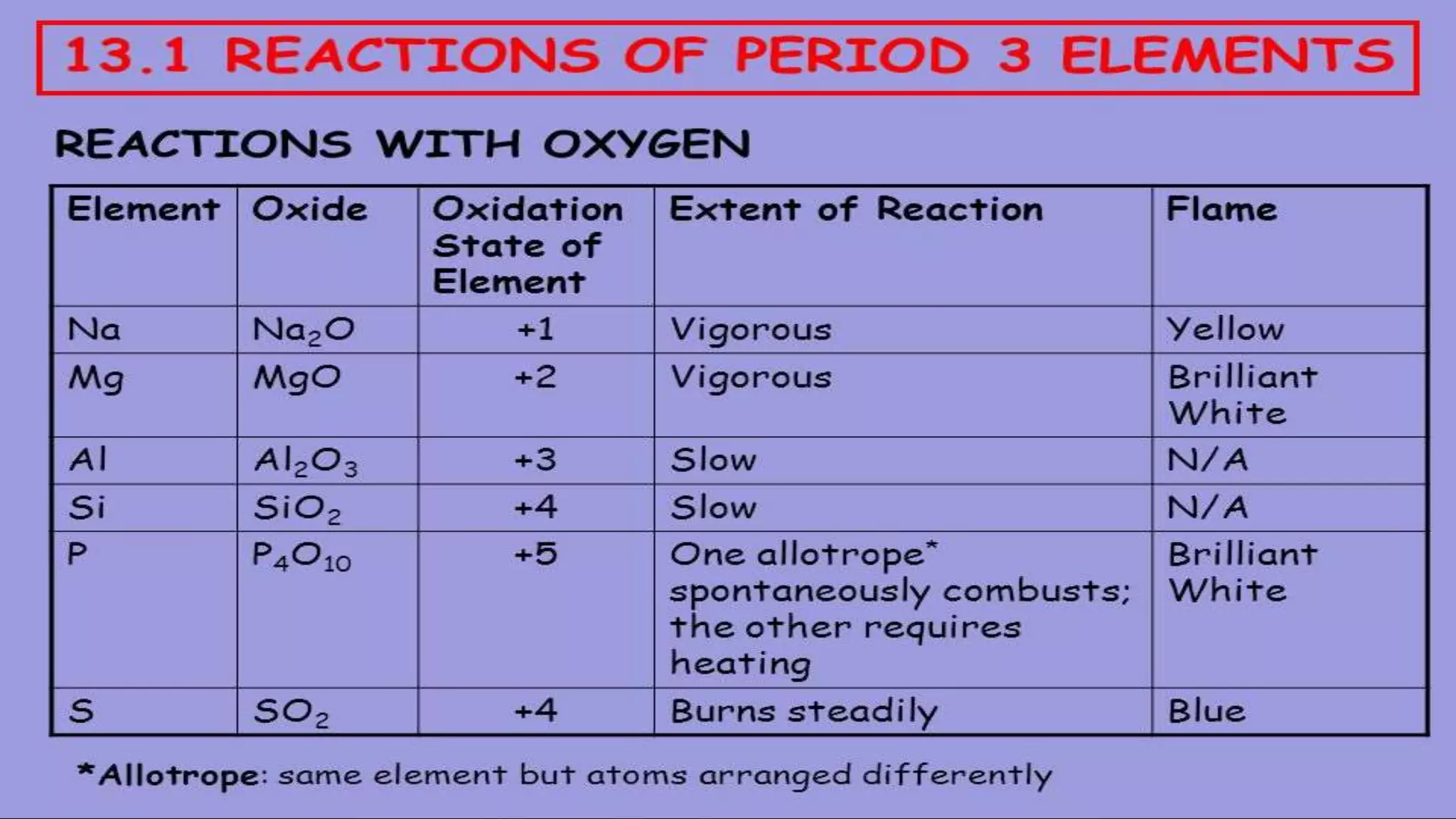

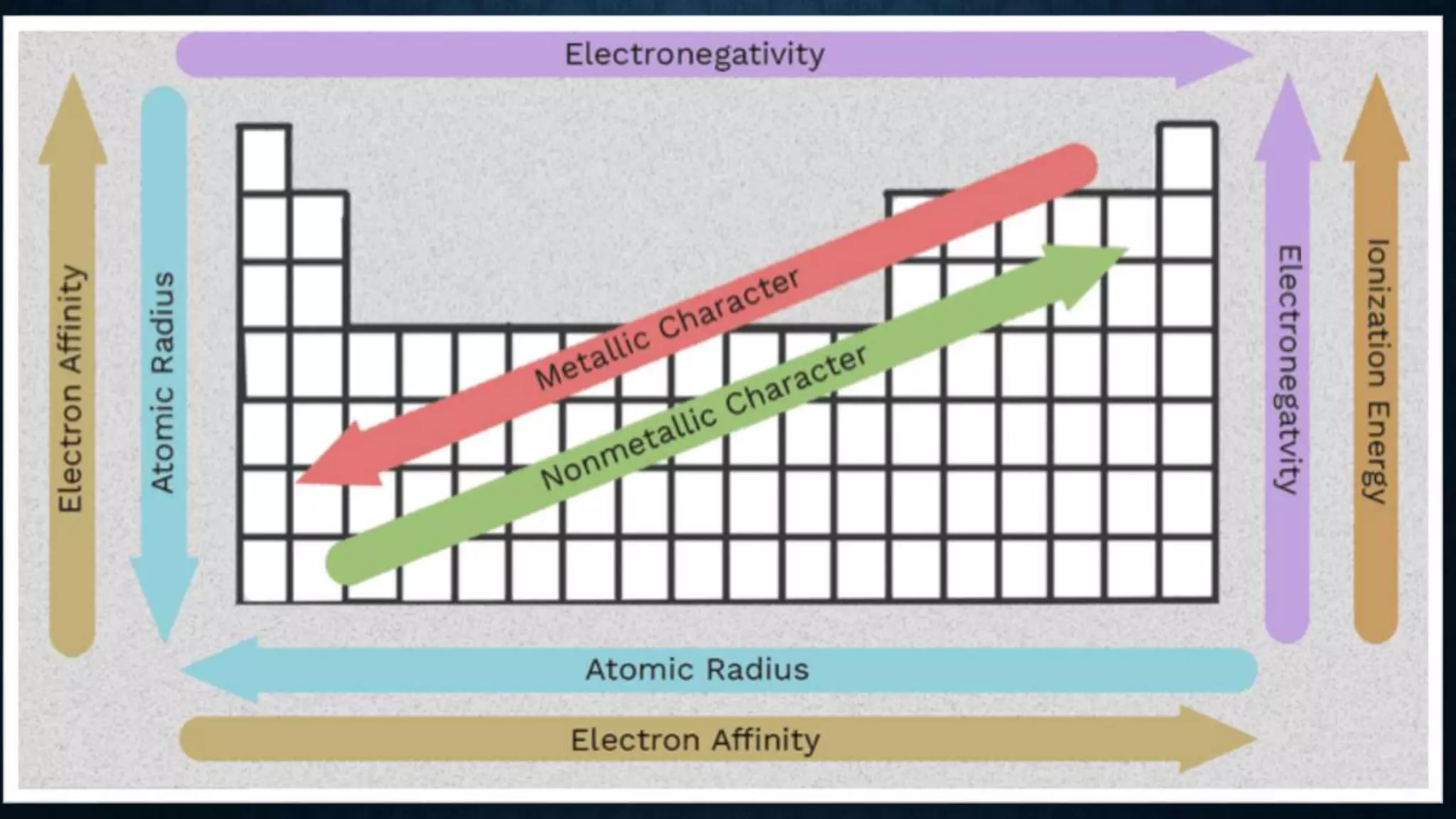

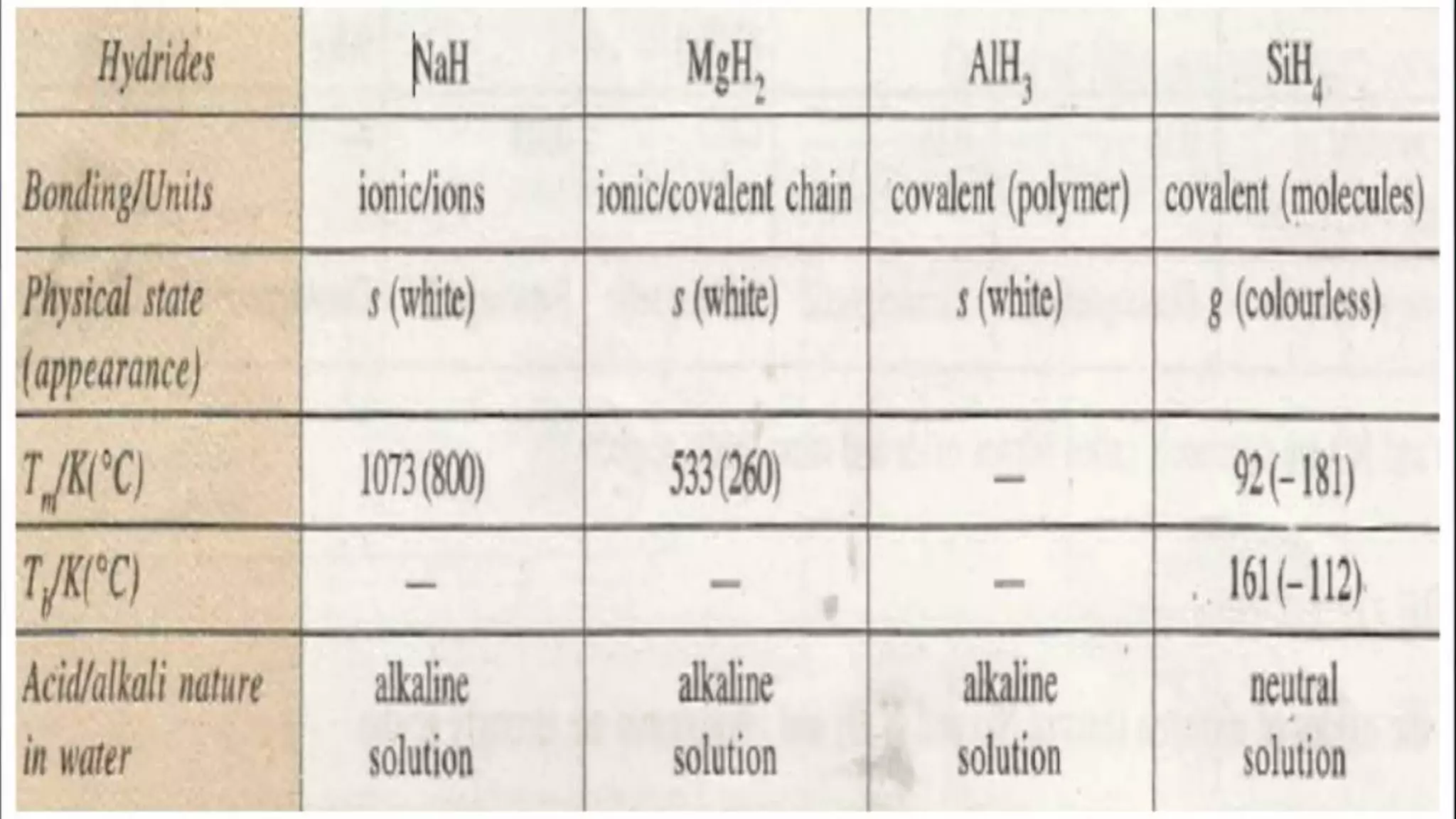

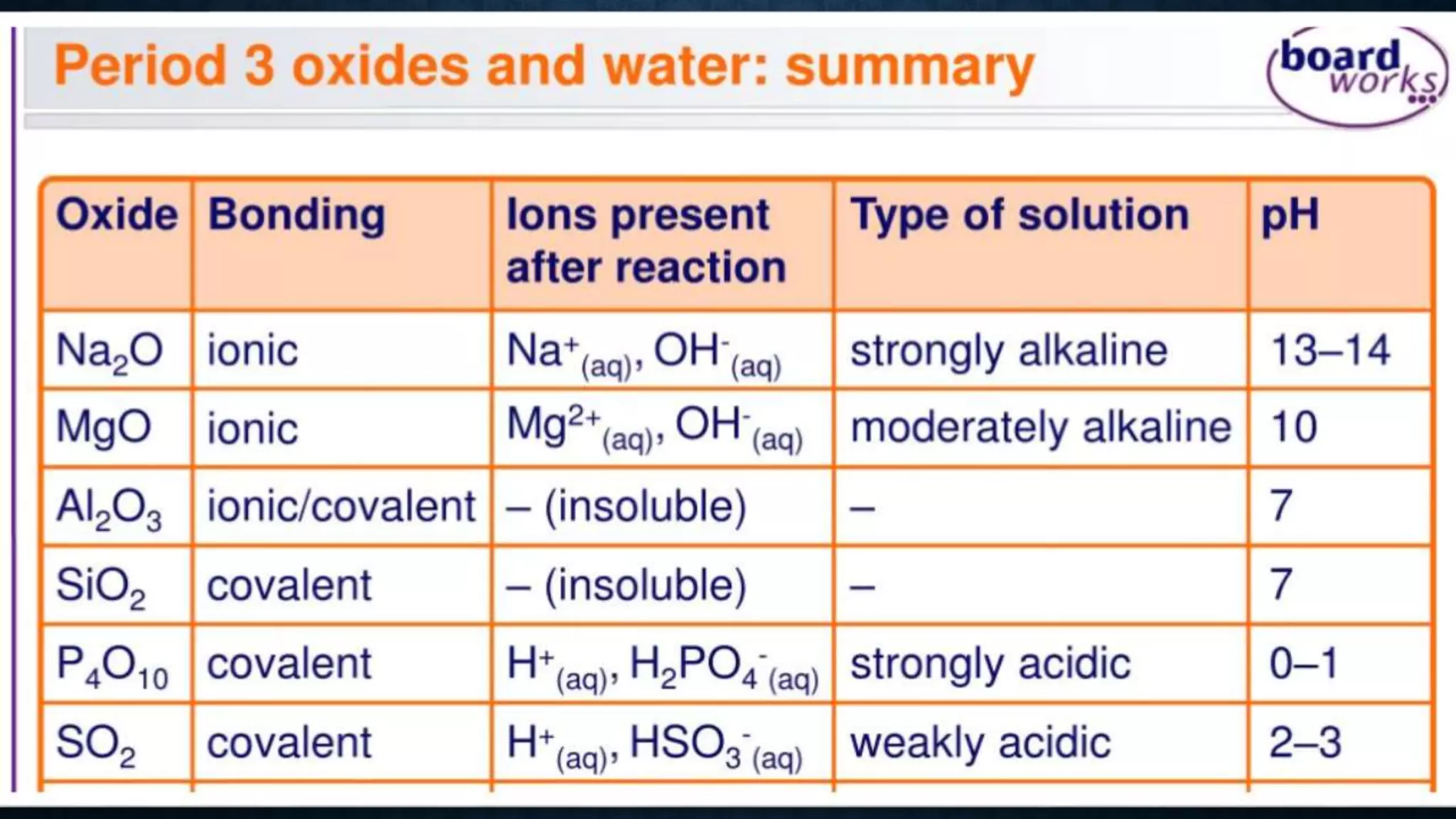




