Dr. K. Rajender Reddy gave a lecture on electrochemistry that covered several topics:
1) Electrode potential is the tendency of a metal to lose or gain electrons when in contact with a solution of its own salt. Zn undergoes oxidation in ZnSO4 by releasing electrons, while Cu undergoes reduction in CuSO4 as copper ions are deposited.
2) The standard electrode potential is measured at 25°C with a 1M electrolyte concentration and represents the potential of an oxidation or reduction reaction.
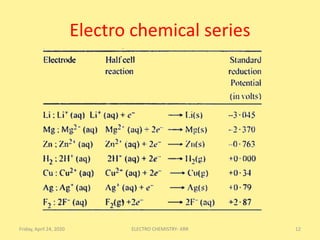
3) The electrochemical series arranges electrodes in order of increasing standard reduction potentials, ranging from the strongest reducing agent Li to the strongest oxidizing agent F.


![Electrode potential
• The tendency of a metal to lose the electrons (oxidation) or gain the
electrons (reduction), when it is in contact with solution of its own salt is
called electrode potential.
• When a metal [M] is placed in a solution containing its own ions [Mn+],
then the metal may undergo either oxidation or reduction. If the metal
undergoes oxidation, then the positive metal ions may pass into the
solution
• M Mn+ + ne‒
• If the metal undergoes reduction, then the negative ions may get
deposited over the metal.
• Mn+ + ne‒ M
Friday, April 24, 2020 3ELECTRO CHEMISTRY- KRR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electrodepotentialelectrochemicalseries-200424063654/85/Ele-ctrode-potential-electrochemical-series-3-320.jpg)