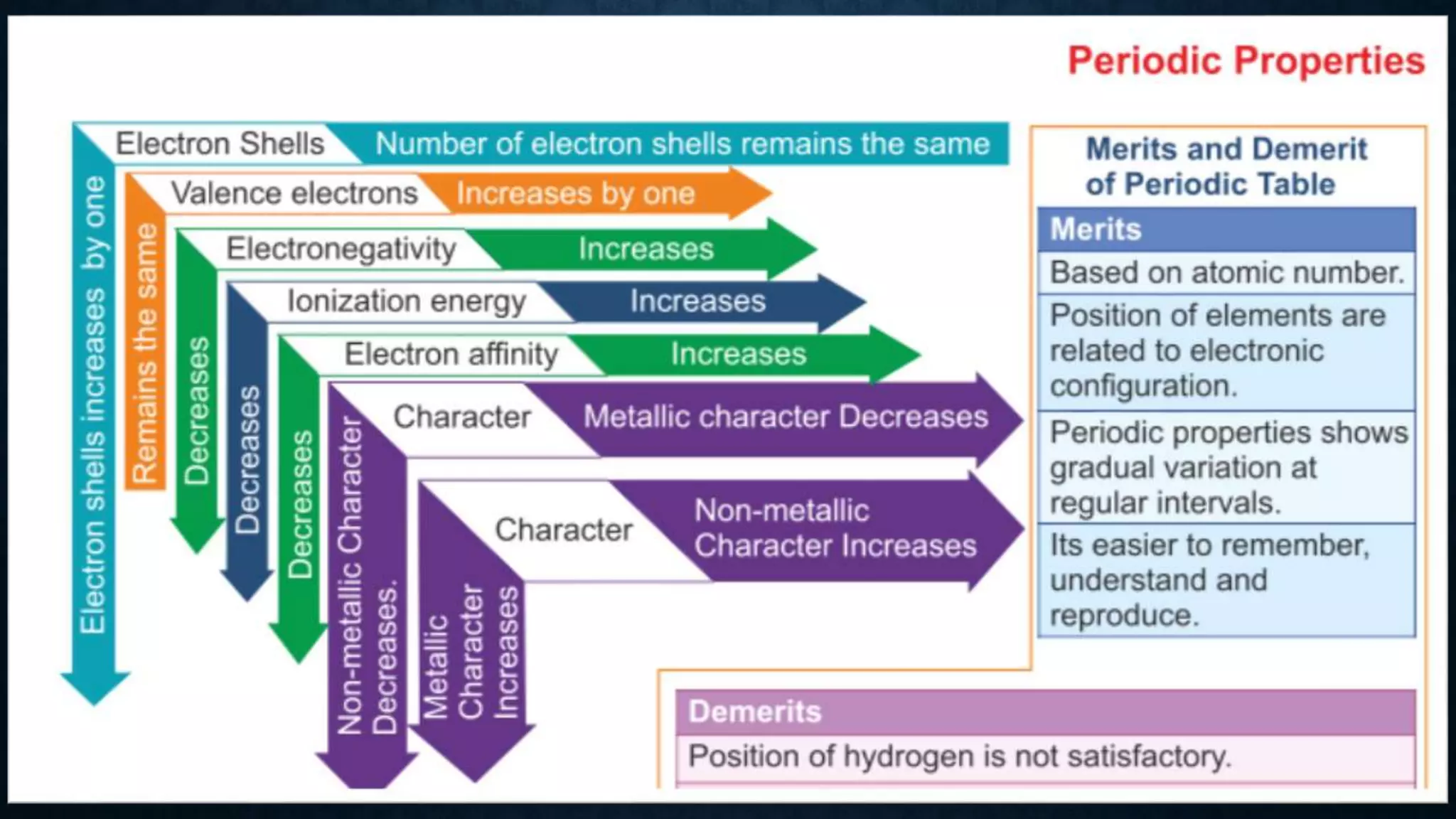

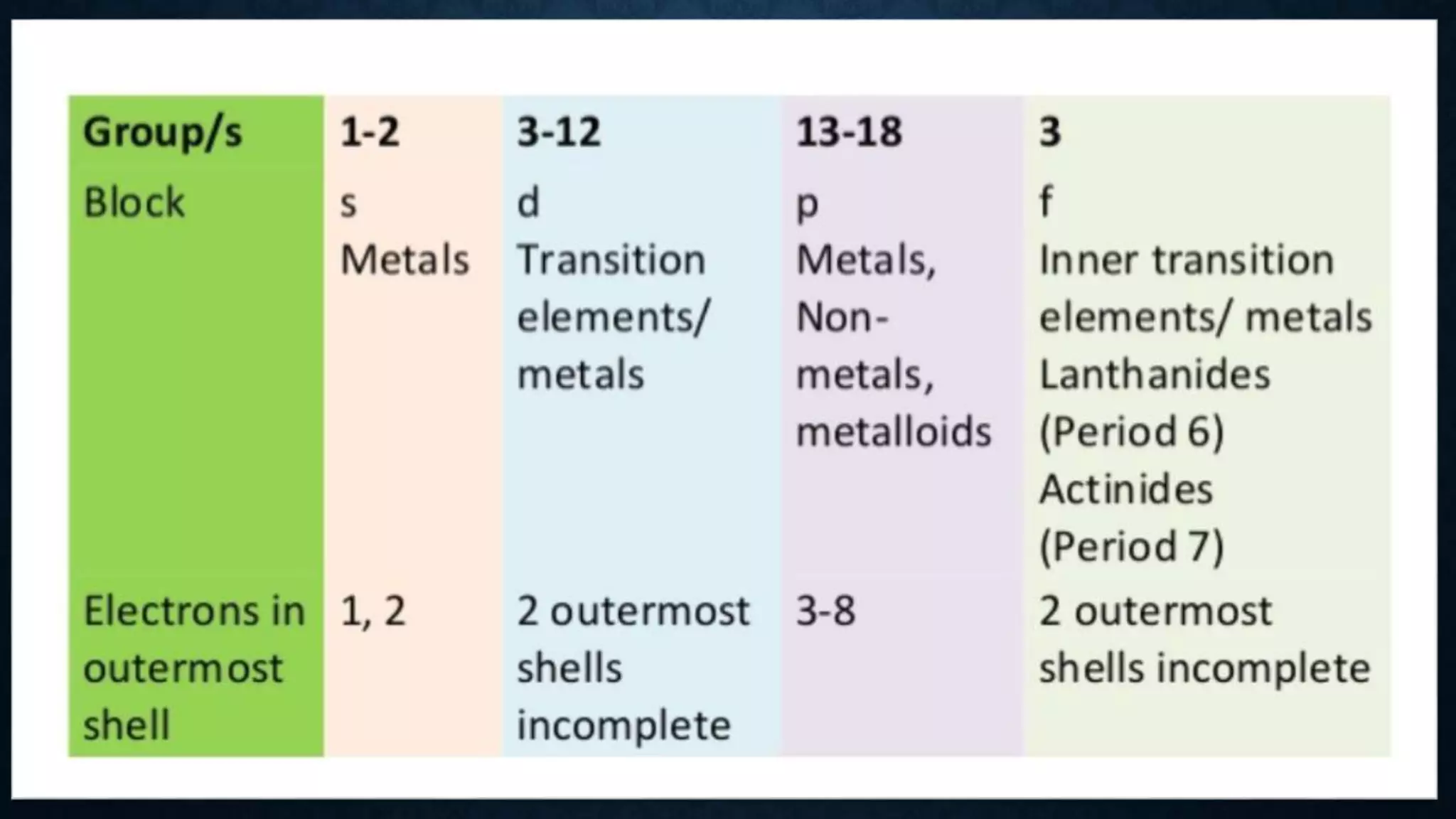

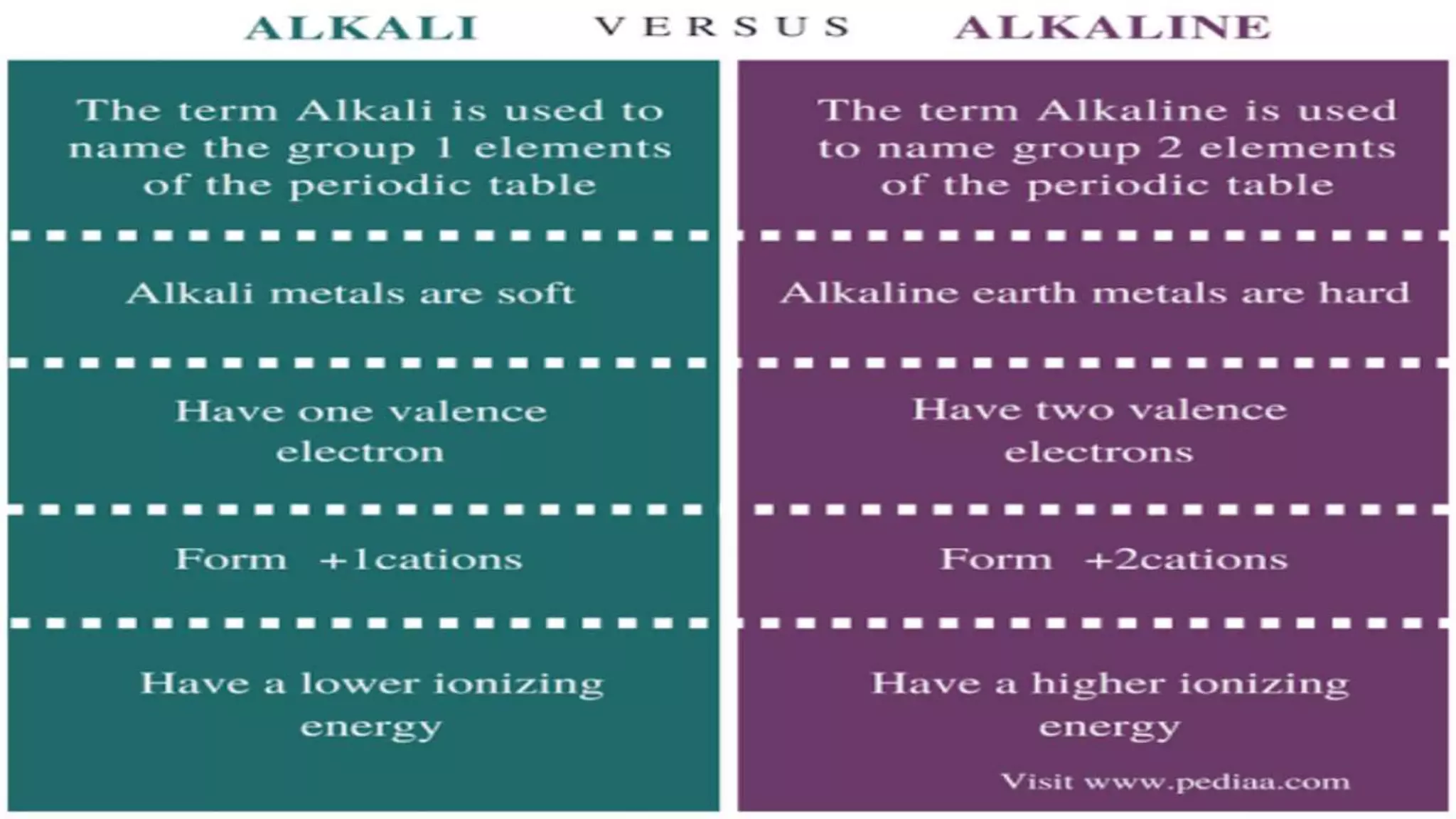







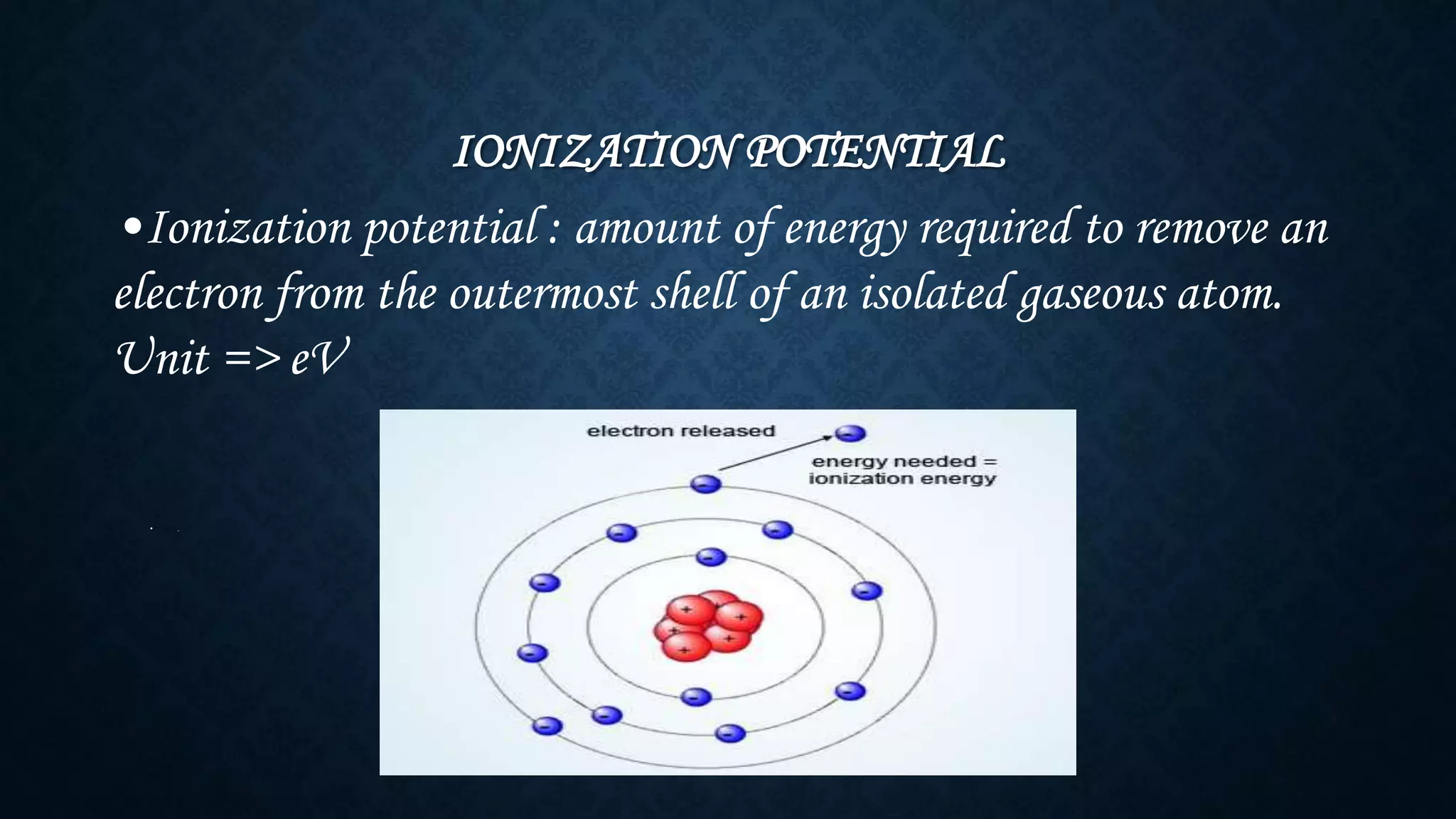



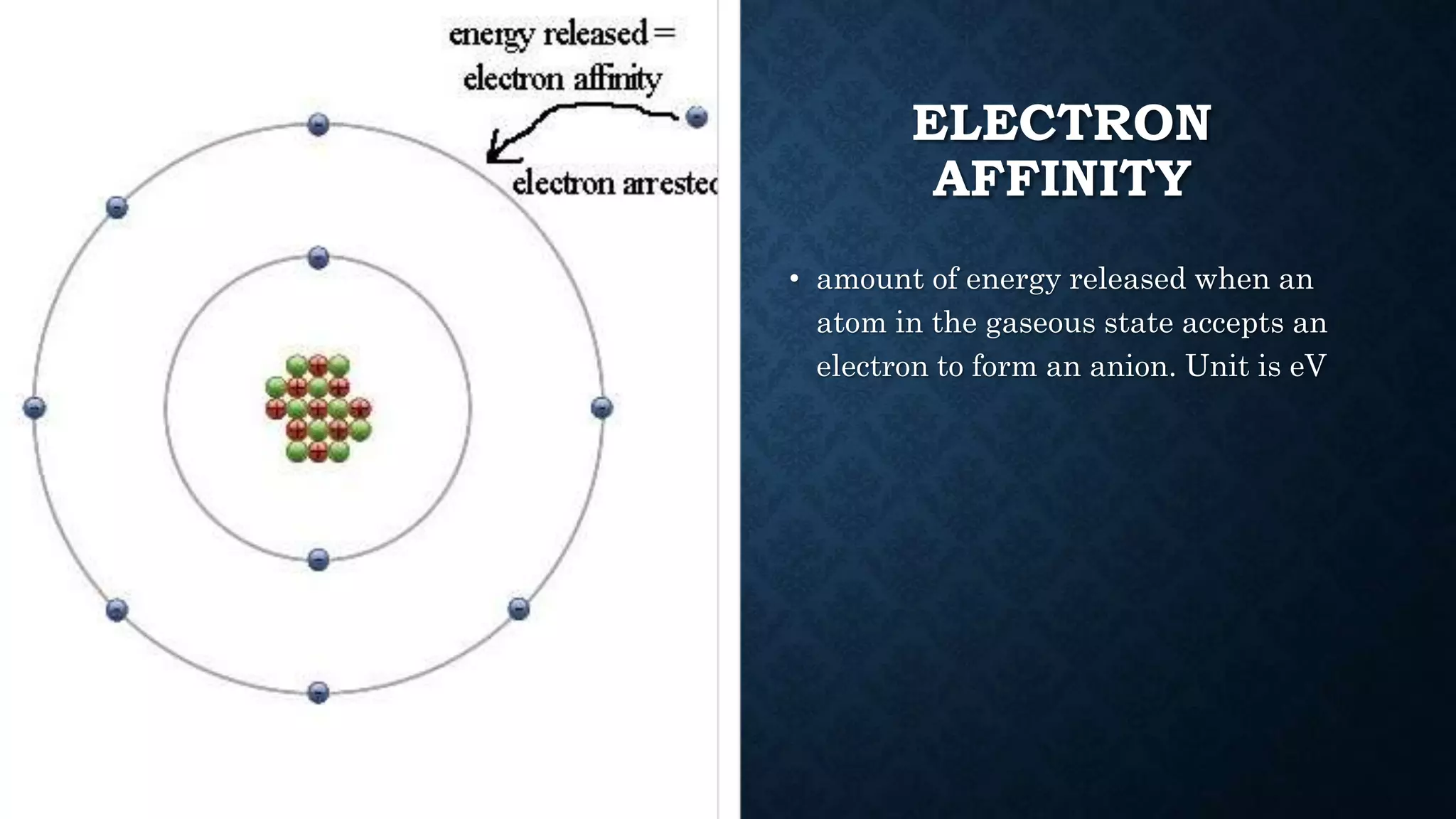












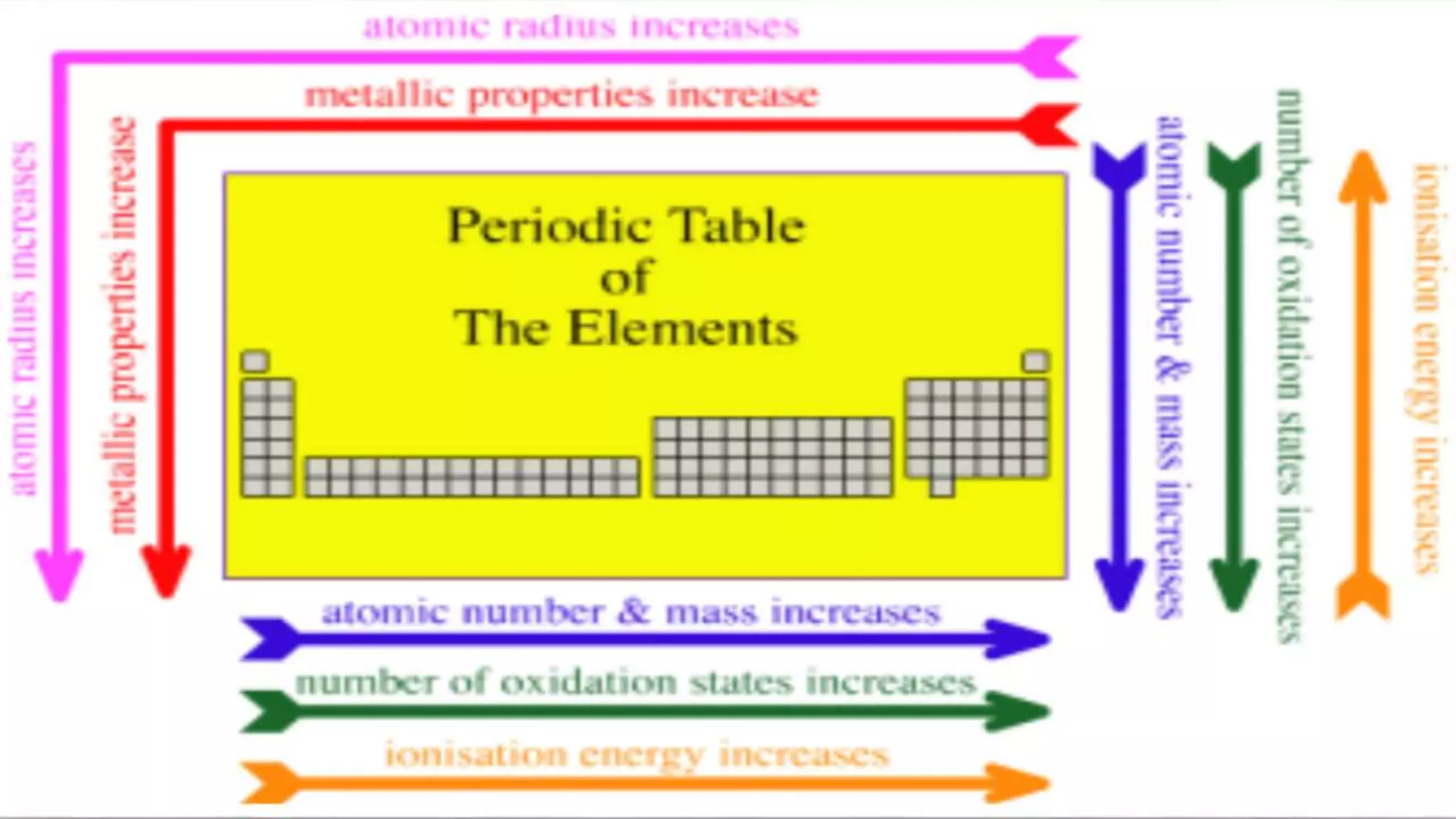









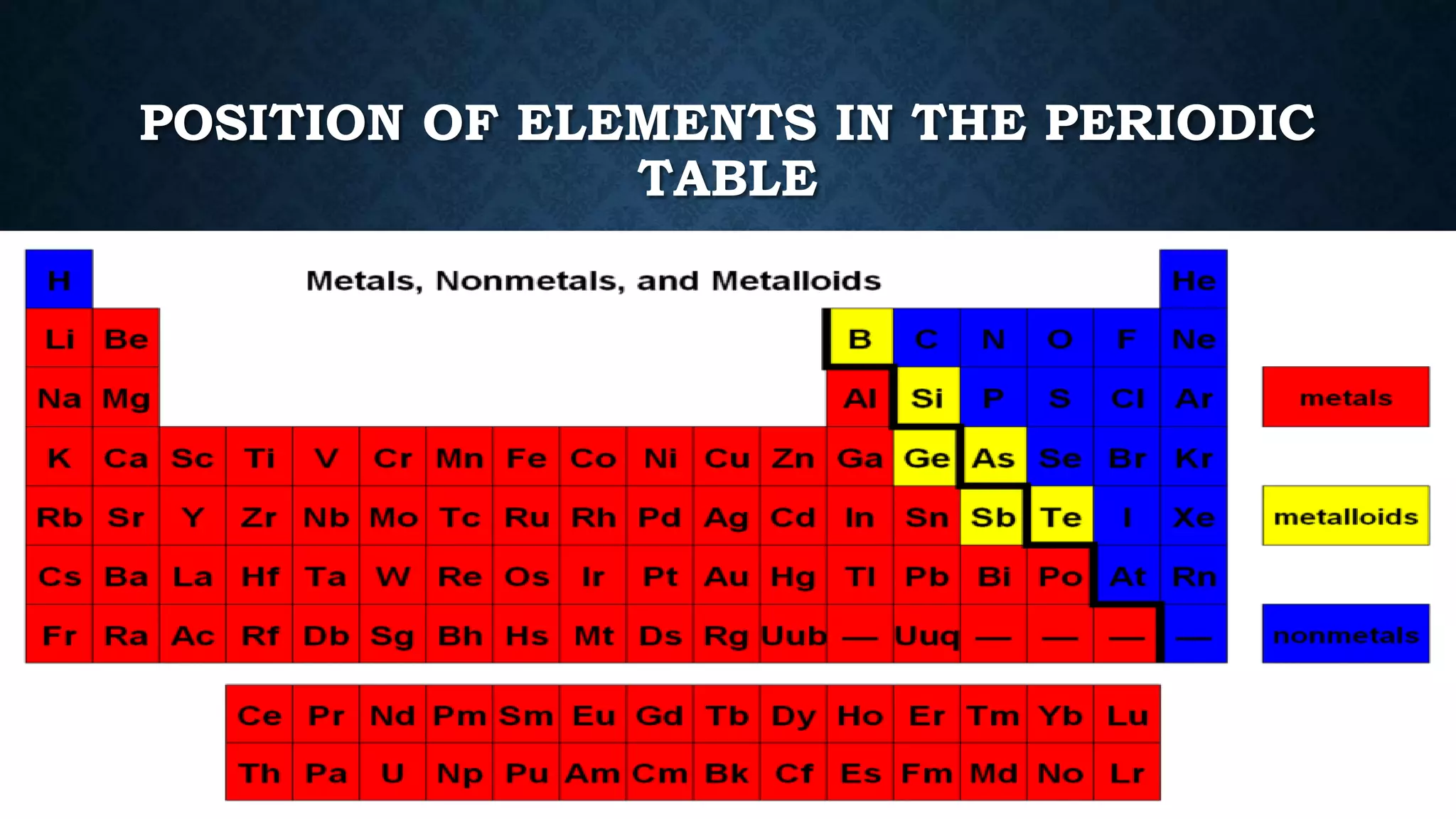








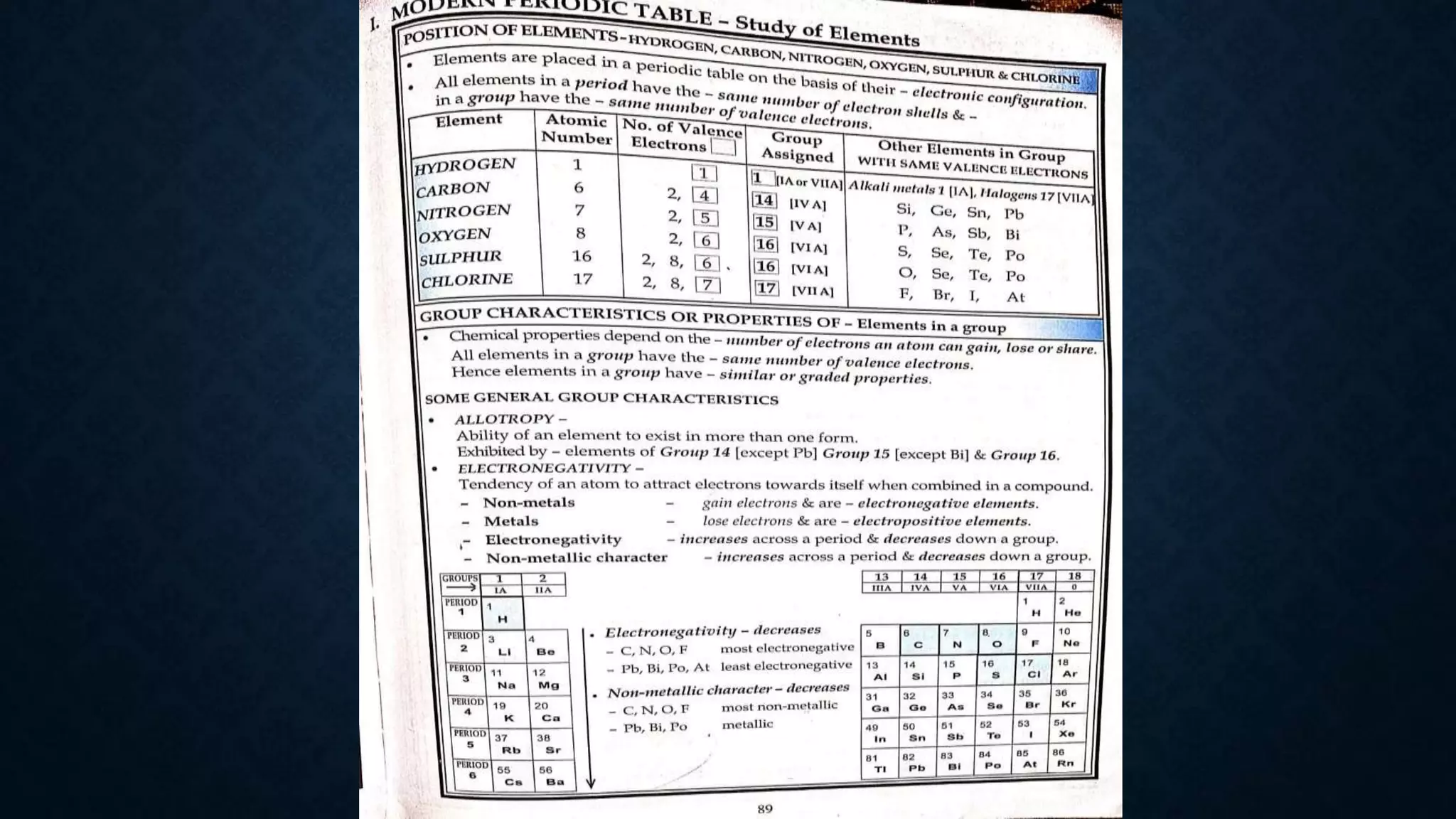

The document discusses the development of the periodic table. It describes early classification systems by Dobereiner and Newlands that grouped elements based on properties but had limitations as new elements were discovered. Mendeleev organized the elements into the first recognizable periodic table based on atomic mass and predicted properties of undiscovered elements. Moseley later modified this to be based on atomic number. The modern periodic table is arranged into periods and groups with trends in properties like atomic radius, ionization potential, and electronegativity explained by variation in nuclear charge and number of electron shells across and down the table.













































































